- Part 1. Overview of 3.6V battery
- Part 2. Types of 3.6V batteries
- Part 3. Typical models of 3.6V batteries
- Part 4. Is 3.6V lithium battery the best battery?
- Part 5. What is a 3.6V battery pack?
- Part 6. 3.6V battery vs 3.7V battery vs 3.8V battery
- Part 7. Can I use a 3.7V battery instead of 3.6V?
- Part 8. Charger and charging tips
- Part 9. Maintenance and storage
- Part 10. Customized 3.6V battery
In our everyday lives, we rely on a variety of devices powered by batteries, from smartphones and laptops to medical equipment and power tools. One of the most commonly used types is the 3.6V battery, which is found in a wide range of applications due to its versatility, reliability, and relatively high energy density. But what exactly is a 3.6V battery? How does it compare to other batteries, and what makes it stand out in different types of devices?
In this comprehensive guide, we will dive into the world of 3.6V batteries, explaining everything from their chemistry and voltage characteristics to their real-world applications. By the end of this article, you’ll not only understand what a 3.6V battery is but also know how to choose the right type and maintain it for optimal performance.
Part 1. Overview of 3.6V battery

At its core, a 3.6V battery refers to a rechargeable or non-rechargeable battery that has a nominal voltage of 3.6 volts. This voltage is the potential difference between the positive and negative terminals of the battery, and it plays a critical role in how the battery performs in different devices.
Voltage Characteristics
While the nominal voltage of a 3.6V battery is usually around 3.6V, it’s important to understand that batteries don’t operate at a constant voltage. Several voltage characteristics come into play, each influencing the charging and discharge behavior:
- Charging Voltage: For most lithium-based 3.6V batteries, the charging voltage typically goes up to 4.2V when fully charged. This is because lithium-ion cells, the most common type of 3.6V battery, need a higher voltage for efficient charging.
- Discharge Voltage: As a 3.6V battery discharges, its voltage decreases. Depending on the battery’s chemistry and design, the battery will generally discharge to around 3.0V to 3.2V before the device starts to experience a loss of power.
- Cut-off Voltage: The cut-off voltage refers to the lowest permissible voltage a battery should be discharged to. For lithium-ion 3.6V batteries, this is generally around 2.5V, though it’s best to avoid discharging below 3.0V to prolong battery life.
Understanding these voltage characteristics is crucial when using and charging 3.6V batteries. For instance, using a charger that exceeds the recommended charging voltage can damage the battery or reduce its lifespan.
Part 2. Types of 3.6V batteries
When discussing 3.6V batteries, it’s essential to recognize that there are different chemistries and designs that can impact their performance. Each chemistry has its own set of strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice depends on your specific application.
Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) 3.6V Batteries
- Chemistry: The most popular type of 3.6V battery today, lithium-ion batteries use lithium compounds as the primary electrochemical material.
- Advantages:
- High Energy Density: Li-ion batteries are lightweight and compact while offering higher energy storage than other types.
- Long Lifespan: They can last for hundreds to thousands of charge cycles, making them highly cost-effective in the long run.
- No Memory Effect: Unlike older technologies, lithium-ion batteries don’t suffer from the “memory effect,” where they lose capacity if not fully discharged before recharging.
- Disadvantages:
- Temperature Sensitivity: Li-ion batteries are sensitive to high temperatures, which can lead to overheating or degradation.
- Safety Concerns: If damaged, overcharged, or improperly handled, lithium-ion batteries can overheat, catch fire, or even explode.
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) 3.6V Batteries
- Chemistry: NiMH batteries use a nickel metal hydride alloy for their electrochemical reactions.
- Advantages:
- More Environmentally Friendly: NiMH batteries are more eco-friendly than lithium-ion, with fewer toxic materials.
- Lower Cost: Generally cheaper than lithium-ion batteries, making them a good option for low-cost devices.
- Disadvantages:
- Lower Energy Density: NiMH batteries are bulkier and heavier than lithium-ion for the same energy output.
