Battery performance is largely determined by a factor known as the nominal voltage. Whether you’re powering your smartphone, an electric vehicle (EV), or a renewable energy system, understanding nominal voltage is crucial for ensuring optimal device performance, efficiency, and longevity. This guide will explain what nominal voltage is, how it differs from peak and cut-off voltage, and how this knowledge impacts your daily use of various devices. Let’s dive into the essentials of battery nominal voltage, particularly in lithium-ion batteries.
Part 1. What is battery nominal voltage?
Nominal voltage, also referred to as the battery’s average operating voltage, is a key metric that determines how a battery will perform in various devices. Understanding nominal voltage is essential for choosing the right battery for your needs, from mobile phones to electric vehicles.
Why Nominal Voltage Matters?
The nominal voltage is crucial because it provides a baseline for comparing different batteries. Knowing the nominal voltage lets you determine if a battery suits a specific application. For instance, designers create many electronic devices to operate efficiently within a particular voltage range, and using a battery with the correct nominal voltage ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Part 2. How is nominal voltage determined?
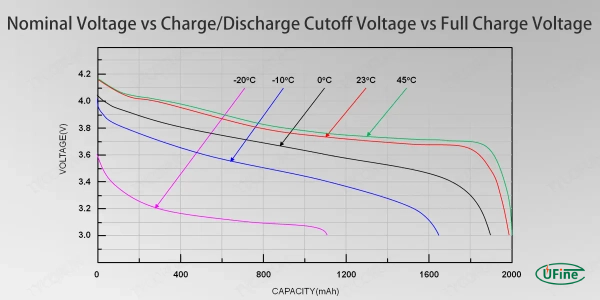
Nominal voltage is usually determined by the battery chemistry, which dictates the voltage range for specific types of batteries. For example, lithium-ion batteries typically operate within a range of 3.0V (discharged) to 4.2V (fully charged). Understanding this voltage range is essential for choosing the right battery for your devices and ensuring optimal battery efficiency and performance. The voltage value is critical in measuring how a battery will perform in a device and its expected battery lifespan over time.
Example: Lithium-Ion Batteries
For example, lithium-ion batteries typically have a nominal voltage of 3.7 volts. The operating range usually spans about 3.0 volts (discharged) to 4.2 volts (fully charged), determining this value.
Part 3. Difference between nominal, peak, and cut-off voltage
Understanding the difference between nominal voltage, peak voltage, and cut-off voltage is essential for battery management and application.
What is Nominal Voltage, and Why Does It Matter for Your Devices?
Nominal voltage, often considered the heart of battery performance, determines how well a battery will perform under various loads. For example, in a lithium-ion battery, the nominal voltage is typically around 3.7V, representing the battery’s average operating voltage during discharge. This is the most important metric for determining compatibility with your device.
Peak Voltage
Peak voltage is the maximum voltage a battery can reach when fully charged. For a lithium-ion battery, this is typically around 4.2 volts. Understanding the voltage measurement is important to ensure that devices operate within safe and efficient voltage ranges, thus improving both battery efficiency and battery lifespan.
Cut-Off Voltage
Cut-off voltage refers to the minimum voltage at which the battery is considered fully discharged. For lithium-ion batteries, this is often around 3.0 volts. Monitoring this voltage ensures that the battery remains within the optimal voltage range and contributes to better battery performance and longevity.
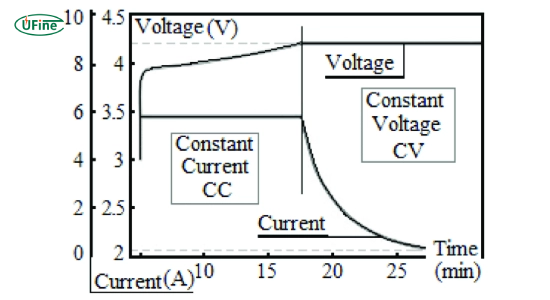
Voltage vs Current: What is the Difference?
Part 4. Factors affecting battery nominal voltage
Several factors can influence the nominal voltage of a battery, including:
- Battery Chemistry: Different materials have different electrochemical properties. The most significant factor is battery chemistry. For example, lead-acid batteries have a nominal voltage of 2 volts per cell. In comparison, nickel-cadmium batteries are typically around 1.2 volts per cell. For further understanding of the chemistry behind batteries and their voltage characteristics, visit Battery University’s article on battery nominal voltage.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect the voltage.
- Age and Usage: A battery’s performance and voltage characteristics can degrade over time.
Battery Chemistry
The most significant factor is battery chemistry. For example, lead-acid batteries have a nominal voltage of 2 volts per cell. In comparison, nickel-cadmium batteries are typically around 1.2 volts per cell.
