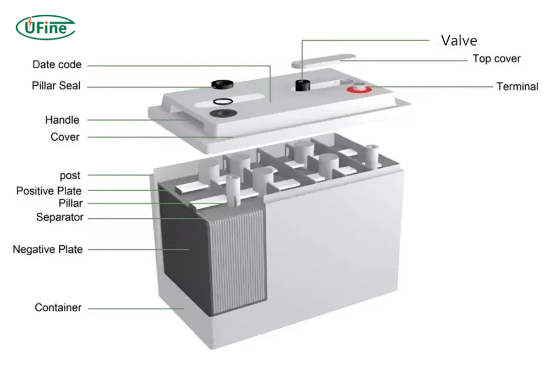
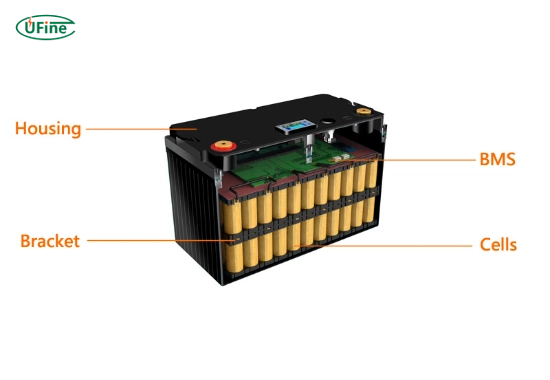
Batteries come in many shapes and sizes. They store and deliver energy for a variety of applications. In the simplest terms, a battery converts chemical energy into electrical energy. Based on their design and intended use, there are many types of batteries. Two of the most common types are deep-cycle batteries and regular batteries.
Batteries can vary in capacity, lifespan, and the rate at which they deliver power. Deep cycle batteries are built for endurance, able to provide a steady flow of power over a long period, and are repeatedly discharged and recharged. On the other hand, regular batteries are typically designed to deliver a high burst of power quickly. Still, they are not meant for deep, repeated discharges.
This article compares these two battery types, using the phrase deep cycle vs. regular battery to guide our discussion.
Part 1. What is a deep cycle battery?
A deep-cycle battery is designed to be discharged to a large portion of its capacity before recharging. It is made with thicker plates and denser active material, which allows it to handle long-term, deep discharges without suffering damage.
These batteries are widely used in applications where power is needed steadily over a long period. They are popular in solar energy systems, marine applications, recreational vehicles (RVs), and backup power systems. Because of their design, deep-cycle batteries are known for their reliability and long service life when properly maintained.
Key features of a deep cycle battery include:
- Robust construction: Designed for repeated deep discharges.
- Long cycle life: Can be charged and discharged many times.
- Steady power output: Provides consistent energy over extended periods.
Deep cycle batteries are ideal when you need a battery that can run for several hours continuously, even if that means using a significant portion of its capacity.
Part 2. What is a regular battery?
A regular battery, often called a starting or cranking battery, is designed to deliver a quick burst of high power. These batteries are typically found in cars, motorcycles, and other vehicles where a rapid energy surge is required to start the engine.
Unlike deep-cycle batteries, regular batteries are not built to sustain long-term deep discharges. Their construction focuses on delivering high current for a short duration. Once the engine is started, the alternator replaces the battery’s role and keeps it charged.
The key characteristics of a regular battery include:
- High burst power: Provides the surge of energy needed for ignition.
- Limited deep discharge ability: Not designed for extended energy draw.
- Maintenance focused on short-term use: Primarily used for starting rather than long-term power supply.
Regular batteries are engineered for quick, reliable performance. They are perfect for applications where immediate high power is needed. Still, they are less suited to applications that require long-term energy output.
Part 3. Key differences between deep cycle vs regular battery
Several significant differences emerge when comparing deep-cycle batteries to regular batteries. Understanding these differences can help you choose the correct battery for your needs.
- Design and Construction:
Deep cycle batteries have thicker plates and denser active material to support deep discharges.
Regular batteries have thinner plates optimized for high current delivery over short periods. - Discharge Characteristics:
Deep cycle batteries are built to discharge a significant portion of their capacity over a long period.
