The world of batteries is evolving rapidly, with technological advancements leading to more efficient, durable, and environmentally friendly options. Among the top contenders in the battery market are LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) and Lead Acid batteries. This article delves into a detailed comparison between these two types, analyzing their strengths, weaknesses, and ideal use cases to help you make an informed decision.
Part 1. What are LiFePO4 batteries?
LiFePO4 batteries are a type of lithium-ion battery using lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material. LiFePO4 batteries, known for their high safety, long cycle life, and environmental benefits, are becoming increasingly popular in various applications, from electric vehicles to solar energy storage.
Part 2. What are lead-acid batteries?
Lead Acid batteries have been used for over a century and are one of the most established battery technologies. They consist of lead dioxide and sponge lead plates submerged in a sulfuric acid electrolyte. Many industries use these batteries in automotive applications, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and renewable energy systems.
Part 3. LiFePO4 vs. lead-acid battery
1. Energy Density
One of the critical factors in evaluating battery performance is energy density. Energy density refers to the energy stored in a battery relative to its weight or volume.
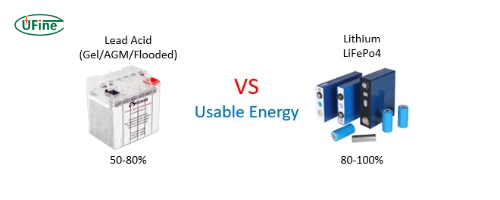
- LiFePO4 Batteries: LiFePO4 batteries have a higher energy density than Lead Acid batteries. This means they can store more energy in a smaller, lighter package, making them ideal for limited weight and space applications.
- Lead Acid Batteries: Lead Acid batteries have a lower energy density. Consequently, they are bulkier and heavier for the same amount of energy storage, which can disadvantage specific applications.
2. Cycle Life
Cycle life refers to the number of charge and discharge cycles a battery can undergo before its capacity significantly degrades.
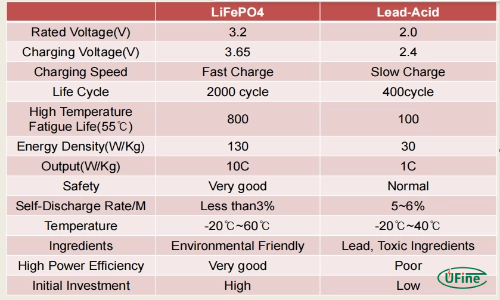
- LiFePO4 Batteries: LiFePO4 batteries boast an impressive cycle life, often exceeding 2000 cycles. This makes them a long-lasting and cost-effective solution in the long run.
- Lead Acid Batteries: Lead Acid batteries typically have a shorter cycle life, ranging from 300 to 500 cycles. This means users must replace them more frequently, which can add to the overall cost.
3. Charging efficiency
Charging efficiency is another crucial factor to consider. It refers to how efficiently a battery can charge and how much energy it can recover during discharge.
- LiFePO4 Batteries: LiFePO4 batteries have a high charging efficiency, often around 95-98%. This means less energy is wasted during charging, making them more efficient.
- Lead Acid Batteries: Lead Acid batteries have a lower charging efficiency, typically around 70-85%. This results in more energy loss during charging, which can be a disadvantage in applications where energy efficiency is critical.
4. Safety and Thermal Stability
Safety is paramount when it comes to battery technology. A battery’s thermal stability and safety features can significantly impact its suitability for various applications.
- LiFePO4 Batteries: LiFePO4 batteries are known for their excellent thermal stability and safety. They are less prone to thermal runaway and are more resistant to overheating, making them safer for use in various environments.
- Lead Acid Batteries: Lead Acid batteries can pose safety risks, especially in high-temperature environments. They are susceptible to thermal runaway and can release toxic gases if not appropriately handled.
5. Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of batteries is an important consideration, especially with the growing focus on sustainability and reducing carbon footprints.
- LiFePO4 Batteries: LiFePO4 batteries are considered more environmentally friendly than Lead Acid batteries. They do not contain toxic heavy metals like lead, and their longer cycle life means people dispose of fewer batteries over time.
- Lead Acid Batteries: Lead Acid batteries contain lead and sulfuric acid, both of which are hazardous to the environment. Proper disposal and recycling are crucial to mitigate their environmental impact.
6. Cost Analysis
Cost is a significant factor in choosing between LiFePO4 and Lead Acid batteries. It is essential to consider both the initial and long-term cost implications.
- LiFePO4 Batteries: LiFePO4 batteries tend to have a higher initial cost than Lead Acid batteries. However, their longer cycle life and higher efficiency can lower overall costs over the battery’s lifetime.
- Lead Acid Batteries: Lead Acid batteries have a lower initial cost, making them an attractive option for applications with limited budgets. However, their shorter cycle life and lower efficiency can lead to higher long-term costs due to more frequent replacements and energy losses.
7. Applications
Different applications require different battery characteristics. Understanding each battery type’s strengths and weaknesses can help select the most suitable option for specific uses.
- LiFePO4 Batteries: Ideal for applications requiring high energy density, long cycle life, and safety. Common uses include electric vehicles, renewable energy storage, portable electronics, and marine applications.
- Lead Acid Batteries: Suitable for applications where cost is a significant factor and high surge currents are required. Typical uses include automotive batteries, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and backup power systems.
8. Maintenance Requirements
The maintenance requirements of a battery can impact its overall usability and cost.
- LiFePO4 Batteries: LiFePO4 batteries are generally low-maintenance. They do not require regular maintenance, and their performance remains consistent.
- Lead Acid Batteries: Lead Acid batteries require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. This includes checking electrolyte levels, cleaning terminals, and ensuring proper charging.
Part 4. FAQs
-
Which battery charges faster, LiFePO4 or Lead Acid?
LiFePO4 batteries charge faster than Lead Acid batteries due to their higher efficiency and ability to handle higher charge currents. -
Are LiFePO4 batteries more expensive than Lead Acid batteries?
Yes, LiFePO4 batteries have a higher initial cost than Lead Acid batteries. Still, their longer lifespan and better performance can make them more cost-effective. -
Can I replace my Lead Acid battery with a LiFePO4 battery?
Yes, you can replace a Lead Acid battery with a LiFePO4 battery. Still, you must ensure your charging system is compatible with LiFePO4 technology. -
Do LiFePO4 batteries require maintenance?
LiFePO4 batteries require very little maintenance compared to Lead Acid batteries, which need regular electrolyte level checks and terminal cleaning. -
How do temperature extremes affect LiFePO4 and Lead Acid batteries?
LiFePO4 batteries perform well in a wide range of temperatures. Still, they can be affected by extreme cold. At the same time, Lead Acid batteries can suffer performance degradation in high and low temperatures.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.