- Higher Self-Discharge Rate: NiMH batteries tend to lose their charge faster when not in use compared to lithium-ion batteries.
Lithium Phosphate (LiFePO4) 3.6V Batteries
- Chemistry: LiFePO4 is a variation of lithium-ion chemistry that uses iron phosphate as the cathode material.
- Advantages:
- Superior Safety: LiFePO4 batteries are much safer than standard Li-ion batteries and less prone to fire hazards.
- Longer Lifespan: These batteries can last longer, especially in high-drain applications.
- Disadvantages:
- Lower Energy Density: They tend to have a lower energy density, which means they are bulkier and heavier for the same amount of energy.
- Higher Cost: LiFePO4 batteries are generally more expensive than standard lithium-ion batteries.
Part 3. Typical models of 3.6V batteries
Now, let’s take a look at some of the common 3.6V battery models that you’ll find in various applications:
- 18650 Li-ion Battery (3.6V): This is one of the most widely used 3.6V battery models, primarily used in laptops, flashlights, power tools, and even electric vehicles. These cylindrical batteries are known for their high energy density and long life.
- CR123A Lithium Battery (3.6V): A smaller, high-performance lithium battery used in cameras, tactical flashlights, and security systems. Its compact size makes it ideal for devices that require a high current draw in a small form factor.
- AA NiMH Battery (3.6V): This battery is often used in household gadgets like remote controls, toys, and other low-power devices. NiMH AA batteries offer a great balance of cost and performance for everyday applications.
- Button Cell Li-ion Battery (3.6V): These small batteries are used in applications such as medical devices, hearing aids, and key fobs, where compact size is a priority.
Part 4. Is 3.6V lithium battery the best battery?
While lithium-ion 3.6V batteries offer numerous advantages, you may wonder if they are the best option for every application. Let’s explore why 3.6V lithium batteries are often considered the best, and what their drawbacks are.
Why 3.6V Lithium Batteries Are Considered the Best:
- High Energy Density: Lithium-ion batteries pack a significant amount of energy into a relatively small and light package, making them ideal for high-performance applications where space and weight are limited.
- Long Cycle Life: With proper care, lithium-ion batteries can last for many years, typically offering 500-1,000 charge cycles.
- Fast Charging: Lithium-ion batteries charge faster than other types like NiMH, making them more convenient for modern devices.
Drawbacks of 3.6V Lithium Batteries:
- Sensitive to Overcharging: While they don’t suffer from the memory effect, lithium-ion batteries are sensitive to overcharging and overheating, which can reduce their lifespan.
- Cost: They tend to be more expensive than other battery types, such as NiMH.
- Safety Concerns: If improperly handled or damaged, lithium-ion batteries can overheat and pose safety risks.
Overall, the 3.6V lithium battery is considered the best for most high-energy applications due to its performance and longevity. However, it’s important to balance performance with cost, safety, and other requirements.
Part 5. What is a 3.6V battery pack?
A 3.6V battery pack consists of multiple 3.6V cells connected together to provide higher energy storage or a different voltage output. These packs are commonly used in high-drain applications, such as:
- Power Tools: Battery packs for drills, saws, and other tools are often composed of multiple 3.6V cells.
- Medical Devices: Devices like pacemakers or insulin pumps might use custom 3.6V battery packs for reliable, long-lasting power.
- Electric Vehicles: Small electric scooters or bikes use 3.6V battery packs to power their motors.
These packs are often designed to deliver a specific voltage and capacity, with protective circuits to ensure safe charging and discharging. They are more efficient than individual cells when higher power output or longer run-time is needed.
