Lithium thionyl chloride (Li-SOCl2 ) batteries are vital in many modern applications. They are known for their high energy density, long shelf life, and ability to operate in extreme temperatures. This guide will delve into the intricacies of Li-SOCl2 batteries, their advantages, applications, and why they stand out in the battery industry.
Part 1. What are lithium thionyl chloride batteries?
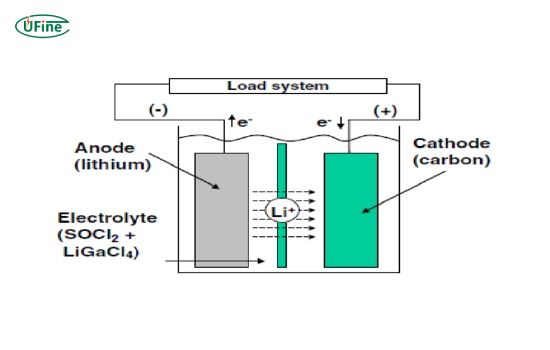
Lithium thionyl chloride batteries are a type of primary battery, meaning they are non-rechargeable. They comprise a lithium anode and a liquid thionyl chloride electrolyte, which also serves as the cathode. This unique chemistry provides several benefits, including high energy density and a long operational life. Notable manufacturers like Tadiran Batteries produce high-quality Li-SOCl2 batteries. At the same time, Ufine Battery offers rechargeable lithium-ion batteries that are more environmentally friendly and can provide tailored energy solutions.
What are the main features of lithium thionyl chloride batteries?
Lithium thionyl chloride batteries are renowned for several key features:
- High energy density: These batteries can store much energy relative to their size.
- Long shelf life: With a low self-discharge rate, they can retain their charge for many years.
- Wide operating temperature range: They function efficiently from -55°C to +125°C.
- Voltage stability: They maintain a consistent voltage throughout their discharge cycle.
What are the typical applications of lithium thionyl chloride batteries?
Li-SOCl2 batteries are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Remote wireless devices: Ideal for devices requiring long-term, reliable power.
- Medical devices: These are used in pacemakers and other critical medical equipment.
- Military equipment: Suitable for high-reliability and extreme condition applications.
- Industrial applications: Used in sensors, meters, and monitoring systems.
Part 2. How do lithium thionyl chloride batteries work?
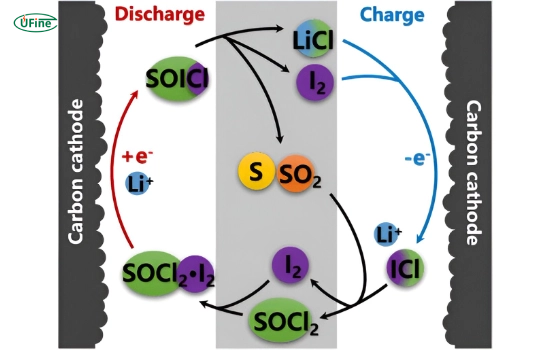
Li-SOCl2 batteries operate through a chemical reaction between the lithium anode and the thionyl chloride electrolyte. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the process:
- Initial State: The battery consists of a lithium anode and a thionyl chloride electrolyte, which also acts as the cathode.
- Discharge Process: When the battery is connected to a load, lithium atoms at the anode oxidize, releasing electrons. These electrons travel through the external circuit, providing electrical power to the connected device.
- Electrolyte Reaction: The thionyl chloride electrolyte undergoes a reduction reaction at the cathode, producing sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and lithium chloride (LiCl).
- Passivation Layer Formation: A passivation layer of lithium chloride forms on the anode, which helps to control the reaction rate and significantly reduces the battery’s self-discharge rate.
- Voltage Stability: The battery maintains a stable voltage output due to the controlled reaction rates and the properties of the passivation layer.
This combination of reactions allows Li-SOCl2 batteries to deliver consistent power over long periods, making them ideal for applications requiring long-lasting and reliable energy sources.
Part 3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of lithium thionyl chloride batteries?
Advantages
- High voltage: A nominal voltage of 3.6V, higher than many other lithium batteries.
- Longevity: It can last up to 40 years in specific applications.
- Durability: Suitable for use in extreme environmental conditions.
- Safety: Non-flammable electrolytes and robust construction reduce risk.
Disadvantages
- Non-rechargeable: These batteries cannot be recharged once depleted, which can be less environmentally friendly.
- Cost: Higher initial cost compared to some other battery types.
- Safety concerns: Requires careful handling due to thionyl chloride’s toxic and corrosive nature.
- Limited availability: They are less widely available than some other battery types, which can limit their use in consumer applications.
Part 4. How do lithium thionyl chloride batteries compare to other battery types?
