Part 1. Understand AGM battery
1. What is an AGM Battery?
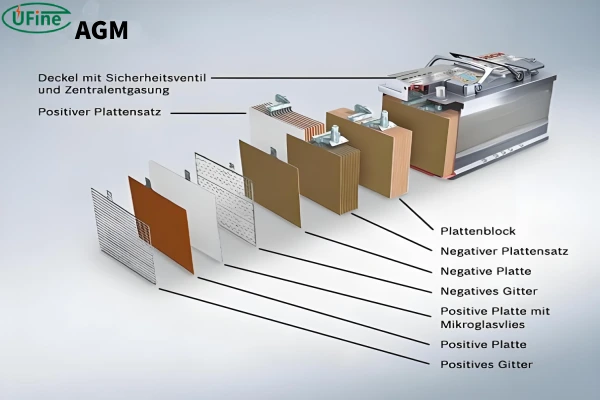
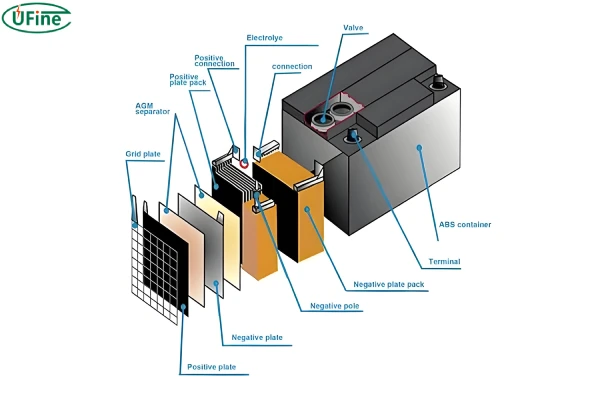
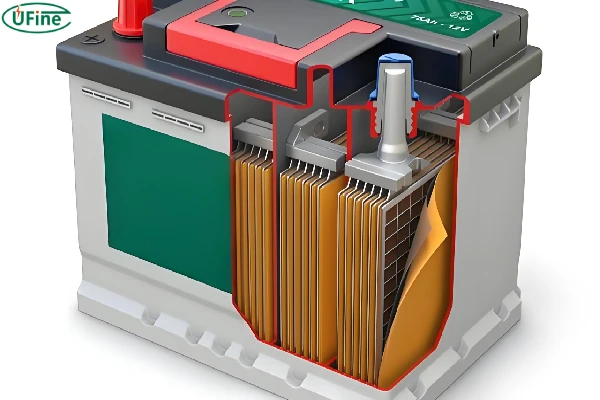
An AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) battery is a type of lead-acid battery that uses a specialized design to offer several advantages over traditional flooded lead-acid batteries.
2. Design and Structure
- Absorbent Glass Mat Technology: AGM batteries utilize thin fiberglass mats between the battery plates. These mats absorb and hold the battery’s acid, which makes the battery spill-proof and maintenance-free. The mats also ensure that the electrolyte remains in close contact with the plates, enhancing the battery’s efficiency.
- Sealed Design: Unlike traditional flooded batteries, AGM batteries are sealed. This means they do not require topping up with distilled water, making them maintenance-free. The sealed design also prevents leaks and spills, even if the battery casing is damaged.
- Valve-Regulated: AGM batteries are valve-regulated, meaning they have a valve to release excess gas pressure safely. This feature helps to prevent damage and maintain safety during charging and discharging cycles.
3. AGM Battery Characteristics
- High Performance: AGM batteries are known for their high performance and durability. They can handle high power demands and have a longer lifespan compared to conventional flooded batteries.
- Deep Cycle Capability: These batteries can be deeply discharged and recharged many times, making them suitable for applications where frequent cycling is required.
- Low Self-Discharge: AGM batteries have a lower self-discharge rate than flooded batteries. This means they can hold a charge for longer periods when not in use.
- Resistance to Vibration and Shock: The robust design of AGM batteries makes them highly resistant to vibration and shock, which is particularly beneficial for automotive and marine applications.
4. AGM battery Pros:
- They have a longer lifespan compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
- They are maintenance-free, so you don’t need to add water or check the electrolyte levels.
- AGM batteries are spill-proof, so you don’t have to worry about leaks or spills.
- They can be mounted in various positions, making them more versatile.
- AGM batteries have a lower self-discharge rate, so they hold their charge longer.
