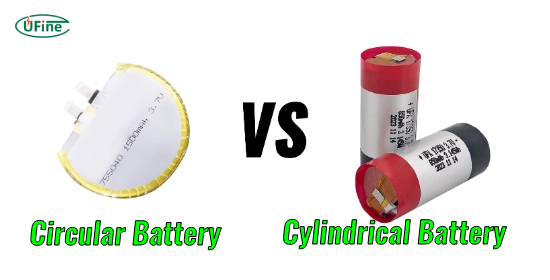
Batteries are integral to modern technology, powering everything from smartphones to electric vehicles. Among the various types of batteries available today, circular and cylindrical batteries are two of the most commonly used formats. Understanding their differences and determining which best suits your needs can be crucial when optimizing performance and efficiency. In this article, we will explore the characteristics, advantages, and applications of both circular and cylindrical batteries, providing you with the information you need to make an informed decision for your application.
Part 1. What is a circular battery?
Circular batteries are designed with a round shape and typically feature a flat, disk-like structure. They are widely used in applications that require a compact power source with a smaller form factor. One typical example of a circular battery is the button cell, which powers devices such as watches, hearing aids, and small electronic gadgets.
Key Features of Circular Batteries:
- Compact size: Circular batteries are designed to fit into small spaces, making them ideal for compact devices.
- Variety of chemistries: Depending on the power needs, they can be found in different chemistries, such as alkaline, lithium, and zinc-carbon.
- Widely available: Circular batteries are easily accessible, and their standardization makes them suitable for a wide range of products.
Part 2. What is a cylindrical battery?
Cylindrical batteries, on the other hand, have a tubular shape that is longer and more uniform in design compared to circular batteries. These batteries are commonly used in applications that require higher energy storage and more substantial power output. Examples of cylindrical batteries include AA, AAA, and 18650 lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly found in consumer electronics, power tools, and electric vehicles.
Key Features of Cylindrical Batteries:
- Higher capacity: Cylindrical batteries offer more energy storage than circular batteries, making them suitable for high-power applications.
- Versatility: These batteries come in various sizes and chemistries, allowing for flexibility in their usage.
- Efficient heat dissipation: The cylindrical shape helps with heat distribution, reducing the risk of overheating.
Part 3. Circular battery vs. cylindrical battery: The shape difference
The most apparent difference between a circular and cylindrical battery is its shape. Circular batteries have a flat design that allows them to fit into smaller, flatter spaces. These are often used in devices that require a low profile, such as hearing aids or small watches. Cylindrical batteries, in contrast, have a more extended, tubular design and are used in devices requiring more energy, such as flashlights, laptops, and electric cars.
Advantages of Circular Battery Shape:
- It is more straightforward to integrate into thin and compact designs.
- Ideal for small, portable devices.
Advantages of Cylindrical Battery Shape:
- Offers more energy storage capacity.
- It can be designed for larger devices that need higher power.
Part 4. Energy capacity: Circular vs. cylindrical
Due to their larger size, cylindrical batteries generally have an advantage in energy capacity. They are designed to hold more charge, meaning they can power devices for extended periods.
Circular Batteries:
- Typically used in smaller devices.
- They have a lower energy density compared to cylindrical batteries.
Cylindrical Batteries:
- Offer higher energy output.
- Suitable for power-hungry applications like laptops and electric vehicles.
Part 5. Cost comparison: Which battery is more affordable?
Cost is always a critical factor when choosing between circular and cylindrical batteries. Circular batteries are generally less expensive because of their simpler construction and smaller size. However, cylindrical batteries may be more cost-effective in high-capacity applications due to their longer lifespan and better energy output.
Circular Batteries:
- Lower cost is due to smaller size and a more straightforward production process.
- It may require more frequent replacement.
Cylindrical Batteries:
- Higher initial cost due to larger size and more complex design.
- Better value in high-power applications.
Part 6. Charging speed: Circular vs. cylindrical
Battery charging speed is a vital consideration for applications where quick charging is necessary. Cylindrical batteries, especially lithium-ion types, offer faster charging times than circular batteries. This is particularly important for devices such as smartphones, laptops, and electric cars, where quick recharging can be crucial.
Part 7. Durability and lifespan: How long do they last?
Both circular and cylindrical batteries offer durability, but their lifespan can vary depending on the specific application. Cylindrical batteries are generally designed to last longer, mainly in high-energy applications. However, the lifespan of any battery is also affected by factors such as usage patterns and charging cycles.
Circular Batteries:
- Typically, they last a shorter period due to their smaller energy capacity.
- It may need to be replaced more frequently.
Cylindrical Batteries:
- It tends to have a longer lifespan.
- They are more suitable for devices that require prolonged power.
Part 8. Safety: Circular vs. cylindrical batteries
Safety is always a priority when selecting a battery type. Both circular and cylindrical batteries have safety features, but cylindrical batteries, particularly lithium-ion types, can have better thermal stability. When used correctly, cylindrical batteries are less prone to overheating or explosion risks.
Part 9. Applications of circular and cylindrical batteries
Although the applications of circular and cylindrical batteries can overlap in some areas, their different features make them better suited for specific uses. Circular batteries are perfect for small, low-power devices, while cylindrical batteries are ideal for high-energy applications.
Circular Battery Applications:
- Watches and clocks.
- Hearing aids and other medical devices.
- Remote controls and small electronic devices.
Cylindrical Battery Applications:
- Electric vehicles (EVs) and e-bikes.
- Power tools and flashlights.
- Laptops, smartphones, and tablets.
Part 10. Which battery is right for your application?
Choosing between a circular and a cylindrical battery depends on several factors, such as the device’s size, energy requirements, and cost considerations.
If you need a compact solution for small devices, a circular battery might be your best option. However, a cylindrical battery may be more appropriate for devices requiring higher energy storage, such as electric vehicles or large electronics.
Part 11. FAQs
-
What is the main difference between circular and cylindrical batteries?
Circular batteries are flat and compact, ideal for smaller devices. In contrast, cylindrical batteries have a tubular shape, offering higher energy storage and power output for larger devices. -
Which type of battery is better for small electronic devices?
Due to their compact size, circular batteries are generally better for small devices like watches, hearing aids, and remote controls. -
Are cylindrical batteries safer than circular batteries?
Cylindrical batteries, particularly lithium-ion ones, have better thermal stability and safety features, making them more suitable for high-power applications. -
Which battery lasts longer: circular or cylindrical?
Cylindrical batteries generally last longer due to their higher energy storage capacity and ability to power devices for extended periods. -
How do circular and cylindrical batteries compare in cost?
Circular batteries are generally less expensive due to their smaller size and more straightforward design. However, cylindrical batteries may offer better long-term value for high-energy applications.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Right Electric Fence Battery?
Choosing the right electric fence battery is key to security. This guide helps you pick a reliable farm, garden, or animal power source.
What Are Lithium Pouch Cells?
Explore how lithium pouch cells work, their structure, advantages, and uses. Learn from a trusted supplier like Ufine Battery for custom lithium solutions.
The Evolution of Ring Battery Pack Technology in Lithium Battery Manufacturing
Ring battery packs are reshaping lithium battery tech. Discover their evolution, key uses, and why they matter for the future of energy storage.
Lithium vs Lithium Salt: What’s the Difference?
Lithium is a pure metal, while lithium salts are stable battery compounds. Learn their key roles and differences in battery manufacturing.
What You Need to Know About AA 3.6V Lithium Battery
Learn all about AA 3.6V lithium batteries—voltage, size, capacity, uses, and the best replacements. Discover why they’re powerful, and highly reliable.