When you’re out on the road or camping off-grid, keeping your batteries charged is essential. Whether it’s powering your appliances, lights, or keeping your food cool, a reliable battery system can make or break your adventure. This is where a DC to DC charger comes in. But what exactly is it, and how does it work? Why should you consider using one? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about DC to DC chargers, including how they work, their advantages, and tips on choosing the right one for your setup.
Part 1. What is a DC to DC charger?

A DC to DC charger, also known as a battery-to-battery charger, is a specialized charging device designed to efficiently charge your secondary battery (also called an auxiliary battery) from your vehicle’s primary battery or alternator. It steps up or regulates the voltage so that your secondary battery receives an optimized charge, regardless of fluctuations from the primary power source.
While traditional alternators provide a charge to secondary batteries, they often can’t supply the consistent voltage necessary for efficient charging, especially with modern lithium batteries. This is where DC to DC chargers excel, as they ensure your secondary battery receives the correct voltage and charge profile, leading to better performance and extended battery life.
The primary use of a DC to DC charger is in dual battery systems. It’s common in RVs, 4×4 vehicles, boats, and off-grid setups where a secondary battery is used to power appliances and electronics. Essentially, a DC to DC charger is an essential tool for those who need reliable, efficient charging while on the go.
Part 2. How does a DC to DC battery charger work?
To understand how a DC to DC charger works, let’s break it down step-by-step:
- Input Power Source: The charger takes power from the vehicle’s alternator or main battery (usually a lead-acid or AGM battery). This input power is often inconsistent due to the fluctuating voltage from the alternator.
- Voltage Regulation: The DC to DC charger regulates the voltage to ensure it matches the requirements of your secondary battery, which could be lead-acid, AGM, or lithium. For example, lithium batteries have specific charging requirements, and a DC to DC charger ensures they get the right voltage. AGM VS Lithium VS Lead-Acid Battery: Comprehensive Comparison
- Smart Charging Stages: Most DC to DC chargers feature smart multi-stage charging profiles. These stages include:
- Bulk Stage: The charger delivers the maximum current until the battery reaches a certain voltage.
- Absorption Stage: The charger reduces the current to avoid overcharging while maintaining the voltage.
- Float Stage: The charger maintains the battery at a safe voltage level, ensuring it stays fully charged without overcharging.
- Output to Secondary Battery: Once the voltage is regulated and the charging profile is applied, the power is delivered to the secondary battery. This process is smooth, ensuring that your secondary battery receives a steady, optimized charge.
The beauty of DC to DC chargers is that they work even when your vehicle is idling or running at low speeds, unlike traditional alternators that might struggle to deliver a consistent charge in those conditions.
Part 3. Advantages and disadvantages of DC to DC chargers
While a DC to DC charger offers numerous benefits, it’s also important to understand its limitations. Let’s explore the pros and cons of using a DC to DC charger in your vehicle.
Advantages:
- Optimized Charging for Different Battery Types: Whether you’re using lead-acid, AGM, or lithium batteries, a DC to DC charger ensures that your secondary battery receives the correct voltage. This is particularly beneficial for lithium batteries, which require a different charging profile compared to other battery types.
- Improved Battery Health: By using smart charging stages, the charger helps prolong the life of your battery by preventing overcharging and undercharging. This means you’ll get more use out of your batteries over time.
- Efficiency: DC to DC chargers are designed to work efficiently, even when your vehicle is idling or operating at low RPMs, ensuring continuous charging even in less-than-ideal conditions.
- Solar Charging Compatibility: Many DC to DC chargers are compatible with solar panels, allowing you to charge your battery using solar energy when off-grid. This feature makes them ideal for those looking for an eco-friendly charging option.
- Protection Features: Most DC to DC chargers come with built-in protections like temperature monitoring, overcharging prevention, and reverse polarity protection, ensuring your setup remains safe and reliable.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: DC to DC chargers are more expensive compared to traditional charging systems. The added complexity and features contribute to the higher price.
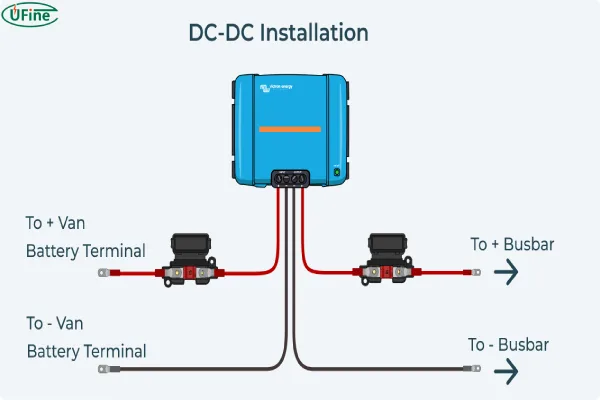
- Complex Installation: Installing a DC to DC charger requires more effort and expertise compared to basic alternator-to-battery setups. It often involves additional wiring and mounting, which could be a hassle for those unfamiliar with electrical systems.
