- Part 1. What is a lithium-ion forklift battery?
- Part 2. Why choose lithium-ion forklift batteries?
- Part 3. Charging lithium-ion forklift batteries
- Part 4. Advantages of using lithium-ion forklift batteries
- Part 5. Disadvantages of lithium-ion forklift batteries
- Part 6. Maintenance of lithium-ion forklift batteries
- Part 7. Cost considerations for lithium-ion forklift batteries
- Part 8. What are the main differences between lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries in forklifts?
- Part 9. FAQs
Lithium-ion batteries have revolutionized the material handling industry, particularly in the operation of forklifts. This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need about lithium-ion forklift batteries, including their benefits, charging methods, maintenance, and more.
Part 1. What is a lithium-ion forklift battery?
Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable batteries that use lithium ions as a key component of their electrochemistry. Lithium-ion batteries offer numerous advantages that make them increasingly popular in various applications, especially forklifts, unlike traditional lead-acid batteries.
How Do Lithium-Ion Forklift Batteries Work?
Lithium-ion batteries move lithium ions between the anode and cathode during charging and discharging. The ions move from the anode to the cathode, storing energy when the battery charges. Conversely, the ions return to the anode during discharge, releasing energy to power the forklift.
Part 2. Why choose lithium-ion forklift batteries?
Lithium-ion forklift batteries provide several compelling benefits over traditional battery types:
- Higher Energy Density: Lithium-ion batteries have a higher energy density to store more energy in a smaller space. This results in longer operating times for forklifts without the need for frequent recharges.
- Faster Charging: These batteries can be charged much faster than lead-acid batteries, often reaching full charge in less than two hours. This rapid charging capability allows for opportunity charging during breaks, maximizing productivity.
- Longer Lifespan: Lithium-ion batteries can endure thousands of charge cycles, significantly outlasting lead-acid batteries. This longevity translates to lower replacement costs over time.
- Reduced Maintenance: Unlike lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries require minimal maintenance. There is no need for watering or equalization, making them easier to manage.
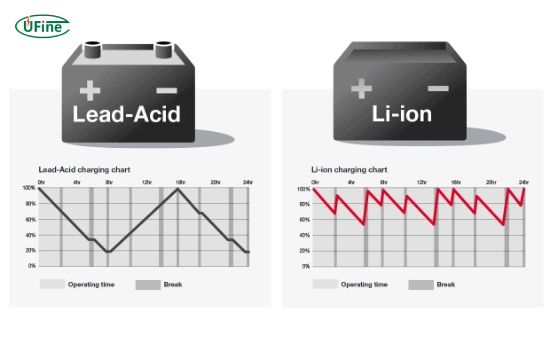
Part 3. Charging lithium-ion forklift batteries
Charging lithium-ion batteries is straightforward but requires specialized chargers designed for their unique chemistry. Here are some key points about charging:
- Opportunity Charging: This method allows for quick top-ups during short breaks, which is not feasible with lead-acid batteries. Forklifts can be charged in 15 to 30 minutes, making running multiple shifts without battery swaps possible.
- Dedicated Chargers: Lithium-ion batteries require specific chargers that match their voltage and current specifications. These chargers are often compact and user-friendly.
- No Cooling Period: Unlike lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries do not require a cooling-off period after charging, allowing continuous operation.
Part 4. Advantages of using lithium-ion forklift batteries
The advantages of lithium-ion batteries extend beyond just performance. Here are some practical benefits:
- Increased Productivity: Lithium-ion batteries help reduce downtime, increasing warehouse operations’ productivity with faster charging times and longer runtimes.
- Space Efficiency: Lithium-ion batteries can be charged anywhere, eliminating the need for dedicated charging rooms and freeing up valuable warehouse space.
- Improved Safety: These batteries do not emit toxic fumes, and their sealed design minimizes the risk of spills or leaks, contributing to a safer working environment.
Part 5. Disadvantages of lithium-ion forklift batteries
While lithium-ion batteries offer numerous benefits, they also come with some drawbacks:
- Higher Initial Cost: Lithium-ion batteries require a significantly higher upfront investment than lead-acid batteries. However, the long-term savings often justify the initial expense.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Lithium-ion batteries can be sensitive to extreme temperatures. Operations in very cold or hot environments may require additional considerations to maintain battery performance.
