Low temperature lithium-ion batteries are specifically engineered to maintain performance and efficiency in cold environments. Traditional lithium-ion batteries often struggle as temperatures drop, decreasing capacity and functionality. This article delves into 9 essential aspects of low temperature lithium-ion batteries, providing insights that can help users maximize their performance in challenging conditions.
Part 1. What is a low temperature lithium ion battery?
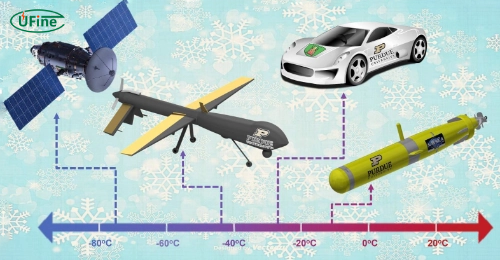
A low temperature lithium ion battery is a specialized lithium-ion battery designed to operate effectively in cold climates. Unlike standard lithium-ion batteries, which can lose significant capacity and efficiency at low temperatures, these batteries are optimized to function in environments as frigid as -40°C. This makes them ideal for applications in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and outdoor technology.
The development of low-temperature lithium-ion batteries addresses the limitations of traditional batteries, which typically experience reduced ion mobility and increased internal resistance when exposed to cold conditions. These batteries, using advanced materials and innovative designs, ensure reliable energy output even in harsh environments.
Part 2. Why do temperatures affect lithium-ion battery performance?
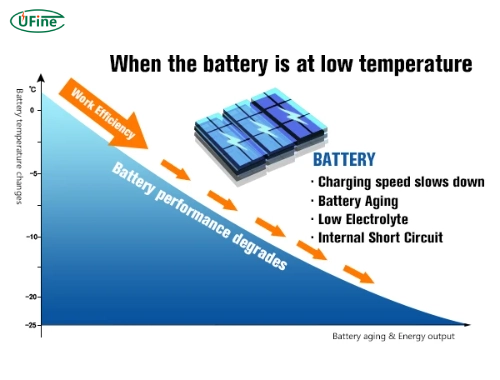
Temperature significantly impacts the chemical processes within lithium-ion batteries. When temperatures drop:
- Decreased Ion Mobility: The movement of lithium ions slows, reducing energy output.
- Increased Viscosity: The electrolyte becomes more viscous at lower temperatures, hindering the transfer of ions between electrodes.
- Chemical Reaction Rates: The overall rate of chemical reactions decreases, resulting in diminished capacity and efficiency.
These factors contribute to a marked decline in battery performance, with potential issues such as voltage drops and accelerated degradation of battery components.
Part 3. What are the key characteristics of low temperature lithium ion batteries?
Low temperature lithium-ion batteries exhibit several unique characteristics that distinguish them from standard lithium-ion batteries:
- Advanced Electrolyte Composition: The electrolytes used in low temperature lithium ion batteries are specially formulated to remain conductive even at low temperatures. This often involves using additives that reduce viscosity and enhance ionic conductivity, allowing for efficient ion transfer.
- Optimized Anode and Cathode Materials: The electrodes are constructed from high-performance materials such as cobalt oxide and graphite. These materials are selected for their ability to facilitate better ion flow under cold conditions, ensuring that the battery can deliver optimal power output.
- Thermal Management Systems: Many low temperature lithium ion batteries incorporate advanced thermal management systems designed to regulate internal temperatures. These systems may include heating elements that activate when external temperatures drop too low, preventing the electrolyte from freezing and maintaining optimal operating conditions.
- High-Quality Insulation: An effective insulation system surrounds the battery components to minimize heat loss. This insulation helps maintain internal temperatures during operation, even when external conditions are icy.
These characteristics collectively enhance the reliability and performance of low temperature lithium ion batteries in demanding environments.
Part 4. How does battery resistance change in cold environments?
Battery resistance is a critical factor affecting performance, especially in cold conditions. As temperatures decrease:
- Increased Internal Resistance: The movement of charged ions within the battery slows down due to the increased viscosity of the electrolyte. This results in higher internal resistance, making it more difficult for the battery to deliver power efficiently.
- Reduced Charge/Discharge Rates: Higher resistance leads to slower charge and discharge rates. Users may notice that their devices take longer to charge or do not perform as expected during operation.
- Potential for Dendrite Formation: There is an increased risk of dendrite formation on the anode surface during charging at low temperatures. Dendrites can create short circuits within the battery, leading to potential failure or safety hazards.
Understanding how resistance changes with temperature is essential for users who rely on these batteries in cold environments. Proper management strategies can help mitigate these effects and prolong battery life.