- Size and Weight: Depending on the model, DC to DC chargers can be bulky, making them challenging to install in tight spaces. However, there are more compact options available.
Part 4. Do you need a DC to DC charger?
Not everyone requires a DC to DC charger, but in many cases, it can be a game-changer. Let’s look at some scenarios where a DC to DC charger is a must-have:
- Dual Battery Systems: If you’re running a dual battery setup, especially in RVs, 4x4s, or boats, a DC to DC charger ensures your secondary battery stays charged without draining your primary battery. This is crucial when running appliances or electronics off your secondary battery.
- Lithium Battery Users: Lithium batteries require specific charging profiles to avoid damage and ensure long life. A DC to DC charger is designed to handle these unique requirements, making it essential for those using lithium batteries.
- Off-Grid Power Needs: For those who rely on solar panels or other off-grid power sources, a DC to DC charger with solar compatibility can help maintain power, even in remote locations.
If any of these apply to you, investing in a DC to DC charger can significantly improve the reliability and lifespan of your battery system.
Part 5. Can I use a DC to DC charger with lithium batteries?
Yes, in fact, a DC to DC charger is one of the best ways to charge lithium batteries. Unlike traditional lead-acid or AGM batteries, lithium batteries require precise voltage regulation and smart charging stages. A DC to DC charger ensures that your lithium battery is charged properly by delivering the correct voltage and using the necessary charging stages (bulk, absorption, and float).
Using a regular alternator or traditional charger can cause issues like undercharging or overcharging, which can reduce the lifespan of your lithium battery. A DC to DC charger eliminates these risks, ensuring that your lithium battery gets the exact charge it needs to stay healthy and perform at its best.
Part 6. How to choose a DC to DC charger?
Choosing the right DC to DC charger depends on a few key factors. Here’s a breakdown of what you should consider:
1. Battery Type
Different battery types require different charging profiles. If you’re using lithium batteries, ensure that the charger is compatible and can handle the specific voltage and charging requirements. Similarly, if you’re using AGM or lead-acid batteries, look for a charger that supports these types.
2. Amps Rating
The amperage rating of the charger determines how quickly it can charge your battery. A higher amperage charger will charge the battery faster, but it may not always be necessary. Consider your power needs and choose a charger with an appropriate amps rating.
3. Solar Integration
If you plan to use solar power to charge your batteries, look for a DC to DC charger that can integrate with solar panels. Many modern chargers come with built-in solar regulators, making it easy to switch between vehicle and solar power for charging.
4. Size and Space
Some DC to DC chargers can be bulky and take up significant space in your vehicle. Make sure you measure the available space before purchasing and opt for a model that fits within your setup.
5. Price
Prices for DC to DC chargers can range from budget-friendly to high-end models with more features. While it’s tempting to go for the cheapest option, remember that quality and performance are key. Look for a charger that fits your budget but doesn’t compromise on essential features like smart charging stages and safety protections.
Part 7. Final words
A DC to DC charger is an invaluable tool for anyone running a dual battery system, especially in vehicles, RVs, or boats. It ensures that your secondary battery gets a proper, efficient charge, whether you’re using lead-acid, AGM, or lithium batteries. With the right DC to DC charger, you can extend your battery’s lifespan, improve performance, and avoid common charging problems.
Whether you’re charging on the go or integrating solar power into your system, a DC to DC charger offers the versatility and efficiency you need to keep your batteries running smoothly. Make sure you choose one that matches your battery type and power requirements, and you’ll be ready for any adventure.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Jigsaw Tool Battery for Long-Lasting Power
Discover the top jigsaw tool batteries for power & runtime. Compare Li-ion vs. NiCd, top brands, and tips to extend battery life. Read now
The Logistics of Bulk Battery Orders: Shipping, Storage, and Hazmat Compliance
Learn how to safely manage bulk battery orders with tips on shipping, storage, and hazmat compliance for smarter, safer logistics.
Microcurrent Facial Device Battery Guide & Tips
Learn all about microcurrent facial device batteries, from types to lifespan, and how to choose a reliable supplier for long-lasting, safe skincare performance.
Power Pack Battery vs. Power Bank: What’s the Difference?
Power pack vs power bank: Learn the key differences, pros, and best uses to choose the right portable power source for your lifestyle.
What Is a Power Pack Battery and How Does It Work?
A power pack battery stores energy for off-grid use, emergencies, or travel. Learn how it works and how to choose the right one for your needs.