- Part 1. Understanding the 24V battery types
- Part 2. 24V battery charger circuit
- Part 3. Buy 24V battery charger: key considerations
- Part 4. 24V lithium battery charger : optimizing performance and lifespan
- Part 5. 24V LiFePO4 battery charger: tailored for safety and durability
- Part 6. Where is the 24V battery charger used?
- Part 7. Price
- Part 8. Where to buy a 24V battery charger
- Part 9. Can I charge a 24V battery with a 12V charger?
- Part 10. Charging and maintenance
Navigating the world of 24V battery chargers can be tricky. This in-depth guide covers everything from charger types and circuits to key considerations and specific features for lithium and LiFePO4 batteries. Find out how to choose the best charger for your needs and get your 24V system running smoothly!
In a world increasingly powered by electricity, 24V battery systems are gaining momentum. From electric vehicles and forklifts to solar energy storage and off-grid power solutions, 24V batteries are becoming a reliable and efficient power source. But with so many different types of 24V battery chargers available, choosing the right one for your needs can feel like navigating a maze. Fear not, dear reader, because this comprehensive guide will illuminate the path to choosing the perfect 24V battery charger for your specific application.

Part 1. Understanding the 24V battery types
The first step in choosing a 24V battery charger is understanding the different types of batteries it can power. Each battery chemistry has its own unique characteristics, charging requirements, and lifespan, so selecting a compatible charger is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Here’s a breakdown of the most common 24V battery types:
-
Lead-Acid Batteries: These workhorses of the battery world are still widely used due to their affordability and readily available nature. However, they come with some drawbacks:
- Maintenance: Lead-acid batteries require regular maintenance, including checking the electrolyte level and topping it off with distilled water.
- Lifespan: They have a shorter lifespan than newer battery technologies, requiring more frequent replacements.
- Weight: They are heavier than other battery types, which can impact the performance of the device they power.
-
AGM (Absorbed Glass Mat) Batteries: These batteries are a significant improvement over standard lead-acid batteries, using a fiberglass mat to absorb the electrolyte. This design offers several advantages:
- Leak-Proof: They are virtually leak-proof, reducing the risk of spills and corrosion.
- Vibration Resistance: They are more resistant to vibration, making them ideal for off-road use in vehicles or equipment.
- Longer Lifespan: They have a longer lifespan than standard lead-acid batteries, reducing the frequency of replacements.
- Performance: They offer better performance in cold weather and have a higher discharge rate, allowing for more power delivery.
-
Gel Batteries: These batteries take the leak-proof design of AGM batteries a step further, using a gel-like electrolyte. This offers even greater protection against spills and leaks, making them ideal for harsh environments.
- Extreme Durability: They are incredibly durable and resistant to vibration, making them perfect for off-road use.
- Deep Cycle Capability: They have excellent deep-cycle capability, meaning they can be discharged and recharged repeatedly without significant damage. This is particularly important for applications requiring long run times or frequent use.
- Longer Lifespan: They have a longer lifespan than both standard lead-acid and AGM batteries, reducing the frequency of replacements.
-
Lithium-Ion Batteries: These batteries represent the cutting edge of battery technology, offering significant advantages over traditional lead-acid batteries:
- Lightweight: They are significantly lighter than lead-acid batteries, improving the performance of the device they power.
- High Power Density: They have a higher power density, meaning they can store more energy in a smaller space. This translates to longer run times and better performance.
- Longer Lifespan: They have a much longer lifespan than lead-acid batteries, reducing the frequency of replacements and saving you money in the long run.
- Faster Charging: They charge faster than lead-acid batteries, making it easier to get back to work or on the road quickly.
However, lithium-ion batteries also come with some drawbacks:
- Cost: They are more expensive than traditional lead-acid batteries.
- Sensitivity: They are more sensitive to extreme temperatures, requiring careful storage and handling.
- Availability: They are not as widely available as lead-acid batteries, making it more challenging to find replacement parts.