Part 5. How to store low temperature lithium ion batteries?
Proper storage is crucial for maintaining the integrity and performance of low temperature lithium-ion batteries:
- Cool and Dry Environment: Store these batteries in a controlled environment away from extreme heat or moisture to prevent degradation.
- Partial State of Charge: Keeping the battery at a partial charge (around 40%-60%) can help prolong its lifespan by reducing stress on the cells during storage.
- Regular Maintenance Checks: Periodically inspect the battery’s condition and charge level to ensure it remains healthy.
Part 6. What applications benefit from low temperature lithium ion batteries?
Low temperature lithium-ion batteries find applications across various industries where reliable performance in cold conditions is critical:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): They ensure consistent performance during winter when standard batteries may falter.
- Aerospace Equipment: Essential for satellites and aircraft operating at high altitudes where temperatures can plummet.
- Outdoor Tools: Power tools designed for outdoor use require batteries that can withstand cold without losing efficiency or power output.
Part 7. Can you charge low temperature lithium ion batteries?
Charging these specialized batteries requires careful consideration:
- Temperature Thresholds: Most manufacturers recommend avoiding charging below 0°C due to risks like lithium plating on the anode, which can cause permanent damage.
- Preconditioning Techniques: Some systems allow the battery to be warmed up before charging begins, ensuring safe operation without risking damage.
- Dedicated Chargers: Use chargers designed explicitly for low-temperature operations to ensure effective charging without compromising safety or performance.
Part 8. What are the safety concerns with low temperature lithium ion batteries?
While designed for cold environments, safety remains a paramount concern:
- Dendrite Formation Risks: Charging at a low temperature can lead to dendrite growth on the anode surface, which poses significant safety risks, including short circuits.
- Thermal Runaway Potential: Even low-temperature batteries can experience thermal runaway if not appropriately managed; hence, monitoring systems are crucial for tracking health status.
- Environmental Considerations: Due to their chemical composition and potential ecological impact, ensure these batteries are disposed of appropriately according to local regulations.
Part 9. How do you identify a quality low temperature lithium ion battery?
Choosing a quality low temperature lithium-ion battery involves several considerations:
- Manufacturer Reputation: Opt for products from well-established manufacturers known for their commitment to quality and reliability in battery technology.
- Specifications Review: Look for detailed specifications regarding operating temperature ranges, capacity retention at cold temperatures, cycle life, and safety features provided by the manufacturer.
- Performance Testing Data: Seek out independent testing results or certifications demonstrating how well the battery performs under various conditions, especially at lower temperatures.
- User Reviews and Feedback: Research user experiences regarding performance in real-world scenarios; this feedback can provide valuable insights into reliability and functionality over time.
Part 10. FAQs
-
What happens if I use a standard lithium-ion battery in cold conditions?
Using a standard lithium-ion battery in cold conditions can lead to significantly reduced capacity and efficiency due to decreased ion mobility and increased internal resistance, ultimately resulting in poor performance or failure. -
Can I leave my low temperature lithium ion battery outside?
It’s not advisable to leave batteries outside for extended periods, as environmental factors could negatively impact their performance and lifespan. Always store batteries in a controlled environment when possible. -
How do I know if my battery is damaged from cold exposure?
Signs of damage may include swelling or leakage, reduced capacity, or failure to hold a charge properly. If these symptoms occur, discontinue use immediately as they indicate potential safety hazards. -
Are there specific chargers for low temperature lithium ion batteries?
Yes, chargers are explicitly designed for low-temperature operations that help manage charging processes safely under cold conditions while preventing cell damage. -
Can I recycle old low temperature lithium ion batteries?
Yes, old batteries can be recycled; however, due to their chemical composition and potential environmental impacts, it’s essential to follow local regulations regarding disposal methods.
Related Tags:
More Articles

What Is a Disk Battery? A Simple Guide for Non-Tech Users
A disk battery is a small, round cell used in watches, remotes, and other electronic devices. It delivers steady power for compact, low-drain devices.
What Battery Powers a Space Heater?
Discover the type of battery that powers space heaters and learn how to choose the right one for efficient heating in your home or office.
What Is an LR14 Battery? Learn About This C-Size Cell
The LR14 battery, also known as a C battery, delivers steady power. Learn its specs, uses, lifespan, and how it compares to other battery types.
Watch Battery Dimensions Chart: Sizes, Voltages, and Equivalents Explained
Understanding watch battery dimensions helps you choose the right size, voltage, and equivalent model to keep your watch running safely and smoothly.
How Long Can You Rely on Battery-Powered Generators?
Discover battery generator runtime & lifespan factors. Learn how to maximize performance and choose the right power solution.