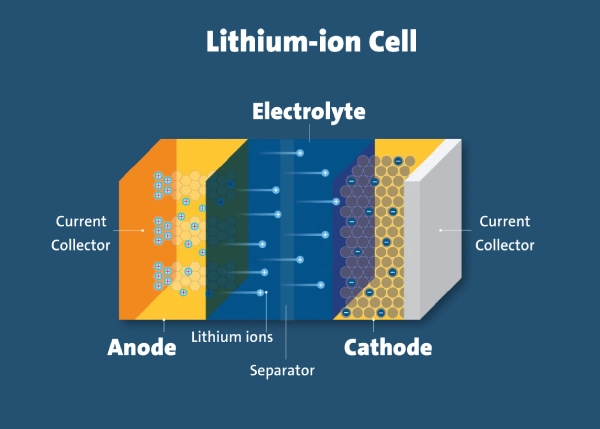
Part1. Are all li ion batteries rechargeable?
Not all lithium batteries are rechargeable. Lithium batteries are divided into two types: rechargeable batteries and non-rechargeable batteries. Among them, rechargeable batteries are divided into lithium-ion batteries and lithium-polymer batteries.
Non-rechargeable batteries (disposable batteries)
Non-rechargeable batteries (disposable batteries) can only convert chemical energy into electrical energy once. They cannot restore electrical energy to chemical energy (or have extremely poor reduction performance). Due to the presence of lithium metal, non-rechargeable batteries (disposable batteries) cannot be recharged once they lose power and can only be recycled.

Rechargeable lithium battery (secondary battery)
Rechargeable batteries are called secondary batteries (also called storage batteries). It can convert electrical energy into chemical energy and store it. When used, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. Rechargeable batteries can be cycled through charge and discharge.
Lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries
Lithium-ion batteries and lithium polymer batteries are both rechargeable batteries. The lithium-ion battery is a relatively common and widely used lithium battery. It is characterized by large capacity, long life, safety, and reliability. It can meet the needs of mobile electronic equipment, electric vehicles, etc.
Polymer lithium batteries have higher capacity, lighter weight, and are safer and are the future development trend.
Part 2. How does a rechargeable battery work?
The charging process of lithium batteries can be divided into three stages: Pre-Charging Mode, Fast Charging Mode, and Constant Voltage Mode.
The charging method of lithium batteries is voltage limiting and constant current, which is controlled by IC chips.
The typical charging method for lithium batteries is first to detect the voltage of the battery to be charged. If the voltage is lower than 3V, precharge must be performed first. The charging current is 1/10 of the set current. After the voltage rises to 3V, it enters the standard charging process.
The standard charging process is constant current charging with a set current. When the battery voltage rises to 4.20V, it changes to constant voltage charging to keep the charging voltage at 4.20V. At this time, the charging current gradually decreases. When the current drops to 1/10 of the set charging current, charging ends.
Part 3. Types of non-rechargeable lithium batteries and application
What is a non-rechargeable lithium battery?
Non-rechargeable lithium batteries are those that cannot be recharged after the battery is used up.
There are many kinds of non-rechargeable lithium batteries. The common ones are lithium-manganese dioxide batteries, lithium-thionyl chloride batteries, and lithium and other compound batteries.
1. Lithium-Manganese Dioxide (Li-MnO₂)
- Voltage: 3V
- Applications:
- Cameras
- Flashlights
- Watches
- Key fobs
- Medical equipment
- Features: High energy density, long shelf life, and reliable performance over a wide temperature range.
2. Lithium-Thionyl Chloride (Li-SOCl₂)
- Voltage: 3.6V
- Applications:
- Utility meters
- Sensors
- Military equipment
- Industrial electronics
- Features:
- Extremely long shelf life (10-20 years)
- Operates in extreme temperatures (-55°C to 150°C)
- High energy density
- Commonly used in low-drain, long-term applications.
3. Lithium-Iron Disulfide (Li-FeS₂)
- Voltage: 1.5V
- Applications:
- Digital cameras
- Toys
- Flashlights
- Portable electronics
- Features:
- Lightweight and high energy density
- Compatible as a direct replacement for standard alkaline batteries in many devices.
- Performs well in low-temperature environments.
4. Lithium-Carbon Monofluoride (Li-CFx)
- Voltage: 3V
- Applications:
- Medical devices (e.g., pacemakers)
- Utility meters
- Memory backup in electronics
- Features:
- Very high energy density
- Long shelf life
- Often used in specialized and critical applications.
