- Part 1. What is a 12V lithium-ion battery?
- Part 2. What is the fully charged voltage for a 12V lithium-ion battery?
- Part 3. Why do voltage discrepancies occur in 12V lithium-ion batteries?
- Part 4. How does a 12V lithium-ion battery differ from a 12V lead-acid battery?
- Part 5. What happens if your 12V lithium-ion battery doesn't reach full charge?
- Part 6. How do you measure the voltage of a 12V lithium-ion battery?
- Part 7. FAQs
Lithium-ion batteries are a popular choice for energy storage due to their efficiency, reliability, and long lifespan. However, many users who rely on 12V lithium-ion batteries often notice discrepancies in voltage readings, especially when the battery doesn’t seem to reach a “full charge.” This can lead to confusion or concerns, mainly because the behavior of lithium-ion batteries differs from traditional battery types like lead-acid.
This guide explores 12V lithium-ion battery voltage science, explains what “fully charged” means, and discusses why voltage discrepancies may occur. We’ll also provide actionable tips to ensure your lithium-ion battery performs at its best.
Part 1. What is a 12V lithium-ion battery?
A 12V lithium-ion battery is a rechargeable power source widely used in applications such as renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, boats, RVs, and backup power supplies. These batteries are known for their high energy density, lightweight design, and longer operational life than traditional lead-acid batteries.
The term “12V” refers to the battery’s nominal voltage. Nominal voltage is the average voltage the battery operates at during everyday use. However, the battery’s actual voltage fluctuates depending on its charge (SOC) state. For example, a fully charged 12V lithium-ion battery will have a higher voltage than one partially charged or discharged.
Part 2. What is the fully charged voltage for a 12V lithium-ion battery?
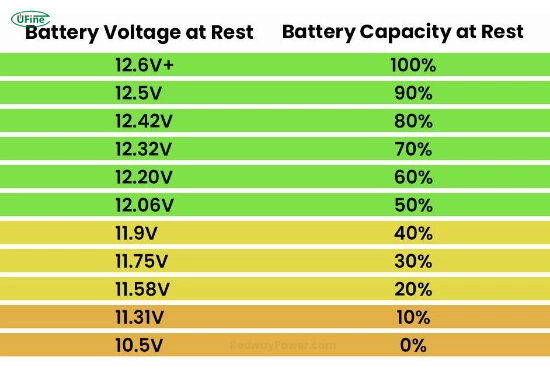
Depending on the specific battery chemistry, a fully charged 12V lithium-ion battery typically reads between 12.6V and 13.6V. This voltage range is narrower and more stable than other battery types, such as lead-acid batteries.
For instance:
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries, a popular lithium-ion battery, usually have a fully charged voltage between 13.2V and 13.6V.
- Other lithium-ion chemistries, such as lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), generally have a fully charged voltage closer to 12.6V to 13.4V.
It’s important to note that the battery’s voltage drops as it discharges. Still, lithium-ion batteries maintain a relatively stable voltage throughout most of their discharge cycle. This stability is one of the reasons lithium-ion batteries are so efficient.
Part 3. Why do voltage discrepancies occur in 12V lithium-ion batteries?
Voltage discrepancies can occur for various reasons, and they don’t always indicate a problem with the battery. Here are the most common causes:
- Battery Chemistry: Different lithium-ion battery chemistries have slightly different voltage ranges. For example, LiFePO4 batteries have a higher fully charged voltage than other chemistries.
- State of Charge (SOC): The voltage of a lithium-ion battery directly corresponds to its SOC. A battery with a 50% charge will have a lower voltage than one fully charged one.
- Temperature Variations: Lithium-ion batteries are sensitive to temperature changes. Cold temperatures can reduce voltage readings, while high temperatures may cause the voltage to appear artificially high.
- Charger Quality: Low-quality or incompatible chargers may fail to bring the battery to full charge, leading to lower-than-expected voltage readings.
- Battery Aging: As lithium-ion batteries age, their capacity and performance decline. Older batteries may not reach the same peak voltage they achieved when new.
- Battery Management System (BMS): Most lithium-ion batteries include a built-in BMS to protect the battery from overcharging or undercharging. Sometimes, the BMS may limit the voltage for safety reasons.
Part 4. How does a 12V lithium-ion battery differ from a 12V lead-acid battery?
Although 12V lithium-ion and 12V lead-acid batteries share the same nominal voltage, they differ significantly in performance and behavior. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Voltage Stability: Lithium-ion batteries maintain a consistent voltage during discharge, whereas lead-acid batteries experience a steady decline in voltage as they discharge.
