- Part 1. What is the AAA rechargeable battery?
- Part 2. AAA rechargeable battery types
- Part 3. Pros and cons
- Part 4. What devices use AAA rechargeable batteries?
- Part 5. AA vs. AAA rechargeable battery: what are the differences?
- Part 6. Should I choose AA or AAA rechargeable batteries?
- Part 7. AAA rechargeable battery chargers
AAA rechargeable batteries may seem small and simple, but they play a significant role in our everyday lives, powering essential devices that keep us connected, entertained, and efficient. From remote controls to wireless keyboards, these batteries are quietly working behind the scenes. In this comprehensive guide, we will dive deep into everything you need to know about AAA rechargeable batteries. You’ll learn about their types, advantages, real-world applications, and how to choose the right charger to get the most out of them.
Part 1. What is the AAA rechargeable battery?
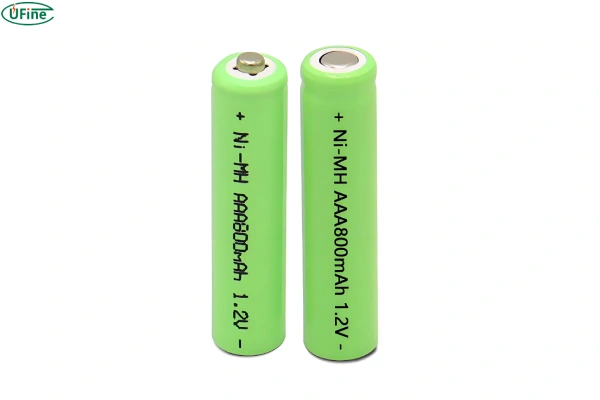
AAA rechargeable batteries are small, cylindrical batteries that typically measure 44.5 mm in length and 10.5 mm in diameter. Despite their size, they pack a considerable punch in terms of performance. Unlike disposable AAA batteries, which are single-use and contribute to environmental waste, rechargeable AAA batteries can be used repeatedly—sometimes for several years, depending on usage and care.
The nominal voltage of most AAA rechargeable batteries is 1.2V, which is slightly less than the 1.5V standard for disposable alkaline batteries. However, modern devices are often designed to handle this difference without noticeable performance drops. These batteries are commonly used in low-power devices but are also becoming increasingly favored in higher-drain gadgets due to their reusability and efficiency.
Part 2. AAA rechargeable battery types
There are two main types of AAA rechargeable batteries, distinguished by their chemistry:
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries
NiMH batteries are the most widely used rechargeable AAA batteries today, and for good reasons. They offer higher capacities than older battery chemistries, such as Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd), usually ranging from 600mAh to 1200mAh. This increased capacity translates to longer run times for your devices. Furthermore, NiMH batteries are environmentally friendly because they don’t contain toxic materials like cadmium.
NiMH batteries also have a longer life cycle. Some of the best models can be recharged over 1,000 times, making them an excellent investment. They are ideal for moderate- to high-drain devices like digital cameras, wireless game controllers, or flashlights.
Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) Batteries
Though not as popular as they once were, NiCd rechargeable batteries still have a few applications where they excel. These batteries tend to be more resistant to extreme temperatures, making them a reliable choice for outdoor devices like solar garden lights or outdoor weather stations. However, NiCd batteries have a lower capacity, generally around 300mAh to 600mAh, and they contain toxic cadmium, which requires special disposal.
Despite their drawbacks, NiCd batteries have a longer shelf life when unused and are less prone to self-discharge than NiMH batteries. However, they suffer from the memory effect, meaning their capacity can reduce if they aren’t fully discharged before recharging.
Part 3. Pros and cons
When choosing between AAA rechargeable batteries and their disposable counterparts, it’s important to weigh their advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Eco-Friendly: AAA rechargeable batteries reduce the amount of waste produced by single-use batteries, which is crucial for minimizing environmental impact. Over time, you’ll significantly reduce the number of batteries you throw away.
- Cost-Effective: Though the upfront cost is higher, rechargeable AAA batteries can be used for years, saving money in the long run. Consider the cost of continually purchasing disposable batteries; rechargeable ones start paying for themselves after a few uses.
- Consistent Voltage: Unlike alkaline batteries that gradually lose power, rechargeable batteries deliver consistent voltage until they are nearly depleted, which is especially useful in devices that require steady performance.
- High-Capacity Options: With capacities as high as 1200mAh, AAA rechargeable batteries are suitable for moderate-to-high power devices.
Disadvantages:
- Lower Initial Voltage: At 1.2V, they offer slightly lower voltage than standard 1.5V disposable batteries. This difference might affect the performance of certain high-drain devices, though most modern gadgets are designed to work with the slight voltage difference.
- Self-Discharge: NiMH batteries tend to lose charge when not in use. However, low self-discharge NiMH batteries have been developed to mitigate this issue, retaining up to 85% of their charge after a year in storage.
- Higher Initial Cost: The upfront cost of both the batteries and the necessary charger can be more expensive than a pack of disposable batteries.