-
LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) Batteries: These are a type of lithium-ion battery known for their exceptional safety and durability. They are becoming increasingly popular for applications where safety and longevity are paramount.
- Outstanding Safety: LiFePO4 batteries are less prone to overheating and fire hazards compared to other lithium-ion chemistries.
- Long Lifespan: They have a very long lifespan, often exceeding 2,000 charge cycles.
- Deep Cycle Capability: They excel in deep-cycle applications, handling repeated deep discharges without significant degradation.
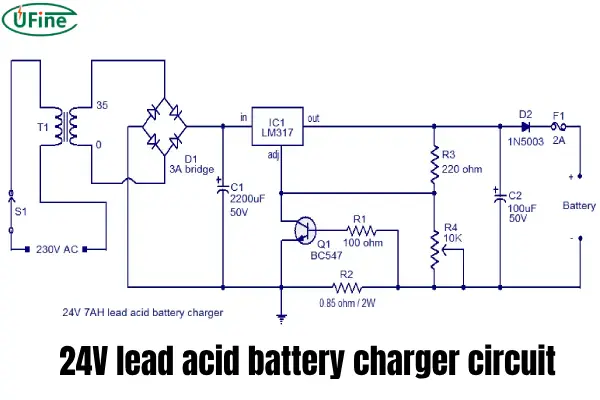
Part 2. 24V battery charger circuit
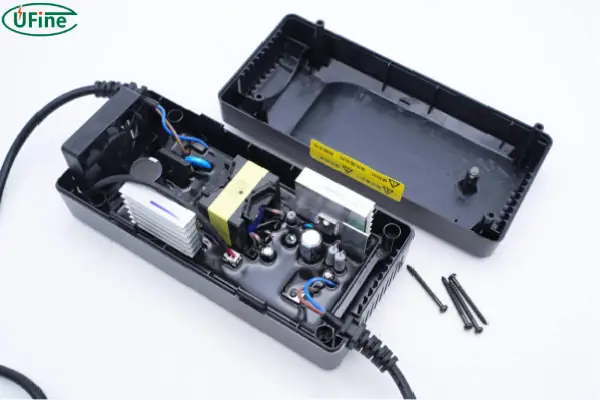
Understanding the basic components of a 24V battery charger circuit is essential for making informed choices. This circuit is responsible for converting AC power from the wall outlet into DC power suitable for charging your battery safely and efficiently. Here’s a breakdown of the key components:
- Rectifier: This component acts as a bridge between the alternating current (AC) from the power outlet and the direct current (DC) required by the battery. It converts the AC power into DC power, which is essential for the charging process.
- Transformer: This component steps down the voltage from the AC power outlet to the appropriate charging voltage for the battery. The voltage conversion is crucial for ensuring the battery receives the correct amount of power without damage.
- Control Circuit: This circuit acts as the brain of the charging process, monitoring the current and voltage flowing to the battery. It adjusts the charging parameters to ensure a safe and efficient charging process.
- Protection Circuit: This circuit acts as a safety net, protecting the battery and the charger from overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits. These safety features are crucial for preventing damage to the battery and ensuring its longevity.
Part 3. Buy 24V battery charger: key considerations
Now that we’ve explored the battery types and charger circuit, it’s time to delve into the key considerations when choosing a 24V battery charger. These factors will help you narrow down your options and find the perfect charger for your specific needs.
-
Battery Type Compatibility: The most crucial factor is ensuring the charger is compatible with the type of battery you’re using. Lead-acid chargers are designed for traditional lead-acid batteries, while AGM chargers are optimized for AGM batteries, and so on. Using the wrong charger can damage your battery and shorten its lifespan.
-
Charging Current: The charging current determines how quickly the battery charges. Higher charging currents mean faster charging times, but they can also generate more heat and potentially shorten the battery’s lifespan. Choose a charging current appropriate for your battery’s capacity and your needs. For example, a smaller battery might require a lower charging current than a larger battery.