- Fully Charged Voltage: A fully charged lithium-ion battery typically reads between 13.2V and 13.6V, while a lead-acid battery reads between 12.6V and 12.8V.
- Weight: Lithium-ion batteries are much lighter than lead-acid batteries, making them ideal for applications where weight is a concern.
- Cycle Life: Lithium-ion batteries can last between 2,000 and 5,000 cycles, while lead-acid batteries typically last between 300 and 1,000.
- Efficiency: Lithium-ion batteries are more energy-efficient, with a discharge efficiency of up to 95%, compared to 70–85% for lead-acid batteries.
Here’s a table summarizing these differences:
| Feature | Lithium-Ion Battery | Lead-Acid Battery |
| Fully Charged Voltage | 13.2V–13.6V | 12.6V–12.8V |
| Discharge Voltage | Stable throughout cycle | Declines steadily |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy |
| Cycle Life | 2,000–5,000 cycles | 300–1,000 cycles |
| Efficiency | Up to 95% | 70–85% |
Part 5. What happens if your 12V lithium-ion battery doesn’t reach full charge?
If your battery isn’t reaching its full charge, it could be due to one or more of the following issues:
- Charger Compatibility: Ensure that you use a charger designed for lithium-ion batteries. For example, using a charger for lead-acid batteries can result in incomplete charging.
- Battery Management System (BMS) Limitations: Your battery’s BMS might limit the charge to protect it from overcharging or other potential risks.
- Battery Aging: As the battery ages, its ability to hold a full charge diminishes. This is a normal part of a battery’s lifecycle.
- Temperature Conditions: Charging in extremely cold or hot environments can impact the battery’s ability to reach full charge.
- Charger Output: A low-quality or underpowered charger may fail to provide the necessary voltage to fully charge the battery.
To address these issues, double-check your charger, charge the battery in a temperature-controlled environment, and monitor its voltage with a multimeter.
Part 6. How do you measure the voltage of a 12V lithium-ion battery?
Measuring the voltage of a lithium-ion battery is a simple process that requires a multimeter. Follow these steps:
- Turn Off All Loads: Disconnect the battery from any devices or systems to ensure an accurate reading.
- Set the Multimeter: Switch your multimeter to DC voltage mode.
- Connect the Probes: Attach the positive (red) probe to the battery’s positive terminal and the negative (black) probe to the negative terminal.
- Read the Voltage: The multimeter will display the current voltage of your battery.
This reading can provide valuable insights into the battery’s state of charge and help identify potential issues.
Part 7. FAQs
-
What voltage is a 12V lithium-ion battery when fully charged?
Depending on its chemistry, a fully charged 12V lithium-ion battery typically reads between 13.2V and 13.6V. -
Why is my 12V lithium-ion battery only charging to 12.8V?
This could be due to a faulty charger, a BMS limitation, or the battery’s age. Check your charger and ensure it’s compatible with lithium-ion batteries. -
Can I use a lead-acid charger to charge a 12V lithium-ion battery?
No. Lead-acid chargers are not designed for lithium-ion batteries and may damage them. Always use a charger specifically designed for lithium-ion batteries. -
How long does it take to charge a 12V lithium-ion battery?
Charging time depends on the battery capacity and charger output, but it typically takes 3–6 hours with an appropriate charger. -
What is the ideal voltage range for a 12V lithium-ion battery?
The ideal voltage range is between 11.0V and 13.6V. Below 11.0V, the battery is considered deeply discharged and may suffer damage. -
What happens if a lithium-ion battery is overcharged?
Lithium-ion batteries are equipped with a Battery Management System (BMS) to prevent overcharging. However, if the BMS fails or the charger malfunctions, overcharging can cause overheating, swelling, or fire hazards.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Battery Load Test: A Comprehensive Guide
Step-by-step battery load test guide for car, solar & industrial use. Learn how to load test a battery, interpret voltage charts, and avoid common mistakes.
The Comprehensive Guide to Battery Balancing and Battery Balancer
Discover how battery balancers improve lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety. Learn types, functions, and tips to choose the right balancer.
What Is the Best Voltage for a Chainsaw Battery?
Compare 12V-80V chainsaw batteries for light pruning, medium firewood, and professional cutting. See best battery chainsaw with runtime charts and safety tips.
Lithium VS. Alkaline Batteries: A Comprehensive Comparison
Lithium batteries last 3–7× longer than alkaline and perform better in cold weather. Compare lifespan, cost, safety, and best uses to choose the right battery.
Comparing Lithium-Sulfur and Lithium-Ion Batteries: Which is Right for You?
Compare lithium-sulfur (Li-S) and lithium-ion batteries on energy, lifespan, cost, safety, and applications. Best choice for drones, EVs, and electronics.