5. AGM battery Cons:
- They are more expensive than traditional lead-acid batteries.
- AGM batteries are sensitive to overcharging, which can reduce their lifespan.
- They may not perform as well in extreme temperature conditions, such as very cold or very hot environments.
- AGM batteries have a lower cranking power than other battery types, so they may not be suitable for high-demand applications.
6. AGM Battery Applications
AGM batteries are used in a variety of applications due to their versatility and reliability:

- Automotive: Commonly used in cars, motorcycles, and recreational vehicles (RVs) for starting, lighting, and ignition (SLI) purposes.
- Marine: Ideal for boats and yachts due to their resistance to vibration and ability to handle deep discharge cycles.
- Off-Grid Power Systems: Used in solar power systems and other off-grid applications where reliable, maintenance-free power storage is needed.
- Backup Power: Utilized in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and emergency lighting systems.
- Industrial and Commercial: Employed in various industrial applications, including forklifts, electric vehicles, and equipment requiring reliable power sources.
Part 2. Understanding lithium-ion batteries
1. What is a Li-ion Battery ?
A Lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery is a type of rechargeable battery that has become the dominant choice for portable electronics, electric vehicles, and a variety of other applications due to its high energy density, light weight, and long cycle life.
2. Li-ion Battery Design and Structure
- Electrochemical Composition: Li-ion batteries consist of an anode (usually made of graphite), a cathode (commonly made from lithium cobalt oxide, lithium iron phosphate, or other lithium compounds), and an electrolyte that facilitates the movement of lithium ions between the electrodes.
- Intercalation: During charging and discharging, lithium ions move back and forth between the anode and cathode through the electrolyte. This intercalation process is highly efficient and allows for high energy storage.
- Sealed Design: Li-ion batteries are typically sealed units, preventing leakage of the electrolyte. This design ensures safety and reliability across various applications.
3. Li-ion Battery Characteristics
- High Energy Density: Li-ion batteries can store a significant amount of energy in a small volume, making them ideal for portable devices.
- Light Weight: Compared to other rechargeable batteries like nickel-cadmium (NiCd) or nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), Li-ion batteries are lighter, contributing to the overall reduction in weight of the devices they power.
- Long Cycle Life: These batteries can undergo hundreds to thousands of charge and discharge cycles before their capacity significantly degrades.
- Low Self-Discharge: Li-ion batteries have a low self-discharge rate, meaning they retain their charge well over time when not in use.
- Variety of Form Factors: Li-ion batteries are available in various shapes and sizes, including cylindrical, prismatic, and pouch cells, allowing for flexibility in design and application.
4. Li-ion Battery Benefits
- High Energy Efficiency: Li-ion batteries have high charge and discharge efficiency, reducing energy loss and improving overall device performance.
- Fast Charging: Many Li-ion batteries support fast charging technologies, allowing for quicker recharges compared to other battery types.
- No Memory Effect: Unlike NiCd batteries, Li-ion batteries do not suffer from memory effect, where partial charging leads to reduced capacity over time.
- Wide Temperature Range: They can operate efficiently across a wide range of temperatures, from -20°C to 60°C, making them suitable for various environmental conditions.
- Environmentally Friendly: Li-ion batteries contain fewer toxic metals compared to lead-acid or NiCd batteries, making them more environmentally friendly and easier to recycle.
5. Lithium-ion Battery Pros:
- They have a high energy density, so they can store much energy in a small size.
- They are lightweight, making them convenient for portable devices.
- Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable, so you can use them multiple times.
- They have a longer lifespan compared to other types of rechargeable batteries
- They have a low self-discharge rate, meaning they can hold their charge for a long time when not in use.
- They can be sensitive to extreme temperatures, affecting their performance.
- If not handled properly, they can be a fire hazard.
- Lithium-ion batteries are more expensive to manufacture compared to other types of batteries.
- They require protection circuits to prevent overcharging or discharging, adding to their cost and complexity.
7. Li-ion Battery Applications
- Li-ion batteries are used in a multitude of applications due to their high performance and versatility:
- Consumer Electronics: Widely used in smartphones, laptops, tablets, cameras, and wearable devices due to their high energy density and light weight.
- Electric Vehicles: Power electric cars, buses, and bikes, providing the necessary energy for extended driving ranges and performance.
- Renewable Energy Storage: Used in solar power systems and other renewable energy setups to store excess energy for later use.