Part 6. Maintenance of lithium-ion forklift batteries
Although lithium-ion batteries require less maintenance than traditional batteries, some primary care is still necessary:
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly check the battery’s charge level to ensure optimal performance.
- Proper Storage: If batteries are not used for extended periods, they should be stored according to the manufacturer’s guidelines to prevent damage.
- End-of-Life Considerations: Monitor battery performance as it approaches the end of its lifespan. If runtime drops significantly or charging times increase, it may be time to consider replacement.
Part 7. Cost considerations for lithium-ion forklift batteries
Lithium-ion forklift batteries vary widely, typically from $17,000 to $25,000 per battery. While this is higher than the cost of lead-acid batteries, the overall cost of ownership may be lower due to reduced maintenance and a longer lifespan.
Part 8. What are the main differences between lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries in forklifts?
Understanding the differences between lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries is crucial for making informed decisions about forklift power sources.
Lithium-ion batteries are known for their higher energy density, which allows them to store more power in a smaller space. This makes them an ideal choice for modern, space-saving forklift designs. They also charge much faster, typically in just 1 to 2 hours, and have a longer lifespan, lasting between 2,000 and 5,000 charge cycles. Another advantage of lithium-ion batteries is their low maintenance, as they don’t require regular watering or equalization.
On the other hand, lead-acid batteries are a more traditional option, offering lower energy density, meaning they are bulkier and take up more space for the same power output. Charging them is a slower process, often taking up to 8 hours. Additionally, they need regular maintenance, such as watering and equalization, to ensure optimal performance. However, their initial cost is lower than lithium-ion batteries, making them a more affordable option. Lead-acid batteries are also more robust in varying temperature conditions. In contrast, lithium-ion batteries can be sensitive to extreme temperatures.
Here’s a comparison of the two:
| Feature | Lithium-Ion Batteries | Lead-Acid Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | Higher energy density, more power in less space | Lower energy density, larger size for the same power |
| Charging Time | Fast charging (1-2 hours) | Slow charging (up to 8 hours) |
| Lifespan | 2,000 to 5,000 cycles | 1,000 to 1,500 cycles |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance required | Regular maintenance needed (watering, equalization) |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Temperature Range | Sensitive to extreme temperatures | More robust in varying temperatures |
Part 9. FAQs
-
Do forklifts use lithium batteries?
Yes, many modern forklifts are now powered by lithium-ion batteries, especially in operations that require high efficiency and minimal downtime. -
How much does a lithium forklift battery cost?
Lithium forklift batteries generally cost between $17,000 and $25,000, significantly more than lead-acid batteries. -
What is the most significant advantage of a lithium-ion forklift battery?
The primary advantage is increased runtime and productivity due to faster charging and longer operational life. -
Are lithium-ion batteries safe?
Lithium-ion batteries are considered safe for use in forklifts, as they do not emit toxic fumes and have built-in safety features to prevent accidents. -
How long do lithium-ion forklift batteries last?
Lithium-ion batteries can last 2 to 4 times longer than lead-acid batteries, depending on usage and maintenance.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Battery Load Test: A Comprehensive Guide
Step-by-step battery load test guide for car, solar & industrial use. Learn how to load test a battery, interpret voltage charts, and avoid common mistakes.
The Comprehensive Guide to Battery Balancing and Battery Balancer
Discover how battery balancers improve lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety. Learn types, functions, and tips to choose the right balancer.
What Is the Best Voltage for a Chainsaw Battery?
Compare 12V-80V chainsaw batteries for light pruning, medium firewood, and professional cutting. See best battery chainsaw with runtime charts and safety tips.
Lithium VS. Alkaline Batteries: A Comprehensive Comparison
Lithium batteries last 3–7× longer than alkaline and perform better in cold weather. Compare lifespan, cost, safety, and best uses to choose the right battery.
Comparing Lithium-Sulfur and Lithium-Ion Batteries: Which is Right for You?
Compare lithium-sulfur (Li-S) and lithium-ion batteries on energy, lifespan, cost, safety, and applications. Best choice for drones, EVs, and electronics.