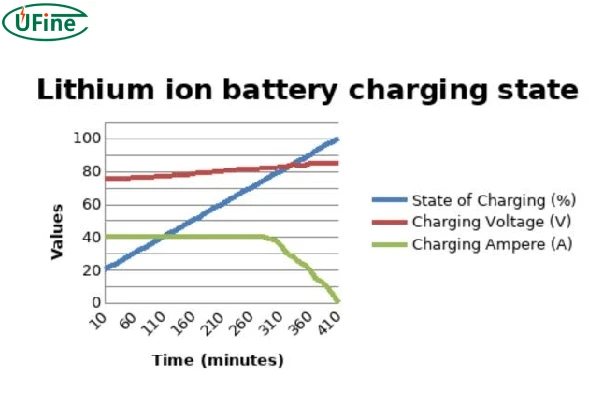
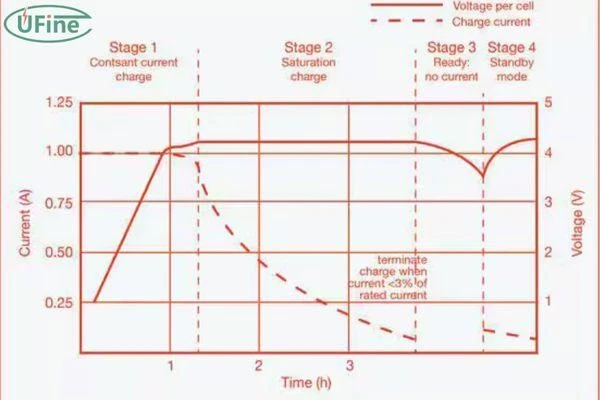
Many factors are vital in achieving higher performance and a longer lifespan. One of the main factors is the suitable charger and battery charging voltage. A battery needs to charge hundreds and even thousands of times, so if the charger does not charge the battery according to the required battery charging voltage, it can cause early battery degradation. Therefore, this article will cover all about battery charging voltage and clear all of the doubts one by one.
Part 1. What is battery charging voltage?
A battery charging voltage is an electrical pressure applied to the battery during the charging process. If there is a high charging voltage means the battery will charge at a faster speed and a low charging voltage means it will take time to charge the battery. However, the important thing to consider is to charge the battery according to the required battery charging voltage. Rather than normal, the higher and lower charging voltage tends to damage the battery’s health.
Part 2. Charging voltage of different battery types
There are many types of batteries used in electrical appliances. Each battery has different chemistry and materials. Therefore, charging every battery at the same battery charging voltage is not advisable.
1.Lithium Battery Charging Voltage
This battery is mostly used in mobile phones, laptops, and power tools. The ideal lithium battery charging voltage is between 3.6 volts to 4.2 volts per cell.
2. LiFePO4 Battery Voltage
LiFePO4 batteries are popular for electric vehicles and solar systems. These are commonly known for their long lifespan and deep discharge abilities. However, LiFePO4 battery voltage is lower compared to lithium-ion batteries. The charging voltage range of Lithium Iron phosphate is between 3.2V and 3.65V per cell.
3. Lead-Acid Battery Voltage
Lead-acid batteries are traditional batteries that mostly use these batteries in vehicles to power the starter. It has a different charging voltage from the lithium ion battery charging voltage. Lead-acid charging voltage is between 13.8V to 14.4V.
4. Leisure Battery Voltage
Designed for deep discharges in recreational vehicles and boats, leisure battery voltage (often lead-acid) typically follows a charging range of 14.4 V to 14.8 V.
Part 3. Battery charging voltage chart
For a better understanding of the battery charging voltage range, we have made a 12V Lithium Battery Charging Voltage Chart (0% to 100% SOC):
| State of Charge | Lithium-ion Voltage | LiFePO4 Voltage | Charging Current |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 10.0V | 11.0V | Constant Current: 20A max |
| 10% | 11.1V | 12.0V | Constant Current:20A max |
| 20% | 11.6V | 12.4V | Constant Current 20A max |
| 30% | 12.0V | 12.8V | Constant Current: 20A max |
| 40% | 12.3V | 13.0V | Constant Voltage: 10-15A tapering |
| 50% | 12.6V | 13.2V | Constant Voltage: 5-10A tapering |
| 60% | 12.9V | 13.4V | Constant Voltage: 2-5A tapering |
| 70% | 13.2V | 13.6V | Constant Voltage: 1-2A tapering |
| 80% | 13.5V | 13.8V | Constant Voltage: 0.5-1A tapering |
| 90% | 13.8V | 14.0V | Constant Voltage: 0.1-0.5A tapering |
| 100% | 14.0V – 14.4V | 14.2V – 14.4V | Float Voltage: 0.05A or less |
Part 4. 12v and 24v battery charging voltage
The battery charging voltage for 12V and 24V are different from each other. You cannot charge both batteries with the same charger.