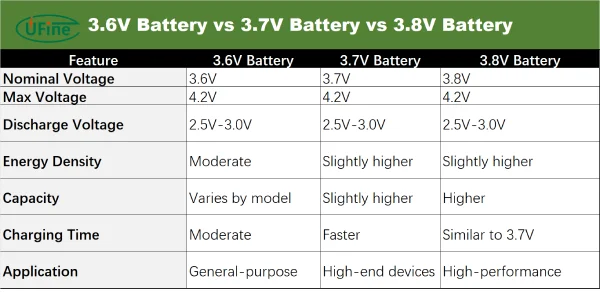
Part 6. 3.6V battery vs 3.7V battery vs 3.8V battery
You might wonder, is there really a noticeable difference between a 3.6V, 3.7V, and 3.8V battery? While the voltage differences are slight, they do have an impact on performance. Let’s compare these three types of batteries across several key aspects:
While the differences are not drastic, the voltage can impact how well the battery performs under load. A 3.7V or 3.8V battery may offer a little more power for devices requiring higher energy consumption.
Part 7. Can I use a 3.7V battery instead of 3.6V?
Generally speaking, yes, you can use a 3.7V battery instead of a 3.6V battery in most cases. The voltage difference is relatively small, and most devices can tolerate a 0.1V increase. However, it’s always best to check the manufacturer’s recommendations, especially for sensitive or safety-critical applications like medical devices or high-performance electronics.
Part 8. Charger and charging tips
When charging a 3.6V battery, it’s crucial to use the right type of charger. For lithium-ion 3.6V batteries, you should always use a charger that is designed specifically for lithium-ion cells, as these chargers regulate the voltage and prevent overcharging. Here are a few essential charging tips:
- Avoid Overcharging: Lithium batteries should never be overcharged. Always use a charger with built-in safety features to cut off charging once the battery reaches its maximum voltage.
- Charge in a Safe Area: Ensure the battery is charged in a cool, dry place. High temperatures can degrade the battery over time.
- Monitor Charge Cycles: While modern lithium-ion batteries are designed to handle many charge cycles, it’s still a good idea to avoid unnecessary charging and discharging to prolong battery life.
Part 9. Maintenance and storage
To maximize the lifespan of your 3.6V battery, proper maintenance and storage are essential. Here are a few tips:
- Keep Batteries Cool: High temperatures can reduce the battery’s lifespan, so always store it in a cool, dry place.
- Avoid Full Discharge: Never let your 3.6V battery discharge completely, as this can permanently damage the battery. A partial discharge is always better.
- Check for Wear and Tear: If the battery shows any signs of swelling, leakage, or damage, stop using it immediately and dispose of it properly.
Part 10. Customized 3.6V battery
A customized 3.6V battery refers to a battery that is tailor-made according to the precise specifications of a customer’s application. These batteries are typically produced by manufacturers who have the capability to design and produce lithium-ion, lithium polymer, NiMH, or other battery chemistries in specific shapes, sizes, capacities, and voltage ratings.
The customization of Ufine Battery can vary from simply modifying the capacity to adapting the battery’s dimensions to fit into a specific device. It can also involve creating multi-cell packs with unique configurations, or adding specific protection circuits, charging features, or connectors. Contact us now to get your 3.6V battery custom solution.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Battery Load Test: A Comprehensive Guide
Step-by-step battery load test guide for car, solar & industrial use. Learn how to load test a battery, interpret voltage charts, and avoid common mistakes.
The Comprehensive Guide to Battery Balancing and Battery Balancer
Discover how battery balancers improve lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety. Learn types, functions, and tips to choose the right balancer.
What Is the Best Voltage for a Chainsaw Battery?
Compare 12V-80V chainsaw batteries for light pruning, medium firewood, and professional cutting. See best battery chainsaw with runtime charts and safety tips.
Lithium VS. Alkaline Batteries: A Comprehensive Comparison
Lithium batteries last 3–7× longer than alkaline and perform better in cold weather. Compare lifespan, cost, safety, and best uses to choose the right battery.
Comparing Lithium-Sulfur and Lithium-Ion Batteries: Which is Right for You?
Compare lithium-sulfur (Li-S) and lithium-ion batteries on energy, lifespan, cost, safety, and applications. Best choice for drones, EVs, and electronics.