Capacitors and batteries are widely used energy storage components with unique characteristics and applications. Understanding the differences and similarities between capacitors and batteries can help us make informed decisions about their usage in different scenarios. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of capacitors and batteries, exploring their advantages, disadvantages, differences, similarities, and applications.
Part 1. What is the capacitor?
A capacitor is an electronic component that stores and releases electrical energy. It consists of two conductive plates separated by a dielectric material. When the plates have a voltage potential across them, they generate an electric field, which allows the capacitor to store charge. However, unlike batteries, capacitors do not produce or generate electrical energy. They merely store the charge for a short period.
Capacitor Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Capacitors:
- Fast Charging and Discharging: Capacitors can charge and discharge rapidly, making them ideal for applications that require quick bursts of electrical energy.
- Longevity: Capacitors have a longer lifespan than batteries as they do not undergo chemical reactions during operation.
- High Efficiency: Capacitors are highly efficient in energy transfer due to their low internal resistance.
Disadvantages of Capacitors:
- Limited Energy Storage: Capacitors have a relatively lower energy storage capacity than batteries. They are better suited for short-term energy storage rather than long-term usage.
- Voltage Dependence: The voltage across a capacitor decreases as it discharges, affecting its performance in specific applications.
- Limited Voltage Range: Capacitors have voltage limitations, and exceeding these limits can lead to failure or damage.
Part 2. What is the battery?
A battery is an electrochemical device that converts stored chemical energy into electrical energy. It consists of one or more electrochemical cells, each comprising positive and negative electrodes separated by an electrolyte. This chemical reaction allows the battery to produce and store electrical energy.
Battery Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Batteries:
- High Energy Density: Batteries offer a higher energy storage capacity than capacitors, making them suitable for applications requiring sustained power.
- Portability: Batteries are portable and easily integrated into various devices, providing a convenient power source.
- Stable Voltage Output: Batteries provide a consistent voltage output until their charge depletes, ensuring steady performance.
Disadvantages of Batteries:
- Limited Lifespan: Batteries have a limited lifespan and eventually degrade over time, requiring replacement.
- Slow Charging and Discharging: Batteries generally take longer to charge and discharge than capacitors.
- Environmental Impact: Improper disposal of batteries can harm the environment due to their chemical components.
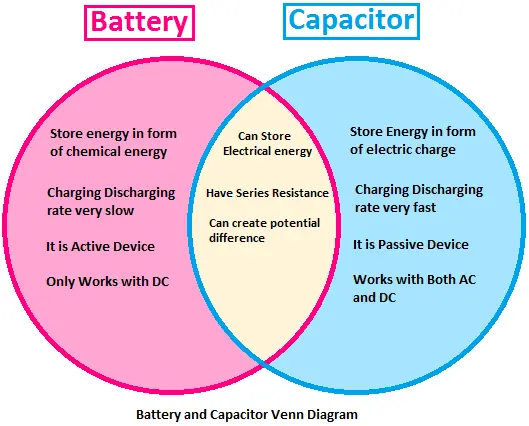
Part 3. Capacitor and battery differences
While capacitors and batteries serve the common purpose of energy storage, several key differences set them apart:
- Chemical Composition: Capacitors store energy electrostatically, whereas batteries store energy chemically.
- Charge and Discharge Rate: Capacitors can charge and discharge quickly, while batteries have slower charging and discharging rates.
- Voltage Output: Capacitors deliver a constant voltage until discharge, while batteries provide a gradually decreasing voltage as their charge diminishes.
- Charging Time: Capacitors charge and discharge almost instantaneously, while batteries require more time to charge and discharge.
- Energy Density: Capacitors store less energy compared to batteries of similar size.
- Lifetime: Capacitors generally have a longer lifespan than batteries due to the absence of chemical degradation.
- Voltage Stability: Capacitors maintain a more stable voltage output over their discharge cycle, while batteries exhibit voltage drop as they discharge.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Capacitors are less sensitive to temperature variations than batteries, which can experience performance issues in extreme temperatures.
- Maintenance: Capacitors typically require less maintenance than batteries, as they do not suffer from issues like electrolyte leakage or sulfation.
Part 4. Capacitor and battery similarities
While capacitors and batteries differ in several aspects, they also share some similarities:
- Energy Storage: Both capacitors and batteries store electrical energy using different mechanisms.
- Application Variety: Capacitors and batteries find applications in various industries, including electronics, automotive, and renewable energy sectors.
- Power Backup: Both components can serve as power backup sources in case of power outages or during the operation of critical systems.
- Voltage Output: Both can provide electrical power at a specific voltage level.
- Environmental Impact: Both capacitors and batteries have environmental considerations regarding disposal and recycling.
Part 5. Capacitor and battery applications
Capacitor Applications:
- Electronic Circuits: People widely use capacitors in electronic circuits for energy storage, filtering, and coupling.
- Motor Starters: Capacitors provide the initial energy required to start electric motors, improving efficiency.
- Power Quality Improvement: Capacitors help compensate for reactive power and enhance the power factor in electrical systems.
Battery Applications:
- Portable Electronics: Batteries power various portable devices such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets.
- Electric Vehicles: Batteries serve as the primary energy source for electric vehicles, enabling emission-free transportation.
- Renewable Energy Storage: Batteries play a vital role in storing energy generated from renewable sources like solar and wind for later use.
Part 6. Conclusion
Capacitors and batteries are essential for energy storage but have different strengths and weaknesses. Capacitors are excellent for quick bursts of energy, while batteries are better for long-term storage. Choose the right one for your needs!
Part 7. FAQs
-
How long do capacitors last?
Capacitors can last for years, ranging from 5 to 20 years or more, depending on usage conditions, temperature, and manufacturing quality. -
Is A capacitor better than a battery?
It depends on the application. Capacitors have quick charging and discharging advantages, while batteries can store more energy and have longer lifespans. -
Why don’t we use capacitors instead of batteries?
While capacitors have advantages like fast charging and discharging, they store less energy compared to batteries of similar size, limiting their use in specific applications where high-energy storage is needed. -
Do capacitors charge faster than batteries?
Yes, capacitors generally charge faster than batteries because they can instantly store and release energy due to their mechanism of storing energy in an electric field. -
Can a battery replace a capacitor?
In some cases, it depends on the application’s specific requirements. Batteries and capacitors have different characteristics, so they’re often used in various scenarios based on energy storage capacity, charging time, and lifespan.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.