-
Voltage: The charger’s output voltage must match the battery’s voltage. 24V chargers are designed for 24V batteries. Using a charger with a different voltage can damage the battery.
-
Features: Some chargers offer additional features, such as automatic charging modes, temperature compensation, and battery health monitoring. These features can enhance the charging process, extend the battery’s lifespan, and provide valuable insights into the battery’s health.
-
Safety Features: Look for chargers with safety features like overcharge protection, over-discharge protection, and short-circuit protection. These features will help protect your battery and charger from damage.
-
Price: 24V battery chargers range in price depending on their features, capacity, and brand. Set a budget before you start shopping and compare prices from different manufacturers.
Part 4. 24V lithium battery charger : optimizing performance and lifespan
Lithium battery chargers often have specialized features designed for optimal performance and safety, ensuring the battery receives the right amount of power for a long and healthy lifespan.
-
Constant Current (CC) and Constant Voltage (CV) Charging: This charging method ensures the battery receives a constant current until it reaches its full voltage, then switches to a constant voltage to maintain a full charge. This two-stage charging process helps prevent overcharging and maximizes battery life.
-
Temperature Compensation: This feature adjusts the charging current based on the battery’s temperature, preventing overcharging and ensuring optimal performance. Lithium-ion batteries are sensitive to temperature, and this feature helps maintain their health and extend their lifespan.
-
Balancing: Lithium-ion batteries consist of multiple cells. Balancing ensures each cell charges evenly, maximizing the battery’s lifespan. This feature is crucial for maintaining the balance of the battery pack and preventing individual cells from becoming overcharged or undercharged.
Part 5. 24V LiFePO4 battery charger: tailored for safety and durability
LiFePO4 battery chargers often have features specific to this battery chemistry, ensuring they receive the optimal charging profile for maximum safety, longevity, and performance.
-
Lower Charging Voltage: LiFePO4 batteries have a lower charging voltage than other lithium-ion batteries. LiFePO4 chargers are designed for this specific voltage, ensuring the battery receives the correct amount of power without damage.
-
Higher Charging Current: LiFePO4 batteries can handle higher charging currents, allowing for faster charging times. This feature is beneficial for applications where quick charging is essential.
-
Deep Discharge Protection: LiFePO4 batteries are less susceptible to damage from deep discharges. LiFePO4 chargers often include features that prevent deep discharges, further extending the battery’s lifespan.
Part 6. Where is the 24V battery charger used?
24V battery chargers are used in a wide range of applications, powering everything from electric vehicles to off-grid solar systems. Here are some of the most common uses:
-
Electric Vehicles: Some electric vehicles, especially smaller models like golf carts and forklifts, use 24V battery systems. 24V battery chargers are essential for keeping these vehicles running smoothly.
-
Solar Energy Storage: 24V battery chargers are used to charge batteries in off-grid solar power systems, providing a reliable source of energy for homes, businesses, and remote locations.
-
Backup Power Systems: 24V battery chargers can be used to charge batteries in backup power systems, providing power during outages and ensuring a continuous power supply.
-
Industrial Equipment: Some industrial equipment, such as electric forklifts and pallet jacks, use 24V battery systems. 24V battery chargers are essential for keeping these machines running efficiently.
-
Marine Applications: 24V battery chargers are used to charge batteries in marine applications, such as boats and yachts. These chargers are designed to withstand the harsh marine environment and ensure reliable power for navigation, communication, and onboard systems.
Part 7. Price
The price of a 24V battery charger can vary significantly depending on its features, capacity, and brand. Generally, you can expect to pay anywhere from $50 to $500 or more for a high-quality 24V battery charger.
-
Budget-Friendly Options: Entry-level chargers are available for under $100, offering basic functionality for charging lead-acid batteries.
-
Mid-Range Chargers: These chargers offer a balance of features and affordability, typically ranging from $100 to $300. They often include features like automatic charging modes and temperature compensation.
