The world of batteries can be a confusing labyrinth, especially when choosing between AGM and lead acid batteries. Both are popular choices for various applications, from powering vehicles to storing renewable energy. However, they differ significantly in their construction, performance, and suitability for specific needs. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of each type, exploring their advantages, disadvantages, and ultimately helping you determine which one reigns supreme for your particular application.
AGM VS Lithium VS Lead-Acid Battery: Comprehensive Comparison

Part 1. What are AGM batteries?

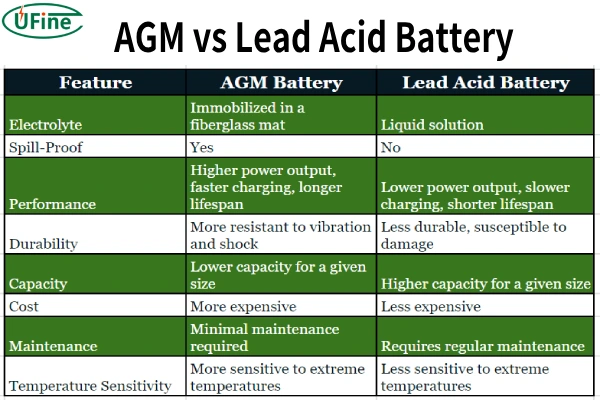
AGM stands for Absorbent Glass Mat. These batteries are essentially a sophisticated evolution of the traditional lead acid battery, incorporating a critical technological advancement. Instead of using a liquid electrolyte solution, AGM batteries utilize a special fiberglass mat that absorbs the electrolyte, effectively immobilizing it. This ingenious design offers several key benefits:
Advantages of AGM Batteries
-
Enhanced Safety: The immobilized electrolyte eliminates the risk of spills and leaks, making AGM batteries significantly safer than their traditional counterparts. This is crucial in applications where battery placement is confined or where accidental spills could cause damage or pose a hazard.
-
Superior Performance: AGM batteries boast a higher power output and can deliver more energy than traditional lead acid batteries. This translates to a more robust performance in demanding applications requiring sustained power delivery, like high-performance vehicles or solar energy systems.
-
Extended Lifespan: Due to the immobilized electrolyte, AGM batteries experience less internal corrosion and degradation. This results in a longer lifespan, requiring fewer replacements and reducing long-term costs.
-
Improved Durability: The robust construction and immobilized electrolyte make AGM batteries more resistant to vibration and shock. This makes them ideal for applications involving rough terrain or frequent movement, like off-road vehicles or heavy-duty equipment.
-
Faster Charging: AGM batteries can charge faster than traditional lead acid batteries due to their improved internal conductivity. This is particularly advantageous in applications where quick charging is essential, such as in emergency power systems or high-demand situations.
Disadvantages of AGM Batteries
-
Higher Cost: The advanced technology and construction of AGM batteries make them more expensive than traditional lead acid batteries. This cost difference can be a significant factor in budget-conscious applications.
-
Limited Capacity: While AGM batteries offer superior performance, they generally have a lower capacity than traditional lead acid batteries of the same size. This means they can store less energy, potentially limiting their suitability for applications requiring extended run times.
-
Temperature Sensitivity: AGM batteries are more sensitive to extreme temperatures than traditional lead acid batteries. They can experience reduced performance or even damage in very hot or cold environments.
Part 2. What are lead acid batteries?
Lead acid batteries are the most common and widely used type of battery, powering countless applications, from vehicles to backup power systems. Their simple construction and affordability have made them a mainstay in the battery industry.
Advantages of Lead Acid Batteries
-
Affordability: Lead acid batteries are significantly cheaper than AGM batteries, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious applications. This cost advantage can be crucial in situations where initial investment is a major consideration.
-
High Capacity: Traditional lead acid batteries typically have a higher capacity than AGM batteries of the same size. This means they can store more energy, making them suitable for applications requiring extended run times, such as off-grid power systems or long-distance travel.
-
Wide Availability: Lead acid batteries are readily available worldwide, making them easy to find and replace. This accessibility is particularly valuable in remote locations or during emergencies when sourcing specialized batteries might be challenging.
Disadvantages of Lead Acid Batteries
-
