Can you overcharge a lithium battery? This question is crucial for anyone who uses devices powered by lithium batteries, such as smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. Understanding the effects of overcharging can help you maintain your battery’s health and ensure your safety. This article will explore what overcharging means, its consequences, and how to prevent it.
Part 1. What is a lithium battery overcharging?
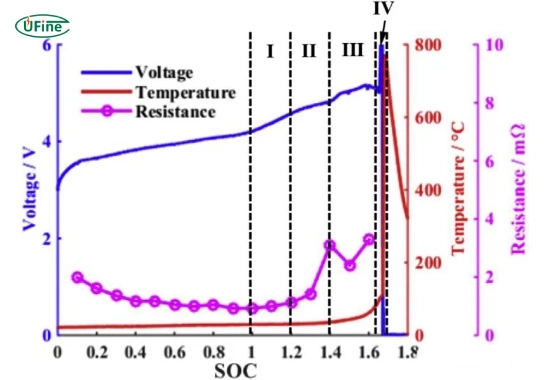
A lithium-ion battery overcharges when charged beyond its maximum voltage limit, which is around 4.2 volts per cell for most batteries. Excessive voltage can lead to various harmful effects.
Overcharging can happen for several reasons. Sometimes, it may be due to an incorrect charger that continues charging at the right time. Other times, it may occur because of a malfunction in the device’s charging system. Regardless of the cause, overcharging can significantly affect the battery’s performance and safety.
Part 2. What happens when you overcharge a lithium battery?
When you overcharge a lithium battery, several negative processes can occur:
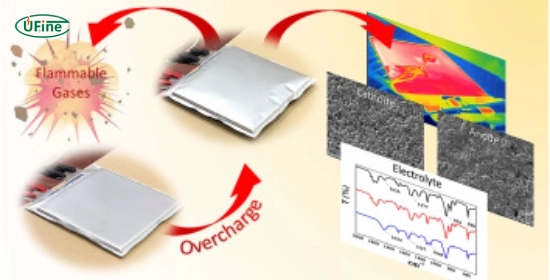
- Increased Temperature: Overcharging generates excess heat, which can cause the battery to become dangerously hot. In extreme cases, it may lead to thermal runaway, where the temperature rises uncontrollably, resulting in fires or explosions.
- Gas Formation: Overcharging can cause the electrolyte inside the battery to break down, resulting in gas buildup. This gas can create pressure inside the battery casing, leading to swelling or even rupture.
- Dendrite Formation: Lithium ions can form dendrites—tiny, needle-like structures that grow within the battery during overcharging. These dendrites can create short circuits inside the battery, which may further damage it and pose serious safety risks.
- Reduced Lifespan: Continuous overcharging degrades the battery’s internal components, significantly reducing its lifespan and overall performance.
Part 3. What is the role of the Battery Management System (BMS) in preventing overcharging?
The Battery Management System (BMS) protects lithium batteries from overcharging. A BMS is an electronic system that monitors and manages various aspects of a battery’s operation. Its primary functions include:
- Voltage Monitoring: The BMS continuously checks the voltage levels of each cell in the battery pack. If any cell approaches its maximum voltage limit (usually 4.2 volts), the BMS will cut off charging to prevent overcharging.
- Temperature Control: The BMS monitors the battery’s temperature during charging and discharging. If it detects excessive heat, it may reduce or stop charging until temperatures return to safe levels.
- Balancing Cells: The BMS ensures that all cells are charged evenly in multi-cell batteries. This balancing helps prevent some cells from becoming overcharged while others are undercharged.
A well-designed BMS significantly reduces the risk of overcharging and enhances overall battery safety by performing these functions.
Part 4. How does overcharging a LiFePO4 battery affect its lifespan?
LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries are known for their stability and safety compared to other lithium-ion chemistries. However, they are still susceptible to damage from overcharging. Overcharging a LiFePO4 battery can lead to:
- Decreased Cycle Life: Like other lithium batteries, overcharging LiFePO4 batteries reduces their cycle life. Each charge cycle becomes less efficient as internal damage accumulates.
- Increased Internal Resistance: Overcharging causes chemical reactions that increase internal resistance within the battery. This increased resistance leads to lower efficiency and more heat generation during use.
- Potential for Thermal Runaway: Although LiFePO4 batteries are more stable than other lithium types, they are not immune to thermal runaway if consistently overcharged. This can lead to catastrophic failure under extreme conditions.
Avoiding voltage limits and following proper charging practices are essential for maximizing the lifespan of a LiFePO4 battery.
Part 5. How to safely charge lithium batteries?
To ensure safe charging of lithium batteries and avoid overcharging:
- Use Compatible Chargers: Always use chargers specifically designed for your type of lithium battery. Generic chargers may need accurate voltage control, which can lead to overcharging.
- Monitor Charging Conditions: Monitor your device while it’s charging. If you notice excessive heat or swelling, disconnect it immediately.
- Avoid Leaving Batteries Charging Unattended: It’s best practice not to plug lithium batteries in overnight or when you are away from home.
- Charge in a Safe Environment: Avoid charging batteries in hot or humid environments. A cool, dry place is ideal for charging.
How to Charge a Lithium-ion Battery?
Part 6. Can you repair an overcharged lithium battery?
Unfortunately, if you overcharge and damage a lithium battery, you cannot repair it. The internal damage caused by overcharging is often irreversible. An overcharged battery poses significant safety risks, including potential fires or explosions.
If you suspect your battery has been overcharged or shows signs of damage (like swelling or leakage), it’s best to dispose of it safely according to local regulations.
Part 7. What are the signs of an overcharged lithium battery?
Recognizing the signs of an overcharged lithium battery can help you take action before severe damage occurs:
- Swelling: One of the most apparent signs of an overcharged battery is swelling or bulging of the casing.
- Unusual Heat: There may be a battery issue if your device feels excessively hot during charging or after unplugging.
- Leakage: Any signs of liquid leaking from the battery are severe and require immediate attention.
If you notice these signs, stop using the device immediately and seek professional help.
Part 8. FAQs
-
What is the maximum voltage for charging a lithium battery?
The maximum voltage for most lithium-ion batteries is around 4.2 volts per cell. Exceeding this voltage can lead to severe damage and safety hazards. -
Can I leave my lithium battery plugged in overnight?
It’s generally not recommended to leave lithium batteries plugged in overnight due to potential overheating and risks of overcharging. -
How do I know if my lithium battery is damaged?
Signs of damage include swelling, unusual heat during charging, or leakage from the battery casing. -
What should I do if my lithium battery swells?
If your lithium battery swells, stop using it immediately and dispose of it safely according to local regulations. -
Is it safe to use generic chargers for my lithium batteries?
Using generic chargers can be risky as they may need to provide the proper voltage-required regulation for safe charging. Always use chargers specifically designed for your device.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Learning Car Battery Voltage
Wondering what voltage a car battery operates at? Learn about the importance of car battery voltage, how to check it, common causes of voltage drops.
Understanding 9V Battery Amps
Discover how many amperes a 9V battery delivers, its capacity, discharge rate, and much more. Get all the details on current, types, lifespan, and alternatives.
Understanding the Difference Between AA and AAA Batteries
Wondering about the difference between AA and AAA batteries? Learn the key differences, similarities, and when to use each in this detailed guide.
Understanding AAA Battery Voltages in Simple Terms
Understand AAA battery voltages easily. Explore their uses in everyday devices. Get the facts you need to choose the right battery today!
Which Lithium Ion Battery Is Best for Solar?
Solar energy needs reliable storage, and lithium-ion batteries store excess energy for later use. Here’s how to choose the best one for your solar system.