- Part 1. What are lithium batteries?
- Part 2. How are lithium batteries made?
- Part 3. What is the environmental impact of lithium mining?
- Part 4. Do lithium batteries contribute to pollution?
- Part 5. Are lithium batteries better for the environment than alternatives?
- Part 6. Can lithium batteries be recycled?
- Part 7. What are the alternatives to lithium batteries?
- Part 8. What actions can we take to reduce the environmental impact of lithium batteries?
- Part 9. Are lithium batteries sustainable in the long term?
- Part 10. FAQs
Lithium batteries have become integral to modern technology, powering everything from smartphones to electric vehicles. As the global push toward renewable energy and sustainability accelerates, the demand for lithium batteries grows exponentially. However, with this surge in popularity comes a critical question: Are lithium batteries bad for the environment?
In this article, we’ll explore the environmental impact of lithium batteries, from their raw material extraction to their disposal. By the end, you will clearly understand their pros and cons and what steps you can take to minimize their ecological footprint.
Part 1. What are lithium batteries?
Lithium batteries are rechargeable energy storage devices that use lithium ions to transfer energy between electrodes. Unlike traditional lead-acid or nickel-cadmium batteries, lithium batteries are lightweight, have a high energy density, and offer better performance over time.
There are several types of lithium batteries, including lithium-ion (Li-ion) and lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), each designed for specific applications such as electronics, electric vehicles (EVs), and renewable energy storage systems.
Part 2. How are lithium batteries made?
Manufacturers make lithium batteries using raw materials such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite, which they mine and process before assembling them into battery cells. The process includes:
- Mining: Extracting raw materials like lithium from salt flats or hard rock mines.
- Processing: Refining the raw materials into usable forms.
- Manufacturing: Workers assemble battery cells and then group them into battery packs.
The production of lithium batteries is energy-intensive and involves several stages that can have significant environmental consequences.
Part 3. What is the environmental impact of lithium mining?
The mining of lithium and other materials required for battery production raises several environmental concerns:
- Water depletion: Lithium is often extracted from salt flats, requiring vast amounts of water. Producing a single ton of lithium can take up to 500,000 gallons of water, creating water scarcity issues in regions like Chile and Argentina.
- Habitat destruction: Mining operations disrupt local ecosystems, leading to habitat loss for flora and fauna.
- Soil contamination: Chemicals used in the mining process can seep into the soil, affecting agriculture and local biodiversity.
- Carbon emissions: Mining and processing activities release greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change.
Part 4. Do lithium batteries contribute to pollution?
Yes, lithium batteries can contribute to pollution if not appropriately handled. While they are considered cleaner than fossil fuels, there are several ways they can harm the environment:
- Toxic waste: Improper disposal of used lithium batteries can result in harmful chemicals, such as lead and cobalt, leaching into the soil and water.
- Non-biodegradability: Lithium batteries are not biodegradable, meaning they remain in landfills for decades.
- Recycling challenges: Although people can recycle lithium batteries, the process is costly and inefficient, and many throw batteries away as waste.
Part 5. Are lithium batteries better for the environment than alternatives?
People often consider lithium batteries a greener alternative to traditional fossil fuels because they enable renewable energy storage and reduce carbon emissions. However, they are not without flaws. Here’s how they compare to other batteries:
- Lead-acid batteries: While cheaper, they are significantly heavier, have a shorter lifespan, and are more toxic when discarded.
- Nickel-metal hydride batteries are safer but have lower energy densities than lithium-ion batteries.
- Hydrogen fuel cells: Though promising, hydrogen fuel cells are still in the developmental stage and are not as widely available as lithium batteries.
While lithium batteries have their downsides, they remain the best option for long-term energy storage and the mass adoption of electric vehicles.
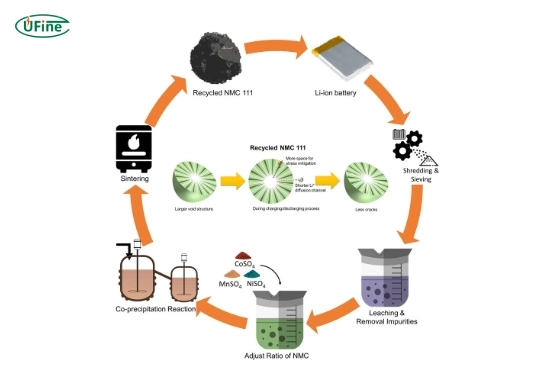
Part 6. Can lithium batteries be recycled?