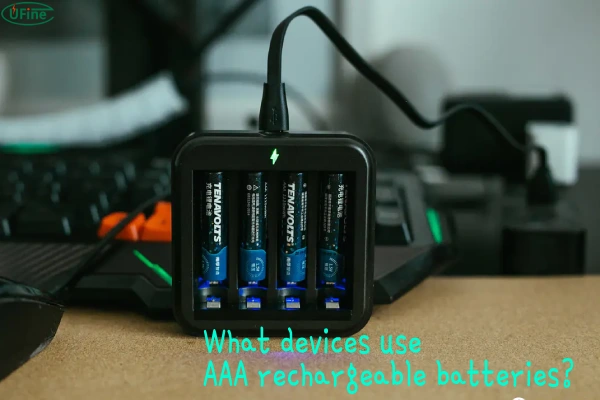
Part 4. What devices use AAA rechargeable batteries?
AAA rechargeable batteries are extremely versatile and are used in various devices, especially those that don’t require large amounts of power but need consistent performance. Some common applications include:
- Remote Controls: The most common household devices powered by AAA batteries are remote controls for TVs, audio systems, and other electronics.
- Wireless Keyboards and Mice: Offices and homes rely on these gadgets, and using rechargeable AAA batteries keeps them running without the need for frequent replacements.
- Flashlights: Whether you’re camping, exploring, or dealing with a power outage, AAA rechargeable batteries provide consistent light when needed.
- Digital Cameras: Some cameras, especially older models, still use AAA batteries to power their functions, making rechargeables an economical option.
- Toys: Many children’s toys require AAA batteries, and using rechargeables can be a lifesaver when those toys seem to run out of power during playtime.
- Clocks and Alarms: Keeping household clocks and alarms running smoothly without the hassle of constantly replacing batteries is another great use of AAA rechargeable batteries.
- Electric Shavers and Toothbrushes: Personal grooming devices benefit from the consistent power of rechargeable AAA batteries, making them ideal for daily use.
Part 5. AA vs. AAA rechargeable battery: what are the differences?
All About AA Rechargeable Batteries
Though both AA and AAA rechargeable batteries are similar in terms of function, they differ in several key ways:
- Size: The most obvious difference is their size. AA batteries are larger (50.5 mm in length and 14.5 mm in diameter), whereas AAA batteries are smaller (44.5 mm in length and 10.5 mm in diameter).
- Capacity: AA rechargeable batteries generally have a higher capacity than AAA batteries, making them more suitable for high-drain devices like digital cameras or game controllers. AAA batteries, on the other hand, are better suited for devices with low to moderate power consumption.
- Weight: AAA batteries are lighter, making them ideal for portable devices like flashlights and remote controls.
- Applications: While both types are widely used, AA batteries are often found in devices that need more power for longer durations, such as power tools or larger toys. AAA batteries are more common in smaller, everyday electronics.
Part 6. Should I choose AA or AAA rechargeable batteries?
Choosing between AA and AAA rechargeable batteries depends on the devices you use. If your devices require more power, AA batteries are the best choice due to their higher capacity. For smaller gadgets, AAA rechargeable batteries are typically more than sufficient. Consider your device’s energy demands and how frequently you use them. For example, a wireless mouse may need AAA batteries, while a digital camera could benefit from the extra juice provided by AA batteries.
In real-life scenarios, if you’re someone who relies on remotes and wireless devices throughout the day, having a set of AAA rechargeable batteries ready to go can save you from the hassle of constantly replacing them. Likewise, AA batteries will keep your high-powered devices running without interruptions.
Part 7. AAA rechargeable battery chargers
Charging your AAA rechargeable batteries correctly is crucial for maximizing their lifespan. Here’s what you need to know about choosing the right charger:
- Smart Chargers: Smart chargers automatically adjust the charging rate based on the battery’s current level and condition, preventing overcharging and overheating. These chargers are highly recommended for preserving the longevity of your batteries.
- Multiple Slots: If you use a lot of devices that require AAA batteries, opt for a charger with multiple slots so you can charge several batteries at once, saving time and effort.
- Fast Chargers vs. Slow Chargers: Fast chargers can recharge batteries in as little as 1-2 hours, but they may shorten the battery’s overall lifespan if used too frequently. Slow chargers, which can take up to 8 hours, are gentler on your batteries, extending their life over the long term.
- LED Indicators: Chargers with LED indicators show when your batteries are fully charged, allowing you to safely remove them from the charger and prevent overcharging.
By selecting the right charger, you can ensure your AAA rechargeable batteries last as long as possible, powering your devices for years without interruptions.
Related Tags:
More Articles
What is the Difference Between Silver Zinc Battery vs. Lithium-ion Rechargeable?
Compare silver zinc and lithium-ion rechargeable batteries: energy density, cycle life, safety, cost, and uses in drones, medical devices, EVs, and electronics.
What are Watts and Watt Hours in Battery?
Understand watt vs watt-hour in batteries: key differences, how to calculate capacity, and why they matter. Includes free comparison table.
Best 10 Blood Pressure Monitor Battery Review: Finding the Most Reliable
Are you looking for a reliable Blood Pressure Monitor battery? Here is a complete guide with the top 10 best blood pressure monitor batteries.
Bluetooth Headphone Battery Guide: All You Need to Know
Maximize headphone battery life with expert tips! Learn how to charge, check, troubleshoot, and choose the best bluetooth headphone battery in 2025.
LiFePO4 Battery VS. Lithium-ion Polymer Battery: Which One Is Best?
Comprehensive comparison of LiFePO4 vs Lithium Ion Polymer batteries: energy density, safety, lifespan, cost. Find out which battery suits your needs in 2025.





