Can lithium batteries be in water? This question uncovers the repercussions when lithium batteries interact with water, highlighting key safety concerns. From hydrogen gas release to potential fire risks, understanding these reactions is crucial to battery safety. Whether in everyday use or emergency scenarios, this guide provides insights into hazards and preventive measures to ensure safe handling.
Part 1. Lithium battery chemistry: The key components
Lithium batteries rely on a complex interaction of key components that enable efficient energy storage and release. These include:
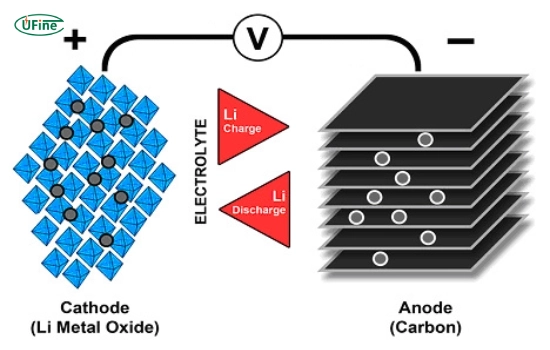
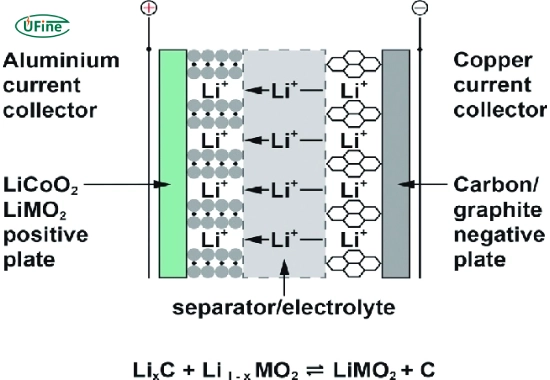
1. Battery Cathode and Anode
- Cathode: Composed of materials such as lithium cobalt oxide, lithium iron phosphate, or lithium manganese oxide, the cathode serves as the source of lithium ions during discharge.
- Anode: Typically made of carbon (graphite), the anode facilitates the storage and release of lithium ions, balancing the battery’s charge flow.
2. Battery Electrolyte
- This liquid medium contains lithium salts dissolved in an organic solvent, enabling ion transfer between the cathode and anode. The electrolyte’s fluid nature supports the battery’s charge-discharge cycles.
3. Battery Separator
- Acting as a physical barrier, the separator prevents the cathode and anode from direct contact, reducing the risk of short circuits while allowing lithium ions to pass during operation.
These chemical components work in harmony to define the battery’s performance and reactions under diverse conditions.
Part 2. Lithium battery and water reactions
Water can trigger hazardous reactions in lithium batteries due to the highly reactive nature of lithium with moisture. When water infiltrates a lithium battery, it instigates a series of detrimental reactions that can lead to heat generation, hydrogen gas release, and potential fire hazards.
Immediate Effects
Upon contact with water, lithium batteries swiftly display signs of malfunction. This includes heat generation and the emission of smoke. These immediate reactions occur due to the rapid interaction between water molecules and the battery’s internal components.
Generation of Hydrogen Gas
Water’s presence triggers the breakdown of lithium compounds within the battery, generating hydrogen gas. When this gas combines with air, it forms an explosive mixture. This elevates the risk of fire or explosion if ignited or triggered.
Heat Generation
Water ingress can incite an exothermic reaction within the battery, leading to a noticeable increase in temperature. This heat rise can escalate rapidly, potentially causing the battery to catch fire or even explode, posing severe safety risks.
Fire and Thermal Hazards
The combination of increased heat, the presence of flammable gases (like hydrogen), and potentially combustible battery components can lead to fire outbreaks. Once ignited, these fires can be challenging to control and might cause significant property damage and pose risks to personal safety. Containing or extinguishing such fires becomes challenging due to the nature of the materials involved and the volatility of the situation.
Potential Water Exposure Scenarios:
Lithium batteries may come into contact with water during floods, spills, or even improper storage. Each situation presents unique risks, and understanding them helps users mitigate potential dangers.
For instance, in 2019, a warehouse storing lithium batteries caught fire after significant water exposure due to flooding. This highlights the risks of improper storage.
Part 3. How to waterproof a battery pack?
Waterproofing batteries is a critical process to safeguard them from potential water damage, especially in environments where exposure to moisture is likely. Several strategies can be employed to waterproof batteries effectively, ensuring their functionality and safety.
Encapsulation and Coating
One approach involves encapsulating or coating the battery components with water-resistant materials. Silicone-based coatings or encapsulation using potting compounds can provide a protective layer that seals the battery, preventing water penetration. This method helps maintain the integrity of the battery and protects its internal components.
