You pick up your phone, and suddenly, it starts emitting smoke or, worse, explodes. This is a nightmare for many users, but it’s something that can be prevented with the right knowledge and safety measures. In this article, we will break down the main causes of lithium(liop) battery explosions, how to recognize signs of failure, and practical tips to reduce the risk of an explosion. By the end, you’ll know exactly what to do to keep your devices—and yourself—safe.
Part 1. Why do lipo batteries explode?
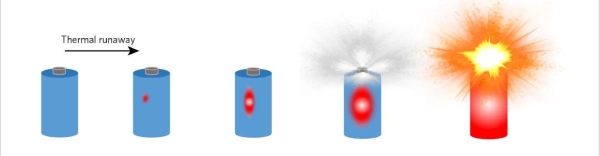
Lithium-ion batteries(lipo batteries) are popular because they offer high energy density, which is ideal for devices that need lightweight, long-lasting power sources. However, their high energy density also makes them potentially dangerous if something goes wrong. The primary cause of lithium battery explosions is a phenomenon known as thermal runaway.
Thermal Runaway and the Chain Reaction
Thermal runaway occurs when a battery’s internal temperature rises uncontrollably, triggering a chemical reaction that generates even more heat. This heat can cause the electrolyte inside the battery to break down, producing gases that build up pressure inside the battery. If this pressure exceeds the battery’s structural limits, it can cause the battery to rupture, catch fire, or explode.
What causes thermal runaway? There are several factors that can lead to it:
- Overcharging: Charging a battery beyond its recommended voltage can cause it to overheat. Most modern devices have built-in protection against overcharging, but using substandard chargers or charging the device improperly can override these protections.
- Physical Damage: Dropping a device or puncturing a battery can cause internal short circuits, leading to a rapid increase in temperature and potentially causing thermal runaway.
- Manufacturing Defects: Even high-quality batteries can have defects, such as improperly sealed cells or flawed separators between the anode and cathode, which can cause short circuits and overheating.
- Exposure to High Temperatures: External heat sources, such as leaving a device in direct sunlight or a hot car, can cause internal battery temperatures to rise beyond safe levels, triggering thermal runaway.
While incidents of battery explosions are still relatively rare, the consequences of a failure can be severe, making it essential to understand the causes.
Part 2. What are the common warning signs of a failing lithium battery?
Lithium-ion batteries do not fail without warning. In fact, there are several key signs you can look out for that indicate a battery is at risk of malfunctioning. Recognizing these signs early can help you take action before disaster strikes.
1. Swelling or Bulging Battery
One of the most obvious signs that a battery is in trouble is swelling or bulging. This occurs when gas builds up inside the battery due to chemical reactions. A swollen battery is a major red flag and should be replaced immediately. If you notice that the device’s shape has changed or the back cover appears to be lifting, don’t wait—take action right away.
2. Overheating
Lithium batteries should not feel excessively hot during normal use. If your device feels unusually warm or hot, it could indicate that the battery is not functioning properly. Continuous overheating can cause damage to the battery and increase the risk of thermal runaway. If your phone, laptop, or electric vehicle gets hot to the touch, it’s time to turn it off and inspect the battery.
3. Rapid Discharge or Reduced Battery Life
As batteries age, they naturally lose capacity, but a sharp decline in battery life can be a warning sign of an underlying issue. If your battery is no longer holding a charge as expected or drains very quickly, it might be deteriorating. This is especially true if the device is used less than usual and the battery still loses power faster than normal.
4. Leaks or Visible Damage
Any visible damage to the battery, such as cracks, leaks, or punctures, is an immediate cause for concern. A leaking battery is not only a sign that the internal integrity has been compromised, but it also poses a fire risk. In such cases, turn off the device and stop using it immediately.
If you notice any of these signs, you should stop using the device and replace the battery as soon as possible to prevent further risk.
Part 3. Can lipo batteries explode when not in use?
It’s a common misconception that lithium batteries only pose a danger when in active use. While rare, lithium-ion batteries can still explode or catch fire even when they are not in use. This can happen due to several factors:
- Long-term Storage: Storing a lithium battery for long periods without proper care can lead to degradation of its internal components. This can increase the risk of an explosion when the battery is eventually used.
- Age of the Battery: As lithium batteries age, their performance deteriorates, and the risk of failure increases. An old, unused battery may still be at risk of overheating, even without being in active use.
- Improper Storage: Storing batteries in high temperatures, in direct sunlight, or near a heat source can cause them to overheat, even when the device is off. Keeping the battery in a cool, dry place is essential for preventing thermal runaway.
To avoid these risks, it’s important to store your devices and batteries in the right conditions. If you plan to store a battery for an extended period, it’s best to leave it partially charged (about 50%) and keep it in a temperature-controlled environment.
Part 4. Practical tips for safely using lithium batteries
While lithium battery explosions are rare, they are a serious concern. By following some basic safety tips, you can significantly reduce the risk of an explosion or fire.
