Lithium-ion batteries power many modern devices, from smartphones to electric vehicles. But with their widespread use, concerns about safety arise. Are lithium-ion batteries safe? This article delves into key safety concerns, compares them to other battery types, and highlights advancements improving their safety.
Part 1. What makes lithium-ion batteries potentially unsafe?
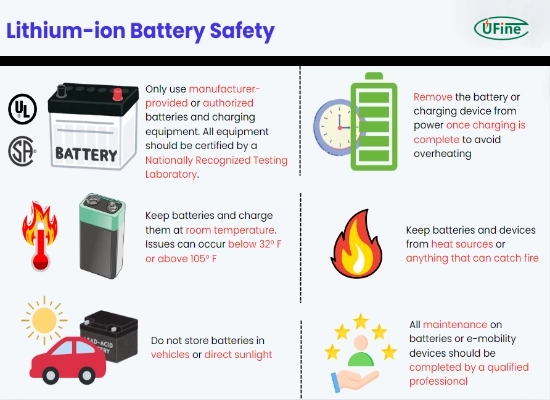
Lithium-ion batteries are generally safe when used and maintained correctly. However, they can pose risks under certain conditions, such as:
- Overcharging: Overcharging a lithium-ion battery can lead to thermal runaway, a chain reaction that causes the battery to overheat and potentially catch fire or explode.
- Short circuits: If a lithium-ion battery is punctured or experiences a short circuit, it can generate enough heat to ignite the flammable electrolyte, leading to a fire or explosion.
- Mechanical abuse: Dropping, crushing, or piercing a lithium-ion battery can damage the internal components and cause a short circuit, potentially leading to thermal runaway.
- Exposure to high temperatures: Storing or using lithium-ion batteries in high-temperature environments can accelerate the chemical reactions inside the battery, increasing the risk of thermal runaway.
Part 2. How common are lithium-ion battery fires and explosions?
While lithium-ion battery fires and explosions are relatively rare, users can explore battery safety tips to better understand how to prevent such incidents. According to a report by the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), there were 265 incidents involving lithium batteries in aircraft cargo and passenger baggage between 1991 and 2019, with an average of 13 incidents per year.
However, it’s important to note that the number of incidents may be higher, as not all incidents are reported or documented. Additionally, incidents may increase as lithium-ion batteries grow unless manufacturers take proper safety measures.
Part 3. What are the potential consequences of a lithium-ion battery fire or explosion?
The consequences of a lithium-ion battery fire or explosion can vary depending on the size and location of the incident. In the case of a small device like a smartphone or laptop, a battery fire may cause minor burns or property damage. However, a battery fire can have more severe consequences in larger applications like electric vehicles or energy storage systems.
Some potential consequences of a lithium-ion battery fire or explosion include:
- Fire and smoke: The flammable electrolyte inside a lithium-ion battery can ignite, causing a difficult fire to extinguish with water.
- Toxic fumes: Burning lithium-ion batteries can release poisonous gases, such as hydrogen fluoride, which can be harmful if inhaled.
- Explosion: In some cases, the pressure buildup inside a lithium-ion battery can cause it to explode, potentially causing injury or property damage.
- Thermal runaway chain reaction: If one battery in a pack experiences thermal runaway, it can spread to neighboring batteries, causing a chain reaction that is difficult to stop.
Part 4. What should you do in case of a lithium-ion battery fire?
If a lithium-ion battery catches fire, acting quickly and safely is essential. Here are some steps to follow:
- Evacuate the area: Move away from the fire and call emergency services if necessary.
- Use a fire extinguisher: If the fire is small and contained, use a Class ABC or Class D fire extinguisher to put it out. Water can be used as a last resort but may not be effective against lithium-ion battery fires.
- Avoid water: Do not use water to extinguish a lithium-ion battery fire, as it can cause the fire to spread and generate toxic fumes.
- Contain the fire: If possible, place the burning battery in a metal container or sand to contain the fire and prevent it from spreading.
- Seek medical attention: If you are exposed to toxic fumes or suffer burns, seek immediate medical attention.
Part 5. How do lithium-ion batteries perform in extreme temperatures?
Lithium-ion batteries can be sensitive to extreme temperatures, which can affect their performance and safety:
- High Temperatures: Exposure to high temperatures can accelerate chemical reactions within the battery, increasing the risk of thermal runaway and leading to reduced battery life and capacity.
- Low Temperatures: Lithium-ion batteries may experience reduced capacity and performance in cold conditions. While they are less likely to catch fire in freezing temperatures, freezing temperatures can significantly diminish their efficiency.
To mitigate these effects, manufacturers often recommend operating lithium-ion batteries within specific temperature ranges and using thermal management systems in applications like electric vehicles.
Part 6. How do lithium-ion batteries compare to other batteries in terms of safety?
When comparing lithium-ion batteries to other battery types, such as nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) and lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries generally offer higher energy density and longer lifespan, however, they also come with unique safety concerns.
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH): NiMH batteries are less prone to thermal runaway than lithium-ion batteries but have a lower energy density. They are often considered safer for applications where overheating is a concern.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Lead-acid batteries are more stable and less likely to catch fire. Still, they are heavier and have a shorter lifespan. They also contain toxic lead, which poses environmental hazards.
While lithium-ion batteries are efficient and widely used, their safety concerns require careful management and adherence to safety protocols.
Part 7. How can lithium-ion battery safety be improved?
To enhance the safety of lithium-ion batteries, manufacturers can employ several strategies:
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): Implementing advanced BMS in electric vehicles and energy storage systems can monitor battery conditions, including voltage, current, and temperature, to prevent overcharging and thermal runaway.
- Improved Materials: Research into safer electrolyte materials and battery designs can help reduce the risk of fires and explosions. Solid-state batteries, for example, use solid electrolytes that are less flammable than traditional liquid electrolytes.
- Regular Maintenance: Regularly inspecting and maintaining devices that use lithium-ion batteries can help identify potential issues before they escalate into safety hazards.
- Education and Awareness: Educating consumers about the proper use and disposal of lithium-ion batteries can significantly reduce the risks associated with battery fires and explosions.
Part 8. FAQs
-
What are the main risks associated with lithium-ion batteries?
The main risks include overcharging, short circuits, mechanical abuse, and exposure to high temperatures, all of which can lead to fires or explosions. -
How do lithium-ion batteries compare to nickel-metal hydride batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density and longer lifespan but have more significant safety concerns, particularly regarding thermal runaway. -
What materials can improve lithium-ion battery safety?
Research into safer electrolyte materials, such as solid electrolytes, can help reduce the risk of fires and enhance overall battery safety. -
What should I do if my lithium-ion battery is damaged?
Dispose of damaged batteries properly at designated recycling facilities and avoid attempting to repair or disassemble them. -
Can lithium-ion batteries be used in extreme temperatures?
While lithium-ion batteries can operate in a range of temperatures, extreme heat can increase the risk of thermal runaway, and cold temperatures can reduce their performance.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.