Regular batteries are not designed for deep discharge; they perform best when kept near full charge except during short bursts. - Cycle Life:
Deep cycle batteries offer a long cycle life, which means they can be discharged and recharged many times without significant degradation.
Regular batteries have a shorter cycle life when subjected to deep discharge, as they are designed to deliver a high burst of energy rather than continuous output. - Applications:
Deep cycle batteries are ideal for solar energy storage, marine use, and RV power systems.
Regular batteries are commonly used as starting batteries in vehicles and for other applications where high burst power is essential. - Maintenance and Care:
Deep cycle batteries require regular monitoring and maintenance to achieve their entire cycle life.
Regular batteries need less rigorous maintenance under normal usage conditions, as they are usually kept charged by the vehicle’s alternator.
By understanding these differences, you can better assess which battery type will meet your energy needs.
Part 4. Applications of deep cycle battery
Deep cycle batteries are valued for providing reliable power over long periods. This makes them the battery of choice in many renewable and off-grid energy systems.
- Renewable Energy Systems:
Deep cycle batteries are a crucial component of solar and wind energy systems. They store energy generated during the day to be used at night or during cloudy weather. Their ability to handle deep discharges makes them perfect for this role. - Marine and RV Applications:
Many boats and recreational vehicles rely on deep cycle batteries to power lights, appliances, and onboard electronics. These batteries provide a steady energy supply and can handle the frequent discharging and recharging that comes with extended use away from shore power. - Backup Power:
Deep-cycle batteries are often part of backup power systems in areas prone to power outages. They ensure that essential devices and appliances continue to run until power is restored. - Electric Mobility:
Electric wheelchairs, scooters, and other mobility devices benefit from the steady energy output of deep cycle batteries. Their long cycle life and reliability are essential for daily transportation users who depend on them.
Overall, the versatility and durability of deep cycle batteries make them an excellent choice for systems that require continuous power over extended periods.
Part 5. Applications of regular battery
Regular batteries are widely used when a quick burst of energy is needed. They are most commonly found in automotive applications, but their usage extends to other areas.
- Automotive Starting:
Regular batteries are most commonly used in cars, motorcycles, and trucks. They deliver the high burst of energy needed to start an engine. The alternator takes over once the engine is running, recharging the battery for the next start. - Emergency Systems:
Some emergency and backup systems use regular batteries to provide immediate power. They are not designed for long-term energy supply but can offer a quick start-up in critical moments. - Portable Devices:
Regular batteries are sometimes used in portable power tools and devices requiring sudden, high power output. They are preferred in these applications because they can deliver energy rapidly. - Small-Scale Electronics:
Many small electronic devices, including toys and gadgets, use regular batteries for short bursts of power. Their compact size and quick recharge capabilities make them ideal for these applications.
While regular batteries do not offer the prolonged energy output of deep cycle batteries, their ability to provide high current quickly makes them indispensable in many everyday applications.
Part 6. How do you choose between deep cycle vs regular battery?
Choosing between a deep cycle and a regular battery depends mainly on your specific energy needs and the application you have in mind. Here are some factors to consider:
- Usage Requirements:
Do I need long-term steady power or a quick burst of energy?
A deep cycle battery is the best choice if you need energy for several hours.
For short, high-energy demands, a regular battery is more suitable. - Cycle Life:
Consider how often you will discharge and recharge the battery.
Deep cycle batteries are designed for many deep discharges and recharges.
Regular batteries may have a shorter cycle life if used outside their intended short-burst applications. - Maintenance Needs:
Think about the level of maintenance you are comfortable with.
Deep cycle batteries often require regular monitoring and maintenance to maximize their lifespan.
Regular batteries generally need less intensive care when used in standard applications. - Cost Considerations:
The upfront cost and long-term value are essential.
Deep cycle batteries might be more expensive initially but offer a longer life in the correct application.
Regular batteries may cost less but require more frequent replacement if misused. - Environmental Conditions:
Consider where the battery will be used. Extreme temperatures and harsh conditions can affect battery performance.
Deep cycle batteries often have features that help them perform well in varying conditions.