1. Avoid Overcharging and Overdischarging
Lithium-ion batteries should not be overcharged or completely drained. Overcharging can cause the battery to overheat, while deep discharging can lead to irreversible damage. Use your device’s built-in charging controls, and unplug it when fully charged.
2. Use the Correct Charger
Always use the manufacturer-approved charger for your device. Charging with an incompatible charger can cause the voltage to exceed safe levels, leading to overheating or short circuits.
3. Protect from Physical Damage
Treat your devices carefully. Dropping a phone or laptop can damage the battery, even if there are no visible signs of damage. Always use protective cases and avoid exposing the battery to sharp objects or impacts.
4. Keep Devices Cool
Avoid leaving devices in places where they can overheat, such as in a hot car or under direct sunlight. If you notice your device getting excessively warm, remove it from use and allow it to cool down.
5. Replace Aging Batteries
Batteries don’t last forever. As they age, their internal chemistry degrades, increasing the risk of failure. If your device’s battery is more than a few years old, consider replacing it with a new one to reduce the risk of explosion.
Part 5. How to minimize the risk of lithium battery explosions
While no battery is completely risk-free, there are several steps you can take to minimize the likelihood of an explosion:
- Choose Reputable Manufacturers: When purchasing devices or batteries, always choose a trusted manufacturer. Companies like Ufine Battery, known for producing high-quality, custom lithium-ion batteries, prioritize safety and reliability. Ufine Battery offers a range of customized solutions, including lithium polymer batteries, 18650 cells, and Lifepo4 batteries, designed to meet specific needs while ensuring safety.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for usage, storage, and charging. If a device or battery shows any signs of malfunction, replace it promptly.
- Invest in Battery Protection Systems: Many high-end devices come with built-in protection systems to prevent overheating, overcharging, and overdischarging. Make sure these protections are enabled, and invest in devices that offer comprehensive safety features.
- Monitor Battery Health Regularly: If you use devices with removable batteries, perform regular checks for signs of wear or swelling. For non-removable batteries, keep an eye on performance and any unusual heating or battery draining.
Part 6. FAQs
-
How long do lithium-ion batteries last before they become a safety risk?
Lithium-ion batteries typically last between 2-3 years or 300-500 charge cycles before they start to degrade. As they age, they become more prone to overheating, swelling, or malfunctioning. If your device’s battery performance noticeably drops or if the battery shows signs of wear, it’s essential to replace it promptly to avoid potential safety hazards. -
What should I do if my lithium-ion battery is overheating?
If your lithium-ion battery is overheating, immediately turn off the device and unplug it from any power source. Allow it to cool down in a safe, well-ventilated area. If the overheating persists, it may indicate a problem with the battery’s internal components, and it’s advisable to replace the battery. Never leave an overheating battery unattended, as it could pose a fire risk. -
Can I repair a lithium-ion battery that is swollen or leaking?
No, you should never attempt to repair a swollen or leaking lithium-ion battery. Doing so can be extremely dangerous and may result in an explosion. If your battery shows signs of swelling or leakage, safely dispose of it according to local regulations and replace it with a new one. Always handle damaged batteries with caution and avoid direct contact with any leaking substance. -
How can I extend the lifespan of my lithium-ion battery?
To extend the lifespan of your lithium-ion battery, avoid charging it to 100% or letting it completely drain to 0%. Keeping your battery’s charge between 20-80% is ideal. Additionally, store your devices in a cool, dry place and avoid exposing them to extreme temperatures, as heat can accelerate the degradation of the battery’s internal components. -
Are there any specific charging habits that can prevent lithium-ion battery explosions?
Yes, adopting proper charging habits is crucial to prevent overheating and explosions. Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger, and never charge a device overnight or for longer than necessary. Avoid charging your device in excessively hot environments, and unplug it once it reaches full charge. If you notice that your charger or cable feels unusually hot, stop using it and check for any visible damage before continuing to use it.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Paper Battery vs. Flexible Battery: What’s the Difference and Which Is Better?
Paper vs. flexible batteries: learn the key differences, benefits, and which power source fits best for wearables, sensors, and smart tech.
What to Know Before Buying a Tiny LiPo Battery for Your Project
Tiny LiPo batteries are powerful and compact. Learn how to choose the right one for your project with specs, safety, and charging tips.
Bloated LiPo Battery: Will It Explode?
Will a bloated LiPo battery explode? Discover the causes, risks, safety steps, and expert tips to avoid disaster and protect your gear. Must-read safety guide!
12V 100Ah Lithium Ion Battery Price: Full Guide
Learn about 12V 100Ah lithium-ion battery price, from cost ranges to best brands, hidden fees, and how to get the best deal. A must-read for smart buyers!
Resistance and Conductivity: What It Means for Your Lithium Batteries
Resistance and conductivity impact lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety—learn how they work and why they matter.