- Medical Devices: Power a variety of medical equipment, including portable defibrillators, pacemakers, and diagnostic devices.
- Industrial Applications: Employed in tools, robotics, and other industrial machinery that require reliable and long-lasting power sources.
- Aerospace and Defense: Utilized in drones, satellites, and other aerospace and defense applications for their reliability and efficiency.
Part 3. Understanding lead-acid battery
1. What is Lead-Acid Battery?
A lead-acid battery is one of the oldest and most widely used types of rechargeable batteries. It is known for its reliability, robustness, and ability to deliver high surge currents, making it suitable for various applications, particularly in automotive and backup power systems.
2. Lead Acid Battery Design and Structure
- Electrochemical Composition: Lead-acid batteries consist of lead dioxide (PbO2) as the positive plate (cathode), sponge lead (Pb) as the negative plate (anode), and sulfuric acid (H2SO4) as the electrolyte.
- Cell Construction: Each cell in a lead-acid battery produces about 2 volts, and cells are connected in series to achieve the desired voltage.
- For example, a 12-volt battery typically has six cells.
- Flooded vs. Sealed Design: There are two main types of lead-acid batteries: Flooded (Wet Cell): These batteries contain liquid electrolytes and require regular maintenance to ensure proper electrolyte levels. Sealed (VRLA): Valve-regulated lead-acid batteries, including Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) and Gel batteries, are sealed and maintenance-free, with the electrolyte immobilized in a gel or absorbed in a mat.
3. Lead Acid Battery Characteristics
- High Surge Currents: Lead-acid batteries can provide high surge currents, making them ideal for applications requiring high power output, such as starting engines.
- Weight: They are relatively heavy compared to other types of rechargeable batteries, which can be a disadvantage in applications where weight is a critical factor.
- Voltage and Capacity: Commonly available in 6V and 12V configurations, lead-acid batteries come in various capacities, typically measured in ampere-hours (Ah).
- Lifespan: They have a moderate lifespan, generally lasting between 300 to 500 charge-discharge cycles depending on usage and maintenance.
4. Lead Acid Battery Benefits
- Cost-Effective: Lead-acid batteries are one of the most cost-effective rechargeable battery options available, offering a lower upfront cost compared to newer technologies like lithium-ion batteries.
- Reliable Performance: They are known for their reliable performance in a variety of applications, especially in delivering high surge currents needed for engine starting.
- Ease of Recycling: Lead-acid batteries are highly recyclable, with established recycling processes that recover lead and other materials, making them environmentally friendly.
- Proven Technology: With over a century of development and use, lead-acid batteries have a well-documented track record of safety and reliability.
5. Lead Acid Battery Pros:
- Lead-acid batteries are reliable and have been used for a long time.
- They provide a high surge of power, making them suitable for starting vehicles.
- They are affordable compared to some other battery types.
- Lead-acid batteries are widely available and easy to find.
6. Lead Acid Battery Cons:
- They are heavy and bulky, which can be inconvenient for portable devices.
- Lead-acid batteries require regular maintenance, such as adding water to the electrolyte.
- They have a limited lifespan and may not hold a charge, unlike some other battery types.
- Lead-acid batteries contain toxic materials like lead and sulfuric acid, which can harm the environment if not disposed of properly
7. Lead Acid Battery Applications
Lead-acid batteries are used in a wide range of applications due to their versatility and dependable performance:
- Automotive: Used as starting, lighting, and ignition (SLI) batteries in cars, trucks, motorcycles, and other vehicles.
- Backup Power: Employed in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), emergency lighting, and backup systems for critical infrastructure.
- Industrial: Used in forklifts, floor scrubbers, and other industrial equipment requiring reliable and powerful energy storage.
- Marine and RV: Provide power for boats and recreational vehicles, offering both starting power and deep-cycle capabilities.
- Renewable Energy Storage: Used in solar and wind power systems to store energy and provide backup power when needed.
Part 4. AGM battery VS lithium battery VS lead-acid battery
- AGM batteries are maintenance-free and resilient, lithium batteries offer high energy density and long lifespan, and lead-acid batteries are known for their reliability and starting power.
- AGM batteries have a moderate service life, while lithium batteries have a long service life.
AGM batteries are heavier and bulkier, while lithium batteries are lightweight and compact.
