Are batteries AC or DC? This question is fundamental for anyone interested in understanding how batteries work and their role in our electronic devices. Batteries are essential in our daily lives, powering everything from smartphones to electric cars. Knowing whether they produce alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC) can help you make informed decisions about using and maintaining your devices.
Part 1. What are batteries?
Batteries are devices that store energy in chemical form and convert it into electrical energy. They consist of one or more electrochemical cells, which generate a flow of electrons through chemical reactions. This flow of electrons powers various devices, from small gadgets like remote controls to larger systems like electric vehicles.
Batteries are classified based on their chemistry, such as alkaline, lithium-ion, or lead-acid. Each type has its characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. For example, lithium-ion batteries are known for their high energy density and long cycle life, making them ideal for portable electronics. In contrast, vehicles commonly use lead-acid batteries due to their reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Part 2. Understanding direct current (DC)
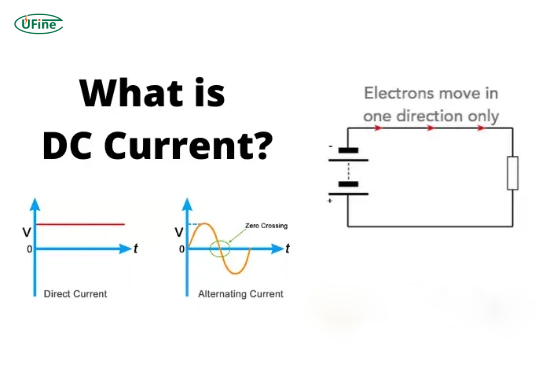
What is Direct Current?
Direct Current (DC) refers to the unidirectional flow of electric charge. In simpler terms, this means that electricity flows in one direction only—from the negative terminal to the positive terminal of a battery. This consistent flow makes DC ideal for powering electronic devices that require stable voltage.
How Do Batteries Produce DC?
Batteries produce DC through chemical reactions that occur within their cells. For instance, in a lead-acid battery, a reaction between lead dioxide and sponge lead in an electrolyte solution generates electrons. These electrons then flow out of the battery to power connected devices. The steady nature of DC power is crucial for many electronic applications, as it ensures that devices receive a consistent voltage level.
Part 3. Understanding alternating current (AC)
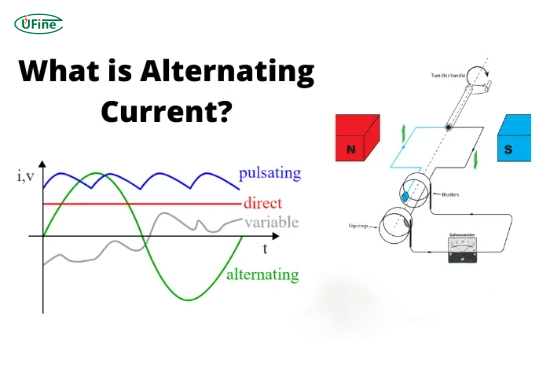
What Is Alternating Current?
Alternating Current (AC) periodically reverses the direction of electric charge, causing the flow of electricity to alternate back and forth, typically at a frequency of 50 or 60 Hz, depending on the region. AC is commonly used in power distribution systems because it can travel long distances with minimal energy loss.
How Is AC Used in Daily Life?
Most household appliances, such as refrigerators, air conditioners, and televisions, operate on AC power supplied by the electrical grid. This system efficiently transmits electricity over long distances by quickly increasing or decreasing voltage levels using transformers.
Part 4. Are batteries AC or DC?
The Definitive Answer
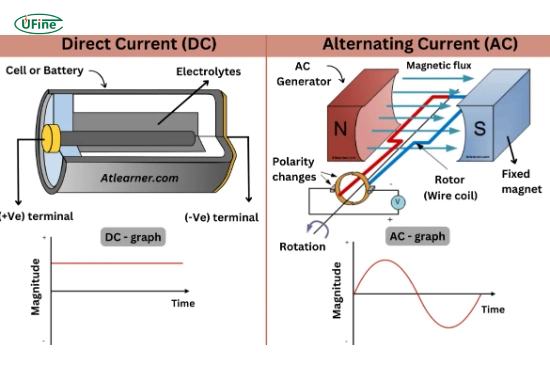
All batteries produce Direct Current (DC) electricity. This includes common types such as alkaline, lithium-ion, and lead-acid batteries. When you use a battery-powered device, it draws DC power directly from the battery.
