As winter approaches, the importance of a cold-weather battery becomes clear for vehicle owners. Cold-weather batteries are designed to perform well in low temperatures, ensuring your vehicle starts reliably even in the harshest conditions. This article will explore essential tips and insights about maintaining your vehicle’s battery during winter months, helping you avoid frustrating situations when you need your car the most.
Part 1. How cold weather affects your battery performance?
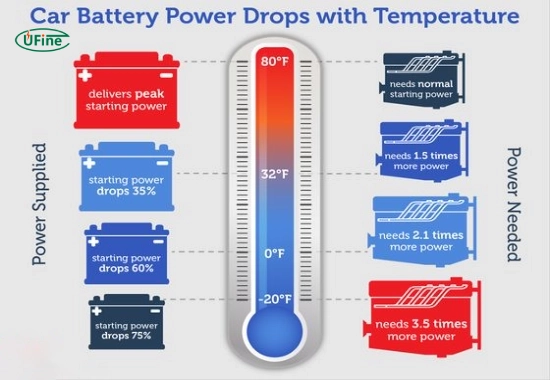
Cold weather batteries are crucial because low temperatures can significantly impact battery performance. Here’s how the cold affects your battery:
- Chemical Reactions Slow Down: Batteries generate power through chemical reactions. When temperatures drop, these reactions slow down, reducing the battery’s ability to produce energy. Even a fully charged battery can struggle to start your vehicle when it is cold outside.
- Loss of Capacity: At around 32°F (0°C), most batteries lose about 20% of their capacity. This loss can increase to 50% or more as temperatures drop further. This means that a battery that usually works perfectly may not have enough power to start your engine in freezing conditions.
- Increased Starting Demands: Cold weather makes it more challenging for engines to start because the oil thickens and creates more resistance. This means your starter motor must work harder, requiring more power from the cold weather battery.
Part 2. Understanding cold weather battery ratings
When choosing or maintaining a cold weather battery, understanding its ratings is essential:
- Cold Cranking Amps (CCA): This rating tells you how much current a battery can deliver at 0°F for 30 seconds while maintaining a voltage of at least 7.2 volts. A higher CCA rating is vital for reliable starts in cold weather. For instance, if you live in an area with extremely low temperatures, look for batteries with a CCA rating of at least 600.
- Reserve Capacity (RC): This rating indicates how long a battery can run on its power without the engine running. A higher RC is beneficial during winter when you need to rely on your battery more than usual, especially if you get stuck in traffic or have to wait for assistance.
Part 3. Preparing your cold weather battery for winter
To ensure your cold weather battery is ready for winter, follow these preparation steps:
- Battery Inspection: Before winter arrives, inspect your battery closely. Look for any signs of wear, such as cracks in the casing or corrosion around the terminals. If you see white or greenish powder on the terminals, clean it off carefully with a mixture of baking soda and water.
- Test Battery Health: Have your battery tested by a professional mechanic or use a multimeter at home. When fully charged, a healthy battery should have a voltage reading of at least 12.6 volts. If it reads lower than this, it may need charging or replacement.
- Replace Old Batteries: If your battery is older than three years, consider replacing it before winter hits. Older batteries are more prone to failure in cold conditions and may leave you stranded when you least expect it.
Part 4. Best practices for maintaining your cold weather battery
Maintaining your cold weather battery during winter involves several best practices:
- Drive Regularly: Regular driving helps keep the battery charged. Aim for longer trips where possible; short trips may not allow enough time for the alternator to recharge the battery fully.
- Avoid Short Trips: Frequent short trips can drain your battery without giving it adequate time to recharge. Try combining errands into one longer trip to keep your battery healthy when possible.
- Turn Off Accessories Before Starting: Before starting your vehicle, turn off all non-essential electrical accessories, such as heated seats or radios. This reduces strain on the battery during startup and gives it a better chance of starting smoothly.
Part 5. Using battery chargers and maintainers
If you anticipate not using your vehicle frequently during winter, consider investing in a battery charger or maintainer:
- Trickle Chargers: These devices provide a slow charge that keeps your battery topped off without overcharging. They are perfect for vehicles that sit idle for extended periods.
- Smart Chargers: Smart chargers automatically adjust their output based on the battery’s charge level and can help maintain optimal health during long periods of inactivity.
Part 6. Recognizing signs of cold weather battery trouble
Being aware of potential issues with your cold weather battery can save you from unexpected breakdowns:
- Slow Engine Crank: If your engine struggles to crank when starting, this slow performance could indicate a weak battery in cold conditions.
- Dashboard Warning Lights: Pay attention to any warning lights related to the electrical system on your dashboard; these could be signs of trouble with your battery or charging system.
- Frequent Jump Starts Needed: If you need jump starts often during winter, it may be time for a new battery or a thorough check-up.
Part 7. Emergency preparedness for cold weather battery issues
Winter can be unpredictable, so it’s wise to prepare for potential emergencies related to your vehicle’s battery:
- Keep Jumper Cables Handy: Always keep a set of jumper cables in your vehicle if you need assistance from another driver or if your battery dies.
- Portable Jump Starter: Consider investing in a portable jump starter. These devices are compact and easy to use, allowing you to jump-start your vehicle without needing another nearby car.
Part 8. Choosing the right cold weather battery
When selecting a new car battery specifically designed for winter conditions, consider these options:
- AGM Batteries: Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) batteries are designed to handle extreme temperatures and have lower self-discharge rates than traditional lead-acid batteries. They also tend to be more durable and resistant to vibration.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Although more expensive, lithium-ion batteries perform well in extreme temperatures and offer faster charging than traditional batteries.
What’s the Good Battery For Cold Weather?
Part 9. FAQs
-
What temperature is too cold for car batteries?
Most car batteries struggle significantly below freezing (32°F or 0°C), and performance drops even more dramatically as temperatures fall below this threshold. -
How often should I check my car battery in winter?
It’s advisable to check your car battery at least once a month during winter, especially if it’s over three years or if you notice any starting issues. -
Can I leave my car plugged in overnight?
Yes, using a smart charger overnight is safe and beneficial as it helps maintain the charge without risking overcharging. -
What should I do if my car won’t start in cold weather?
Check for dashboard lights indicating an electrical issue if your car doesn’t start in cold weather. If not, try jump-starting it or calling for roadside assistance if necessary. -
How long does a cold weather battery take to recharge after being drained?
The time it takes to recharge a drained cold-weather battery depends on several factors, but it generally takes about 30 minutes of driving or several hours with a charger.
Related Tags:
More Articles

A Buyer’s Guide for AA Size Lithium Battery
Discover the power of AA size lithium batteries—types, voltage, capacity, and more! Learn how to choose the best one for your needs. Read now!
Li-Ion Battery Prices – Where to Buy Cheap & Safe
Discover li-ion cell prices, key market factors, and how to find affordable custom batteries from top suppliers like Ufine Battery.
How Long Does a 2200mAh Battery Last?
Discover everything about 2200mAh batteries—types, charging time, lifespan, and whether it’s enough for your device.
Understanding Great Power Battery Technology: The Benefits of Lithium Solutions
Great power batteries deliver high performance for EVs, solar, and more. Learn why lithium is the top choice for power, lifespan, and efficiency.
How to Choose the Right Kayak Battery?
Need power for your fish finder or motor? This guide makes choosing the right kayak battery easy with tips on types, specs, and performance.