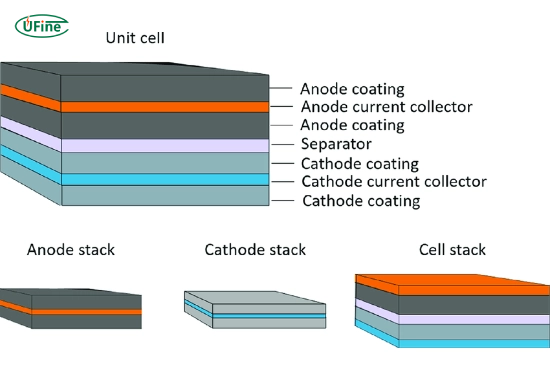
A cell stack is the backbone of any lithium battery system. It’s the structured grouping of individual battery cells that deliver the desired power and energy output together. Whether you’re assembling a small DIY pack or a large-scale battery for solar storage or electric vehicles, how you stack your cells can make or break your project.
Proper cell stack setup affects battery efficiency, thermal performance, lifespan, and safety.
In this detailed guide, we’ll discuss the best practices for assembling lithium battery cell stacks, common mistakes to avoid, and advanced tips for thermal management and battery management systems (BMS). By the end of this article, you’ll fully understand how to build reliable, high-performance lithium battery packs.
Part 1. What is a cell stack in a lithium battery?
A cell stack is a collection of individual battery cells organized and connected to form a battery module or pack. These cells are placed in series (to increase voltage), parallel (to increase capacity) or a combination of both.
In simple terms, it’s your battery cells’ physical layout and electrical configuration.
Each cell in the stack contributes to the battery’s overall performance. The quality of stacking directly impacts the energy output, internal resistance, and even heat distribution during operation.
Part 2. Why is proper cell stacking so important?
When stacking cells, the goal is not just to “fit them together.” The goal is to ensure:
- Uniform pressure across all cells
- Stable electrical connections
- Safe thermal behavior
- Mechanical strength under vibration or impact
Poor stacking can lead to:
- Short circuits
- Cell swelling
- Thermal runaway
- Premature failure
The more consistent and precise your cell stack, the more reliable your battery will be.
Part 3. Series and parallel configurations: What’s the difference?
In lithium batteries, electrical connections between cells fundamentally determine the final voltage and capacity.
Series Configuration (S)
- Each cell adds voltage
- Total capacity remains the same
- Example: 4 cells at 3.7V and 2500mAh → 14.8V, 2500mAh
Parallel Configuration (P)
- Each cell adds capacity
- Total voltage remains the same
- Example: 4 cells at 3.7V and 2500mAh → 3.7V, 10,000mAh
Depending on the application, most lithium battery systems use a combination like 4S2P or 16S3P.
Part 4. How do you physically align and secure lithium cells in a stack?
Aligning cells properly ensures long-term performance and safety.
Best practices:
- Use cell holders or frames to prevent shifting during use.
- Align all terminals to simplify wiring or welding.
- Apply even compression using foam pads or plates.
- Add insulation layers between cells where needed.
- Avoid bending or forcing cells into place.
Tip: Use a jig or 3D-printed fixture for perfect alignment during assembly.
Part 5. What tools and materials do you need for cell stack assembly?
A successful cell stack requires the proper materials:
Essential tools:
- Spot welder or soldering iron
- Multimeter and IR tester
- Heat shrink, Kapton tape, and insulation sheets
- Nickel strips or copper busbars
- Cell holders or brackets
- Compression plates or foam
Safety gear:
- Fire-resistant gloves
- Eye protection
- Fire extinguisher (Class D for lithium)
Even small setups need proper tools to ensure safety and performance.
Part 6. Common mistakes to avoid in cell stack setups
Avoid these costly errors:
- Using mismatched cells: Always use same-brand, same-capacity, and same-cycle cells.
- Improper welding or soldering: Cold welds increase resistance and heat.
- No BMS or wrong BMS: Leads to overcharging/discharging and imbalance.
- Skipping insulation: Risk of internal shorts.
- Ignoring thermal management: Causes overheating and degradation.
A small mistake during stacking can lead to expensive damage—or worse, a fire.
Part 7. How does compression affect lithium battery stacks?
Compression is not just about keeping things tight; it affects:
- Cell expansion control
- Contact resistance
- Thermal behavior
Too much compression = risk of physical damage
Too little compression = loose connections
Solution: Use foam pads or spring-loaded plates that apply even, moderate pressure.
Part 8. All about Battery Management Systems (BMS) and their role in cell stacks
A Battery Management System (BMS) monitors and controls the cell stack to ensure safe operation.
Types of BMS:
Passive BMS
- Redirects excess energy as heat
- Simple and affordable
- Ideal for small DIY or low-voltage stacks
Active BMS
- Redistributes energy between cells
- More efficient and balanced
- Better for large packs or high-drain applications
Smart or CAN-enabled BMS
- Communicates with external systems like EV controllers
- Offers real-time data, alerts, and balancing
- Used in commercial battery systems and EVs
Choose a BMS that matches your stack’s size, voltage, and intended use.
Part 9. Thermal management: How to control heat in large cell stacks?
Heat is a silent killer in lithium battery stacks. As stacks grow larger, thermal management becomes critical.
Effective strategies:
- Use thermal pads or phase change materials (PCMs) between cells
- Install heat sinks or cooling plates
- Design airflow channels for passive cooling
- Use fans or liquid cooling in high-demand applications
- Monitor temperatures with sensors on key cells
A good thermal design prevents cell degradation, swelling, and thermal runaway.
Part 10. Testing your completed lithium cell stack
Before using your battery, proper testing is a must.
Checklist:
- Test total voltage and individual cell voltages
- Check insulation resistance
- Perform load testing with a controlled discharge
- Monitor temperature behaviour
- Inspect welds/solder joints
Never charge or use a new battery stack without thorough testing.
Part 11. Scaling up: Best practices for large battery stack setups
If you’re building larger battery systems for solar, RVs, or backup power:
Guidelines:
- Use modular stacking: Easier to test, repair, and upgrade
- Apply even compression across all module layers
- Label all connections and cells
- Use a high-quality active BMS
- Design for easy disassembly and inspection
Large-scale setups require more planning and better redundancy.
Artikel Terkait: Battery Assembly: Techniques, Tools, and Best Practices
Part 12. FAQs about cell stack
What is a cell stack?
A cell stack is a group of cells arranged physically and electrically to form a complete battery pack. It defines a lithium battery system’s total voltage, capacity, and thermal behaviour.
Can I mix different types or brands of cells in a stack?
No. Mixing cell types, brands, or capacities leads to imbalance and potential failure. Always use identical cells from the same batch.
What type of BMS should I use for my battery?
- Use a passive BMS for small DIY packs.
- Choose an active BMS for large or high-current packs.
- Opt for a smart BMS if you need communication and remote monitoring.
How do I prevent overheating in my battery stack?
Use thermal pads, cooling channels, and temperature sensors. Never enclose a large battery stack without proper ventilation or cooling.
What’s the best compression method for pouch or prismatic cells?
Use spring-loaded plates or foam inserts that apply even, moderate pressure across all cells to prevent swelling and ensure contact.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.