Temperature
Temperature variations can cause fluctuations in battery voltage. High temperatures can increase the voltage, while low temperatures can decrease it.
Age and Usage
As batteries age, their internal resistance increases, which can lead to a decrease in nominal voltage. Usage patterns also play a role; frequent deep discharges can accelerate this degradation.
Part 5. Practical applications of nominal voltage
Consumer Electronics
For consumer electronics such as smartphones, knowing the nominal voltage ensures that the device operates efficiently within the intended voltage range, preventing issues like overheating or rapid battery drain.
Electric Vehicles
For electric vehicles, understanding the nominal voltage of the battery pack is crucial for optimizing range and performance. A nominal voltage of 3.7V in lithium-ion batteries is commonly used, but it can vary depending on the type of battery chemistry.
Renewable Energy Systems
In renewable energy systems, such as solar power installations, batteries with the correct nominal voltage are essential for storing and delivering power reliably.
Part 6. Common battery types and their nominal voltages
Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Nominal Voltage: 3.7V
- Applications: Smartphones, laptops, electric vehicles
Lead-Acid Batteries
- Nominal Voltage: 2V per cell (12V for a 6-cell battery)
- Applications: Automotive, backup power supplies
Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) Batteries
- Nominal Voltage: 1.2V
- Applications: Power tools, emergency lighting
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries
- Nominal Voltage: 1.2V
- Applications: Rechargeable AA and AAA batteries
Part 7. How to measure battery nominal voltage?
Using a Multimeter
To measure the nominal voltage of a battery, you can use a multimeter. Set the multimeter to the appropriate voltage range and connect the probes to the battery terminals. The reading should give you an idea of the current-voltage, which you can compare to the nominal voltage specified by the manufacturer.
Interpreting the Results
When measuring a battery’s voltage, it’s essential to consider the state of charge. A fully charged battery typically shows a voltage higher than its nominal value. In comparison, a discharged battery will show a lower voltage. For the most accurate measurement, ensure the battery rests without any load.
Part 8. Impact of nominal voltage on battery performance
Efficiency
Using a battery with the correct nominal voltage can significantly impact the efficiency of your device. Designers often create devices to operate within a specific voltage range, and deviating from this range can lead to reduced performance and higher energy consumption, directly affecting battery efficiency.
Longevity
A battery’s nominal voltage also affects its longevity. Operating a device outside its intended voltage range can strain the battery, leading to faster degradation and a shorter battery lifespan.
Safety
Safety is another critical factor. Batteries with incorrect nominal voltages can overheat, leak, or even explode, posing severe risks. Always ensure that the battery you use matches the voltage requirements of your device to avoid compromising battery performance and efficiency.
Part 9. Comparing batteries: nominal voltage vs. capacity
Understanding Capacity
While nominal voltage is crucial, capacity (measured in milliamp-hours, mAh, or amp-hours, Ah) is another critical factor. Capacity indicates how much energy a battery can store, whereas nominal voltage indicates the average operating voltage.
Balancing Voltage and Capacity
Choosing the correct battery involves balancing voltage and capacity. For example, a battery with a higher nominal voltage but lower capacity might not last as long as a battery with a lower nominal voltage but higher capacity. Understanding your device’s requirements can help you make an informed choice.
Common Misunderstandings about Nominal Voltage
A common misconception is that a higher nominal voltage always means better performance. However, this is not the case. Battery performance depends on the balance between nominal voltage and capacity, and using a higher nominal voltage battery without considering capacity could lead to inefficiency or damage.
Part 10. FAQs
-
What happens if I use a battery with the wrong nominal voltage?
Using a battery with the wrong nominal voltage can lead to reduced performance, shorter lifespan, or even damage to your device. Always check the voltage requirements before using a new battery. -
Can vominal voltage change over time?
A battery’s nominal voltage can change due to age and usage patterns. Regular monitoring and proper maintenance can help mitigate these changes. -
How do I know the nominal voltage of my battery?
The nominal voltage is usually specified on the battery label or in the manufacturer’s documentation. If this information is unavailable, you can measure the voltage using a multimeter and compare it to typical values for the battery chemistry. -
What factors affect battery nominal voltage?
Battery nominal voltage can be influenced by several factors, including the type of battery chemistry, temperature variations, and the age of the battery. For example, lithium-ion batteries typically have a nominal voltage of 3.7V, but extreme temperatures or battery degradation can cause voltage fluctuations. Regular monitoring can help maintain battery performance over time. -
What is the difference between nominal and charge voltage?
Nominal voltage refers to a battery’s average voltage during everyday use, providing a standard value for compatibility and performance expectations. Charge voltage, however, is the actual voltage applied to the battery during charging, which varies depending on the charging method and battery type.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.