-
Premium Chargers: High-end chargers can cost upwards of $300, offering advanced features like battery health monitoring, balancing, and specialized charging profiles for lithium-ion and LiFePO4 batteries.
Part 8. Where to buy a 24V battery charger
You can purchase 24V battery chargers from a variety of retailers, both online and offline:
-
Online Retailers: Amazon, eBay, and other online retailers offer a wide selection of 24V battery chargers, making it easy to compare prices and features.
-
Specialty Stores: Stores that specialize in batteries and charging equipment often carry a variety of 24V battery chargers, offering expert advice and guidance.
-
Auto Parts Stores: Some auto parts stores carry 24V battery chargers, especially those designed for automotive applications.
-
Electronics Retailers: Electronics retailers, such as Best Buy and Fry’s Electronics, may also carry a selection of 24V battery chargers.
Part 9. Can I charge a 24V battery with a 12V charger?
No, you cannot charge a 24V battery with a 12V charger. Using a charger with a lower voltage than the battery can damage the battery and potentially cause a fire. Always use a charger that matches the battery’s voltage.
Part 10. Charging and maintenance
Proper charging and maintenance are essential for extending the lifespan of your 24V battery and ensuring optimal performance. Here are some general tips:
-
Follow the Manufacturer’s Instructions: Always refer to the battery manufacturer’s instructions for specific charging recommendations. These instructions will provide the optimal charging current, voltage, and charging time for your battery.
-
Use the Right Charger: Use a charger designed for your specific battery type and voltage. Using the wrong charger can damage the battery and shorten its lifespan.
-
Charge in a Well-Ventilated Area: Lead-acid batteries emit hydrogen gas during charging, so it’s important to charge them in a well-ventilated area. This will prevent the buildup of flammable gases and ensure a safe charging environment.
-
Avoid Overcharging: Overcharging can damage the battery. Most chargers have built-in overcharge protection, but it’s still a good idea to monitor the charging process. Overcharging can shorten the battery’s lifespan and potentially cause damage.
-
Keep the Battery Terminals Clean: Corrosion on the battery terminals can prevent a good electrical connection. Regularly clean the terminals with a wire brush and baking soda solution. Corrosion can reduce the battery’s performance and potentially cause damage.
-
Store the Battery Properly: If you’re not using the battery for an extended period, store it in a cool, dry place. A fully charged battery will store better than a partially charged battery. Proper storage can help maintain the battery’s health and prevent premature degradation.
Choosing the right 24V battery charger is an important decision that can significantly impact the performance and lifespan of your battery. By understanding the different types of chargers, their key features, and proper charging and maintenance practices, you can ensure that your 24V battery is properly powered and ready for any task. Whether you’re powering an electric vehicle, storing solar energy, or providing backup power, a reliable 24V battery charger is the key to unlocking the full potential of your 24V system.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Battery Load Test: A Comprehensive Guide
Step-by-step battery load test guide for car, solar & industrial use. Learn how to load test a battery, interpret voltage charts, and avoid common mistakes.
The Comprehensive Guide to Battery Balancing and Battery Balancer
Discover how battery balancers improve lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety. Learn types, functions, and tips to choose the right balancer.
What Is the Best Voltage for a Chainsaw Battery?
Compare 12V-80V chainsaw batteries for light pruning, medium firewood, and professional cutting. See best battery chainsaw with runtime charts and safety tips.
Lithium VS. Alkaline Batteries: A Comprehensive Comparison
Lithium batteries last 3–7× longer than alkaline and perform better in cold weather. Compare lifespan, cost, safety, and best uses to choose the right battery.
Comparing Lithium-Sulfur and Lithium-Ion Batteries: Which is Right for You?
Compare lithium-sulfur (Li-S) and lithium-ion batteries on energy, lifespan, cost, safety, and applications. Best choice for drones, EVs, and electronics.