Materials for Encapsulation and Coating
- Use specialized coatings like polyurethane potting compounds for effective moisture resistance.
- For advanced applications, parylene coatings provide ultra-thin, uniform protection, widely used in industrial and medical equipment.
Waterproof Casing Design
Manufacturers often design battery casings with waterproof features to shield the internal components. Employing robust and sealed casings made from materials like polycarbonate or ABS plastic can act as a barrier against moisture. Gaskets and O-rings are also incorporated into casing designs to create tight seals, preventing water ingress.
Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and adhesives play a crucial role in preventing water intrusion. Applying silicone-based or epoxy sealants to seams, joints, or openings in the battery housing enhances water resistance. These sealants effectively seal any potential entry points for water.
Protective Wrapping
In certain scenarios, employing additional protective wrapping or shrink-wrapping around the battery can offer an extra layer of defense against water. Waterproof shrink-wrap films or tapes specifically designed for battery protection provide an impermeable shield.
Budget-Friendly DIY Waterproofing Tips
For individual use, simple measures can help protect batteries in moist environments:
- Use waterproof bags to enclose small devices, ensuring the bags are properly sealed.
- Apply silicone sealant around vulnerable areas of the battery casing to block water ingress.
- Always test DIY solutions in controlled environments before using batteries in critical applications.
Ingress Protection (IP) Ratings
Utilizing batteries with higher IP ratings is a strategic choice for waterproofing. IP ratings classify the degree of protection against solid particles and water ingress. Batteries with higher IP ratings, such as IP67 or IP68, provide substantial protection against moisture and are suitable for use in challenging environments.
Regular Maintenance
Routine inspections and maintenance are essential to ensure the longevity of waterproofing measures. Checking for any signs of wear, damage, or compromised seals and promptly addressing them can prevent water intrusion and maintain the effectiveness of waterproofing.
By employing these methods and incorporating waterproofing measures into battery design and maintenance routines, batteries can be effectively protected from water damage, ensuring their reliability and safety in various applications.
Explore our range of high-quality lithium polymer, lithium iron phosphate, and 18650 batteries to ensure your lithium batteries remain safe and reliable. Learn more about battery safety and best practices to protect your investment and enhance performance.
Part 4. FAQs
-
What happens if you put a lithium battery in water?
Submerging a lithium battery in water can cause a short circuit, leading to immediate damage, overheating, and potential fire or explosion due to the reaction between water and the battery’s internal components. -
Are lithium batteries waterproof?
Lithium batteries are not inherently waterproof. They lack protective casing or seals to prevent water intrusion, making them vulnerable to damage if exposed to water. -
Do lithium batteries float in water?
Lithium batteries are denser than water and typically sink rather than float. However, the buoyancy could depend on factors like battery size, shape, and packaging. -
What happens if a lithium battery gets wet but not submerged?
Even brief exposure to moisture can lead to internal damage. Dry the battery immediately and avoid using it until inspected. -
Can lithium batteries survive in marine environments?
Specialized marine-grade lithium batteries with high IP ratings (e.g., IP68) are designed for such conditions. Always consult manufacturers for recommendations. -
Why is water bad for batteries?
Water conducts electricity and can create a conductive path between a battery’s terminals, leading to a short circuit and damaging the battery by causing internal reactions that can result in heat generation, leakage, or even combustion. -
How do you protect a lithium battery from water?
To protect lithium batteries from water, use waterproof casings or enclosures for devices containing batteries. Store batteries in dry environments, avoid exposure to moisture and use waterproof containers or bags if there’s a risk of water exposure.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Paper Battery vs. Flexible Battery: What’s the Difference and Which Is Better?
Paper vs. flexible batteries: learn the key differences, benefits, and which power source fits best for wearables, sensors, and smart tech.
What to Know Before Buying a Tiny LiPo Battery for Your Project
Tiny LiPo batteries are powerful and compact. Learn how to choose the right one for your project with specs, safety, and charging tips.
Bloated LiPo Battery: Will It Explode?
Will a bloated LiPo battery explode? Discover the causes, risks, safety steps, and expert tips to avoid disaster and protect your gear. Must-read safety guide!
12V 100Ah Lithium Ion Battery Price: Full Guide
Learn about 12V 100Ah lithium-ion battery price, from cost ranges to best brands, hidden fees, and how to get the best deal. A must-read for smart buyers!
Resistance and Conductivity: What It Means for Your Lithium Batteries
Resistance and conductivity impact lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety—learn how they work and why they matter.