AGM batteries have a wider operating temperature range, while lithium batteries are sensitive to extreme temperatures. - AGM batteries are generally safe, while lithium batteries require careful handling. Lithium batteries are more expensive, while lead-acid batteries are relatively affordable.
- AGM batteries are more environmentally friendly, while lead-acid batteries contain toxic materials.
- These battery types find applications in various sectors, with AGM batteries commonly used in vehicles, backup power systems, and renewable energy, lithium batteries in portable electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy, and lead-acid batteries in automotive, marine, and industrial settings.
Here is a comparison table of the three types of batteries:
| Characteristics | AGM Battery | Lithium Battery | Lead-Acid Battery |
|---|---|---|---|
| Service Life | 4-6 years | 8-10 years | 4-6 years |
| Weight | 20-30 kg (44-66 lbs) | 10-20 kg (22-44 lbs) | 25-40 kg (55-88 lbs) |
| Size | Larger (e.g., 13 x 7 x 8 inches) | Smaller (e.g., 6 x 3 x 2 inches) | Larger (e.g., 10 x 6 x 8 inches) |
| Operating Temp. Range | -20°C to 50°C (-4°F to 122°F) | -20°C to 60°C (-4°F to 140°F) | -10°C to 50°C (14 °F to 122°F) |
| Safety | Low risk of leakage | Stable performance | Risk of leakage, emits gases |
| Price | $150-300 per battery | $10-2000 per battery | $50-150 per battery |
| Environmentally | Recyclable, less harmful | Environmentally friendly, long lifespan | Recyclable, harmful materials |
| Application | Automotive, marine, backup power | Portable electronics, electric vehicles, renewable energy | Automotive, marine, backup power, golf carts |
Part 5.FAQs
-
Are there differences in the sizes of AGM, lithium, and lead-acid batteries?
Yes, AGM batteries are medium-sized, lithium batteries are smaller, and lead-acid batteries are larger. -
Are AGM, lithium, and lead-acid batteries safe to use?
They are generally safe, but each type has different risks. AGM batteries have a low risk of leakage, lithium batteries have stable performance, and lead-acid batteries may emit gases. -
Are AGM, lithium, and lead-acid batteries environmentally friendly?
AGM batteries are recyclable and less harmful, lithium batteries are environmentally friendly with a long lifespan, and lead-acid batteries are recyclable but contain harmful materials. -
What is the main difference between an AGM battery, a lithium battery, and a lead-acid battery?
The main difference lies in their chemistry and characteristics. AGM batteries are valve-regulated lead-acid batteries, lithium batteries use lithium-ion chemistry, and lead-acid batteries use lead plates and sulfuric acid. -
Which battery type has a longer lifespan?
Lithium batteries generally have a longer lifespan than AGM and lead-acid batteries. -
Are AGM batteries lightweight?
No, AGM batteries are heavier compared to lithium batteries but lighter than lead-acid batteries. -
Can I use lithium batteries in extreme temperatures?
Lithium batteries are sensitive to extreme temperatures, and their performance may be affected. -
Are lead-acid batteries affordable?
Yes, lead-acid batteries are relatively affordable compared to AGM and lithium batteries. -
Are AGM batteries maintenance-free?
Yes, AGM batteries are maintenance-free as they do not require regular electrolyte checks or water addition. -
Are lithium batteries safer than lead-acid batteries?
Lithium batteries require careful handling to prevent thermal runaway, while lead-acid batteries have their safety considerations.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Paper Battery vs. Flexible Battery: What’s the Difference and Which Is Better?
Paper vs. flexible batteries: learn the key differences, benefits, and which power source fits best for wearables, sensors, and smart tech.
What to Know Before Buying a Tiny LiPo Battery for Your Project
Tiny LiPo batteries are powerful and compact. Learn how to choose the right one for your project with specs, safety, and charging tips.
Bloated LiPo Battery: Will It Explode?
Will a bloated LiPo battery explode? Discover the causes, risks, safety steps, and expert tips to avoid disaster and protect your gear. Must-read safety guide!
12V 100Ah Lithium Ion Battery Price: Full Guide
Learn about 12V 100Ah lithium-ion battery price, from cost ranges to best brands, hidden fees, and how to get the best deal. A must-read for smart buyers!
Resistance and Conductivity: What It Means for Your Lithium Batteries
Resistance and conductivity impact lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety—learn how they work and why they matter.