Lithium batteries can be recycled, but the process is complicated and underdeveloped in many parts of the world. Recycling involves extracting valuable materials like cobalt, nickel, and lithium from used batteries. However, challenges include:
- High costs: Recycling is expensive compared to mining raw materials.
- Lack of infrastructure: Many countries lack large-scale lithium battery recycling facilities.
- Energy requirements: The recycling process requires energy, which can offset some environmental benefits.
Despite these challenges, researchers are making advancements to improve recycling efficiency, which could significantly reduce the environmental impact of lithium batteries.
Part 7. What are the alternatives to lithium batteries?
As concerns about the environmental impact of lithium batteries grow, researchers are exploring alternative energy storage solutions, including:
- Sodium-ion batteries: Sodium-ion batteries, made from abundant and cheap materials, could become a viable alternative.
- Solid-state batteries promise higher energy density and increased safety but are still experimental.
- Flow batteries: Ideal for large-scale energy storage, flow batteries use liquid electrolytes and are more sustainable than lithium-ion batteries.
While these alternatives show promise, lithium batteries remain dominant due to their maturity and widespread availability.
Part 8. What actions can we take to reduce the environmental impact of lithium batteries?
To minimize the environmental impact of lithium batteries, you can take the following steps:
- Promote recycling: Governments and industries should invest in recycling infrastructure to recover valuable materials and reduce waste.
- Improve mining practices: Sustainable techniques can reduce water usage and habitat destruction.
- Develop alternative technologies: Supporting research into alternative battery chemistries can decrease reliance on lithium.
- Encourage responsible disposal: Educating consumers on proper battery disposal can prevent toxic waste from entering landfills.
By addressing these issues, we can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of lithium batteries.
Part 9. Are lithium batteries sustainable in the long term?
Lithium batteries are a critical component in the transition to renewable energy. Still, their sustainability depends on how well we manage their lifecycle. While they offer significant benefits in terms of reducing greenhouse gas emissions, their long-term sustainability hinges on improvements in:
- Recycling efficiency
- Ethical sourcing of raw materials
- Development of alternative technologies
Investing in these areas will ensure that lithium batteries remain a viable and sustainable energy solution.
Part 10. FAQs
-
Why are lithium batteries considered environmentally harmful?
Lithium batteries are considered harmful due to the environmental impact of mining, high energy consumption during production, and challenges with recycling and disposal. -
Can lithium batteries be fully recycled?
Although people can recycle lithium batteries, the process is costly, energy-intensive, and not widely implemented globally. Researchers are working to improve recycling efficiency. -
Are lithium batteries better than fossil fuels?
Lithium batteries are better than fossil fuels as they enable renewable energy storage and reduce carbon emissions. However, they still have environmental downsides. -
What is the most significant environmental issue with lithium batteries?
The biggest issue is the environmental damage caused by lithium mining, including water depletion, habitat destruction, and carbon emissions. -
Are there greener alternatives to lithium batteries?
Emerging alternatives such as sodium-ion and solid-state batteries show promise. Still, they are not yet commercially viable on a large scale.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Lithium-Ion vs Lead-Acid AMR & AGV Batteries Compared
Discover the pros and cons of lithium-ion and lead-acid AMR & AGV batteries. Learn about cost, lifespan, safety, and which is right for your fleet.
Robot Vacuum Battery Replacement: Easy Step-by-Step Guide
Learn how to replace a robot vacuum battery safely and easily. Step-by-step instructions, battery types, costs, and common mistakes to avoid.
Discover how to choose the right battery for your robot. Compare Li-ion, LiFePO₄, NiMH, and more for performance, safety, and cost.
Inside Humanoid Robot Battery Pack Design
A deep dive into humanoid robot battery pack design, covering battery life, voltage, capacity, safety, and real-world engineering trade-offs.
Humanoid Robot Battery Life: How Long Do They Really Last?
Most humanoid robots run 1.5–4 hours per charge. Learn real-world battery life, battery types, capacity limits, and future improvements.