Safety Concerns: The liquid electrolyte in traditional lead acid batteries poses a significant safety risk. Spills can cause damage to surrounding equipment, pose a health hazard, and require specialized cleanup procedures.
-
Lower Performance: Lead acid batteries have a lower power output and shorter lifespan compared to AGM batteries. This can be a significant drawback in demanding applications requiring sustained performance or extended run times.
-
Maintenance Requirements: Traditional lead acid batteries require regular maintenance, including topping off the electrolyte levels and cleaning the terminals. This can be time-consuming and inconvenient, especially in applications where accessibility is limited.
-
Limited Durability: Lead acid batteries are less durable than AGM batteries and can be damaged by vibration, shock, and extreme temperatures. This can shorten their lifespan and make them unsuitable for applications involving rough conditions.
-
Slower Charging: Lead acid batteries charge slower than AGM batteries due to their lower internal conductivity. This can be a significant drawback in applications requiring quick charging, such as in emergency power systems or high-demand situations.
Part 3. AGM vs lead acid battery – a detailed comparison
To illustrate the key differences between AGM and lead acid batteries, let’s examine them side-by-side:
Part 4. Choosing the right battery: When agm reigns supreme
AGM batteries are the superior choice for applications where performance, safety, and durability are paramount. Here are some scenarios where AGM batteries excel:
-
High-Performance Vehicles: AGM batteries are ideal for powering high-performance vehicles, such as racing cars, motorcycles, and boats, due to their high power output and ability to handle heavy loads.
-
Deep Cycle Applications: AGM batteries are well-suited for deep cycle applications, such as solar power systems, electric golf carts, and marine batteries, where they can withstand repeated deep discharges without significant degradation.
-
Safety-Critical Applications: Their spill-proof design makes them ideal for applications where safety is paramount, such as in medical devices, emergency lighting systems, and backup power systems.
-
Off-Road Vehicles: AGM batteries’ durability and resistance to vibration make them a reliable choice for off-road vehicles and heavy-duty equipment operating in rough terrains.
-
High-Demand Applications: AGM batteries’ faster charging capabilities make them suitable for applications demanding quick recharge times, such as in emergency power systems or high-demand situations.
Part 5. Choosing the right battery: When lead acid batteries are still relevant
Despite their limitations, lead acid batteries remain a viable option for specific applications. Here’s when lead acid batteries might be the better choice:
-
Budget-Conscious Applications: Lead acid batteries are the most cost-effective option for applications where initial investment is a major concern, such as in lawnmowers, small engines, and general-purpose applications.
-
Extended Run Times: Their higher capacity makes them suitable for applications requiring extended run times, such as off-grid power systems or long-distance travel.
-
Wide Availability: Lead acid batteries are readily available worldwide, making them easy to find and replace, particularly in remote locations or during emergencies.
Related Tags:
More Articles

High‑Capacity 3S LiPo Batteries: 5000 mAh vs. 10000 mAh
Compare 3S LiPo 5000mAh vs 10000mAh batteries by weight, power, and use. Find the best fit for your drone, RC car, or boat setup.
Top 5 Applications for Small 3S LiPo Batteries
Small 3S LiPo batteries power drones, RC gear, wearables, and robotics with high energy and low weight. Making them ideal for compact electronics projects.
Building and Charging Your Own 3S LiPo Pack: A Step‑by‑Step Guide
Learn how to build, balance, and charge a 3S LiPo battery pack safely at home with this complete DIY guide for hobbyists and beginners.
How to Choose the Right LiPo Battery Plug Type?
Discover the best LiPo battery plug types, how to choose them, and expert tips for safe usage, soldering, and maintenance.
Choosing the Right Connector for Your 3S LiPo Battery
Choosing the right 3S LiPo connector depends on current, space, and use. Learn the pros and cons of XT60, JST, EC3, and more.