1. 12V Battery Charging Voltage
A 12V battery combines 4 individual cells connected in series as each cell requires a 3.6 to 4.2 charging voltage. Therefore, the charger for 12V would need to deliver a battery charging voltage between 10.8 to 14.8 to charge the battery fully.
2. 24V Battery Charging Voltage
A 24V battery contains 8 Li-ion cells connected in series. This combination needs a charger having a charging range of 21.6 to 29.6 voltage. If you charge a 24V battery with a 12V charger, it will not charge at the proper rate and take much time to charge. Therefore, it is advised to use a suitable charging according to the charging voltage of the battery.
Part 5. What does it mean if the battery charging voltage is too high?
A battery needs to charge within the specified charging voltage range. If the battery charging voltage is too high, that can damage the battery in many ways. For example, a 12V lithium battery charging voltage should be not more than 14.8V. Charging above the battery capacity will have the following consequences.
- Electrolyte Breakdown: Electrolyte solution is the battery’s lifeblood. An excessive charging voltage can break this solution down and reduce the battery lifespan.
- Outgassing: High battery charging voltage can generate excessive gasses in the battery. You will notice the battery may swallow or can cause a battery explosion.
- Plating (Lithium-Ion Batteries): For Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries specifically, high voltage can cause lithium plating on the electrodes. This plating hinders the battery’s ability to store charge, permanently reducing its capacity.
Part 6. What does the battery charging voltage too low mean?
Charging the battery with low voltage will also have a damaging effect on the battery. Low voltage means not having enough electrical push to charge the battery at 100%. Here are the following risks when you charge the at low battery charging voltage.
- Incomplete Charging: Low voltage will only partially charge the battery. The battery can be constantly in a state of charge for many hours. Eventually damages the battery by reducing its lifespan and efficiency.
- Cell Imbalance: A lithium battery is a many small battery cells combination. Due to low charging voltage, all the cells do not charge evenly causing cell imbalance.
- Reduce Capacity: Low charging voltage voltage gradually reduces the battery capacity and life permanently.
Part 7. Factors affecting lithium ion battery charging voltage
Lithium batteries are very tender to charging voltage. Many factors can affect the lithium ion battery charging voltage. We will discuss each factor one by one.
- Battery Chemistry: Lithium ion batteries come in many categories and types. Each battery chemistry is different from the other. For example, Lithium Cobalt Oxide and Lithium Manganese Oxide have different chemistry and need different optimal charging voltage variations.
- High Temperature: In a high temperature the electrolytes become more conductive and can cause intense internal resistance. Therefore, Lithium battery charging voltage might drop down to reduce high temperature and overcharging issues.
- Low Temperatures: Silimarly, a low temperature also affects the battery and hinders Ion movements. So the battery struggles to charge fully. In such a scenario, a battery charger increases the charging voltage to charge the battery completely.
- Cell Age: With time the internal resistance in lithium batteries increases. Therefore, the battery does not tolerate the high battery charging voltage. It means you should be careful and charge the old battery at a slow charging voltage.
Part 8. How to choose the appropriate charging voltage?
Choosing the right battery charging voltage is always important for safety, longevity, and complete charging. However, each battery condition and environment is different, so one rule does not apply the same to the others. However, we have set some parameters to ensure the appropriate charging voltage for every battery.
- Identify the battery type and charge accordingly
- Refer to the SOC of the battery
- Know the battery size and voltage
- Use a compatible charger for your battery
- Read the user manual of the battery
- Keep an eye on the battery temperature
If you want a better battery performance and a long lifespan, you should follow all the instructions about battery charging voltage. This will not only enhance the life but also increase one-charge battery efficiency.
Related Tags:
More Articles

The Best Way to Store Batteries
Discover the best ways to store batteries for longevity and safety! Learn tips to keep them organized and prevent damage. Read now!
Lipo Battery Storage Voltage Explained Simply
Lipo battery storage voltage is key for battery life. Storing at 3.7V–3.85V per cell keeps the ions in a good state, minimizing wear. Read now!
Decoding Lithium Battery Cost: What Drives Pricing?
Lithium battery costs impact many industries. This in-depth pricing analysis explores key factors, price trends, and the future outlook.
Liquid Metal Battery vs Lithium Battery: Comparative Analysis
Liquid metal vs. lithium batteries: Compare features, applications, pros, cons, cost, and future prospects in this in-depth analysis.
Understanding Lipo Batteries: Capacity, Lifespan & More
Learn everything about Lipo batteries—capacity, energy density, cycle life, and more. Optimize performance and avoid common pitfalls with this in-depth guide.