Why Don’t Batteries Use AC?
Manufacturers design batteries to store energy in a form that flows in one direction. The chemical processes within batteries only allow for this unidirectional flow, making them inherently DC devices.
Part 5. How do batteries convert AC power to DC power during charging?
An AC-to-DC converter is used when charging a battery from an AC source, such as a wall outlet. This device transforms the alternating current from the outlet into a direct current suitable for charging the battery.
The process involves several steps:
- Rectification: The AC voltage is converted into pulsating DC using diodes.
- Smoothing: Capacitors smooth out the pulsating DC to create a more stable voltage.
- Regulation: Voltage regulators ensure that the output voltage remains constant and within safe limits for charging the battery.
The conversion process allows chargers to charge batteries efficiently while ensuring they receive the correct type of current needed for storage.
Part 6. What are the main differences between AC and DC power in everyday devices?
Understanding the differences between AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) is essential for grasping how various devices operate. Here are five key points that highlight their differences:
- The direction of Flow: AC power alternates its direction, flowing back and forth, while DC power flows in one consistent direction only. This fundamental difference affects how devices use each type of current.
- Voltage Stability: DC provides a stable voltage, making it ideal for sensitive electronics like computers and smartphones. In contrast, AC voltage fluctuates over time, which can be less suitable for devices that require a constant power supply.
- Common Applications: Household appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, and lighting systems primarily use AC due to their efficiency in long-distance transmission. Battery-powered devices like laptops, smartphones, and electric vehicles commonly use DC.
- Transmission Efficiency: AC can be easily transformed to higher or lower voltages using transformers, allowing it to travel long distances with minimal energy loss. DC is less efficient over long distances without significant voltage drop unless transmitted at high voltages.
- Conversion Needs: Most electronic devices that run on AC power require conversion to DC for their internal components to function correctly. This conversion typically happens through adapters or rectifiers that change AC from the wall outlet into the DC needed by the device.
| Feature | Direct Current (DC) | Alternating Current (AC) |
|---|---|---|
| Direction of Flow | Flows in one direction | Alternates direction |
| Voltage Stability | Provides stable voltage | Voltage varies over time |
| Common Uses | Used in batteries and electronics | Used in household appliances |
| Transmission | Less efficient over long distances | More efficient for long-distance transmission |
| Conversion Needs | Does not require conversion | Requires conversion for battery charging |
Part 7. Common misconceptions about batteries
Do Batteries Ever Produce AC?
There is a common misconception that some batteries can produce AC power directly; however, this is false. While specific systems may involve converting stored DC into AC, the batteries themselves generate DC.
Are There Any Exceptions?
Specific specialized applications may utilize battery systems with built-in converters or inverters to provide both current types; however, these systems still rely on DC at their core.
Part 8. FAQs
-
Are all batteries AC or DC?
All batteries produce Direct Current (DC) electricity. -
Is a car battery powered by AC or DC?
A car battery operates on Direct Current (DC), providing stable power for starting engines and running electrical components. -
How do I know if my battery is AC or DC?
If your device runs on a battery, it uses DC, as all batteries output direct current. -
Why are all batteries DC?
Batteries store energy from chemical reactions that only allow for unidirectional flow; hence, they produce DC rather than AC. -
What happens if you connect a battery to an AC source?
Connecting a battery directly to an AC source can damage the battery and potentially cause safety hazards such as overheating or short circuits.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Choosing Batteries for Trolling Motors Lightweight: Charger Options
Lithium batteries are best for trolling motors as they are lightweight long long-lasting, and efficient. This guide covers selection, charging, and care tips.
Finding 11.1 V LiPo Battery Near Me: B2B Supplier Strategies
Need 11.1V LiPo batteries near you? This guide helps B2B buyers source reliable suppliers, compare specs, and ensure safe, cost-effective deals.
11.1 V LiPo Battery 5000 mAh: Specs That Matter for Industrial Use
An 11.1V 5000mAh LiPo battery offers high capacity and stable power, ideal for drones, robotics, and industrial tools requiring long runtimes.
Lightweight Battery Packs for Trolling Motors: Top Features
Looking for the best lightweight trolling motor battery? This guide covers top features, battery types, and tips to boost your boating performance.
Safe Charging Protocols for Your 11.1V LiPo Battery Charger
Safely charge your 11.1V LiPo battery by following proper rates, using safety tools, and avoiding common charging mistakes.