5. Lithium-Copper Oxide (Li-CuO)
- Voltage: 1.5V
- Applications:
- Military and aerospace applications
- Features:
- High capacity
- Used in niche applications requiring low-to-moderate energy consumption.
6. Lithium-Polycarbon Monofluoride (Li-(CF)n)
- Voltage: 2.8–3.0V
- Applications:
- Medical implants (e.g., pacemakers)
- Military electronics
- Backup power in small devices
- Features:
- Exceptional energy density and reliability.
- Very stable voltage output over extended periods, making it ideal for low-drain, long-life devices.
Other Specialty Primary Lithium Batteries
While the above are the most commonly used types, some niche applications use custom chemistries based on lithium due to specific performance requirements, such as extreme temperatures, extended shelf lives, or precise energy outputs. Examples include lithium-sulfur dioxide (Li-SO₂) batteries, which are often used in military-grade devices and aerospace applications.
Part 4. Why are disposable lithium batteries non-rechargeable?
Disposable lithium batteries are non-rechargeable due to their chemical composition and design:
-
Chemical Composition:
- Primary lithium batteries use chemical reactions that are not reversible. For example, lithium-metal anodes react with cathode materials to produce energy. Once the reactants are depleted, they cannot be restored to their original state.
- Recharging would cause unwanted side reactions, leading to the formation of unstable compounds that can cause overheating, leakage, or explosion.
-
Design:
- Non-rechargeable batteries lack the structural components needed to withstand repeated charging cycles. For instance, their separators and electrodes are not built to handle the physical and chemical stresses of recharging.
- Rechargeable lithium-ion batteries use intercalation chemistry, which allows lithium ions to move back and forth between the anode and cathode during charging and discharging. Non-rechargeable lithium batteries do not use this mechanism.
-
Safety Concerns:
- Attempting to recharge a non-rechargeable lithium battery can result in excessive heat generation, gas buildup, and even catastrophic failure (fire or explosion).
Part 5. Tips for using non-rechargeable batteries
The above two lithium batteries are disposable and are not rechargeable (dangerous when charging).
- There must be no short circuit between the positive and negative terminals of the battery;
- Do not discharge with excessive current (discharge exceeding the maximum discharge current);
- When the battery reaches the end discharge voltage, it should be removed from the electronic device in time;
- Used batteries cannot be squeezed, burned, or disassembled;
- Do not use it beyond the specified temperature range.
Since the voltage of lithium batteries is higher than that of ordinary batteries or nickel-cadmium batteries, do not make mistakes when using them to avoid damaging the circuit. By familiarizing yourself with the CR and ER in the model number, you can know its type and rated voltage. When buying a new battery, be sure to buy it according to the original model. Otherwise, it will affect the performance of the electronic device.
Part 6. FAQs
-
Can I recharge a non-rechargeable lithium battery?
No, non-rechargeable lithium batteries should not be recharged. Attempting to recharge them can lead to safety hazards, such as leakage or explosion. -
How long do non-rechargeable lithium batteries last?
Non-rechargeable lithium batteries have a limited lifespan and typically last for several cycles or usage hours, depending on the application and battery quality. -
Does lithium-ion mean rechargeable?
No, there are rechargeable lithium batteries and non-rechargeable lithium batteries. -
Is there a special charger for lithium batteries?
Yes, there are special chargers designed specifically for lithium batteries. These chargers employ proper charging algorithms and safety features to ensure efficient and safe charging of lithium batteries.
Related Tags:
More Articles
What is the Difference Between Silver Zinc Battery vs. Lithium-ion Rechargeable?
Compare silver zinc and lithium-ion rechargeable batteries: energy density, cycle life, safety, cost, and uses in drones, medical devices, EVs, and electronics.
What are Watts and Watt Hours in Battery?
Understand watt vs watt-hour in batteries: key differences, how to calculate capacity, and why they matter. Includes free comparison table.
Best 10 Blood Pressure Monitor Battery Review: Finding the Most Reliable
Are you looking for a reliable Blood Pressure Monitor battery? Here is a complete guide with the top 10 best blood pressure monitor batteries.
Bluetooth Headphone Battery Guide: All You Need to Know
Maximize headphone battery life with expert tips! Learn how to charge, check, troubleshoot, and choose the best bluetooth headphone battery in 2025.
LiFePO4 Battery VS. Lithium-ion Polymer Battery: Which One Is Best?
Comprehensive comparison of LiFePO4 vs Lithium Ion Polymer batteries: energy density, safety, lifespan, cost. Find out which battery suits your needs in 2025.