Regular batteries are usually optimized for standard conditions and may underperform in extreme environments.
In summary, the choice between deep-cycle and regular batteries comes down to matching the battery’s strengths with your energy needs. For prolonged, steady power, choose a deep-cycle battery. For quick, high-energy bursts, a regular battery is the better option.
Part 7. Maintenance and care for each battery type
Proper maintenance can extend the life of both deep-cycle and regular batteries. Here are some simple tips to keep your battery performing at its best.
Maintenance for Deep Cycle Batteries:
- Regularly check the water levels: Ensure the electrolyte levels are maintained for flooded lead-acid deep cycle batteries.
- Keep the terminals clean: Dirt and corrosion can affect performance, so clean them periodically.
- Avoid deep discharging: Even though they are built for deep discharge, avoid going below the recommended threshold.
- Store in a cool, dry place: Extreme temperatures can reduce the battery’s lifespan.
Maintenance for Regular Batteries:
- Ensure a secure connection: Loose or corroded terminals can cause starting issues.
- Monitor the charge: Avoid letting the battery remain discharged for long periods.
- Use the correct charger: Overcharging or incorrect charger can damage the battery.
- Regular inspections: Check for any signs of wear or damage, especially in harsh weather conditions.
Simple and regular maintenance can help both battery types perform reliably over time. Following these care tips ensures your battery investment pays off with years of consistent performance.
Part 8. Cost and lifespan comparison of deep cycle vs regular battery
Several factors come into play when comparing deep-cycle batteries to regular batteries regarding cost and lifespan. It is essential to consider both the initial investment and the long-term value.
- Upfront Cost:
Deep cycle batteries are generally more expensive than regular batteries. This higher cost is due to their robust design and ability to handle deep discharges.
Regular batteries typically cost less upfront, as they are mass-produced for automotive and other standard applications. - Lifespan and Cycle Life:
Deep-cycle batteries are designed for a long cycle life. They can endure hundreds or even thousands of charge-discharge cycles if maintained correctly.
Regular batteries have a shorter cycle life when used outside their intended purpose. They are best suited for a limited number of deep discharges. - Cost-Effectiveness Over Time:
Even though deep cycle batteries might cost more initially, their longevity can make them more cost-effective in the long run. They reduce the need for frequent replacements.
Regular batteries may need to be replaced more often if used in applications that require deep discharges, which can increase overall costs over time. - Performance Under Load:
Deep cycle batteries provide a steady, reliable power output over a long period, which is crucial for applications like renewable energy systems.
Regular batteries excel at delivering high power quickly, but their performance can drop significantly when used for prolonged periods. - Environmental Impact:
The longer lifespan of deep cycle batteries means less frequent disposal and replacement, which can be better for the environment.
Regular batteries may generate more waste over time if not used for their intended purpose.
Carefully evaluating these factors can help you decide which battery offers the best value for your needs.
Part 9. FAQs about deep cycle vs regular battery
What is the best battery for solar power systems?
A deep-cycle battery is typically the best choice for solar power systems. These batteries are designed to be discharged profoundly and recharged repeatedly, making them ideal for storing solar energy. They also provide a steady power output over long periods.
Can I use a regular battery for deep cycle applications?
No, a regular battery is not ideal for deep-cycle applications. Regular batteries are meant for short bursts of power and do not handle deep discharges well. Using them in deep-cycle scenarios can reduce lifespan and lower performance.
How often should I maintain my deep cycle battery?
A deep-cycle battery should be maintained regularly. This includes checking water levels (for flooded types), cleaning terminals, and ensuring that the battery is not deeply discharged too often. A monthly inspection is a good practice, with more frequent checks during periods of heavy use.
Do deep cycle batteries cost more than regular batteries?
Yes, deep-cycle batteries generally have a higher upfront cost than regular batteries. However, their longer lifespan and better performance in continuous use often make them more cost-effective over time.
What factors affect the lifespan of a battery?
Several factors can affect a battery’s lifespan, including usage patterns, maintenance practices, environmental conditions, and how deeply the battery is discharged regularly. Proper care and adherence to usage guidelines are essential for maximizing longevity for deep-cycle and regular batteries.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.