To understand the unique position of lithium thionyl chloride (Li-SOCl2) batteries in the market, you must compare them with other common battery types. Let’s examine how Li-SOCl2 batteries compare to alkaline, lithium-ion, lead-acid, and nickel-cadmium batteries.
Li-SOCl2 vs. Alkaline Batteries
Energy Density:
- Li-SOCl2: Much higher energy density (1280 Wh/L)
- Alkaline: Lower energy density (320 Wh/L)
Shelf Life:
- Li-SOCl2: Up to 20 years or more
- Alkaline: Typically 5-10 years
Temperature Range:
- Li-SOCl2 : -55°C to +125°C
- Alkaline: -20°C to +54°C
Voltage Stability:
- Li-SOCl2: Maintains stable voltage throughout the discharge
- Alkaline: Voltage decreases gradually during discharge
Li-SOCl2 vs. Lithium-Ion Batteries
Rechargeability:
- Li-SOCl2 : Non-rechargeable
- Lithium-Ion: Rechargeable (500-1000 cycles)
Energy Density:
- Li-SOCl2 : Higher (1280 Wh/L)
- Lithium-Ion: Lower, but still high (250-693 Wh/L)
Self-Discharge Rate:
- Li-SOCl2: Deficient (less than 1% per year)
- Lithium-Ion: Higher (2-3% per month)
Applications:
- Li-SOCl2: Long-term, low-power applications
- Lithium-Ion: High-power, frequent-use applications
Li-SOCl2 vs. Lead-Acid Batteries
Weight:
- Li-SOCl2: Much lighter
- Lead-Acid: Heavier
Energy Density:
- Li-SOCl2: Much higher (1280 Wh/L)
- Lead-Acid: Lower (80-90 Wh/L)
Temperature Performance:
- Li-SOCl2: Excellent in extreme temperatures
- Lead-Acid: Poor performance in cold temperatures
Maintenance:
- Li-SOCl2 : Maintenance-free
- Lead-Acid: Requires regular maintenance
Li-SOCl2 vs. Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) Batteries
Memory Effect:
- Li-SOCl2: No memory effect
- NiCd: Suffers from memory effect
Environmental Impact:
- Li-SOCl2: Less toxic but requires particular disposal
- NiCd: Contains toxic cadmium, heavily regulated
Voltage:
- Li-SOCl2: Higher nominal voltage (3.6V)
- NiCd: Lower nominal voltage (1.2V)
Self-Discharge Rate:
- Li-SOCl2: Extremely low
- NiCd: Higher (15-20% per month)
Part 5. What are the safety considerations for lithium thionyl chloride batteries?
Safety considerations for Li-SOCl2 batteries include:
Handling and Storage
- Proper Handling: Avoid direct contact with the electrolyte, which is toxic and corrosive. Use protective gear when handling.
- Storage Conditions: To prevent degradation, store in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and heat sources.
Usage
- To avoid Short-Circuiting, Ensure that the battery terminals do not come into contact with conductive materials that could cause a short circuit.
- Temperature Monitoring: While they can operate in extreme temperatures, avoid exposing the batteries to temperatures beyond their specified range to prevent leakage or rupture.
Disposal
- Follow Regulations: Dispose of used batteries according to local regulations to prevent environmental contamination and health hazards.
- Recycling Programs: Participate in battery recycling programs to ensure safe and environmentally friendly disposal.
Part 6. How to choose the correct lithium thionyl chloride battery for your application?
When selecting a Li-SOCl2 battery, consider:
- Application requirements: Match the battery’s specifications to your device’s needs.
- Temperature range: Ensure the battery can operate within the required temperature range.
- Longevity: Choose a battery with a shelf life that meets your application’s duration.
- Manufacturer reputation: Opt for reputable manufacturers like Tadiran for quality assurance.
Part 7. FAQs
-
What is the difference between lithium-ion and lithium-thionyl chloride batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable and commonly used in consumer electronics, while lithium-thionyl chloride batteries are non-rechargeable. They have higher energy density and longer shelf life and are suitable for industrial and medical applications. -
Can lithium thionyl chloride batteries be recharged?
Lithium thionyl chloride batteries are primary and cannot be recharged. Attempting to recharge them can lead to safety hazards, including potential fire risks. -
What is the operating temperature range of lithium thionyl chloride batteries?
Lithium thionyl chloride batteries typically operate between -55°C and +125°C, making them suitable for various environmental conditions. -
How long do lithium thionyl chloride batteries last?
With a low self-discharge rate, these batteries can last 10 to 20 years, and some models, like those from Tadiran, can last up to 40 years. -
Are lithium thionyl chloride batteries safe?
Yes, they are safe when handled and disposed of properly. You should follow proper safety protocols because they contain toxic and corrosive materials.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.