In the rapidly evolving world of energy storage, lithium-ion batteries have become a cornerstone of modern technology. Among the various types of lithium-ion batteries, LCO (Lithium Cobalt Oxide) and LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) are two prominent contenders. Understanding the differences between these battery types is crucial for consumers and manufacturers alike, as it can significantly influence performance, safety, and cost. This article will explore the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of both LCO and LFP batteries, helping you make an informed choice based on your needs.
Part 1. What is an LCO battery?
LCO batteries are known for their high energy density. They are commonly used in portable electronics such as smartphones and laptops. They utilize cobalt oxide as the cathode material, which allows for a compact design and efficient power output. However, the reliance on cobalt raises concerns about sustainability and ethical sourcing, as cobalt mining directly contributes to environmental degradation and human rights issues.
Characteristics of LCO Batteries
- High Energy Density: LCO batteries can store more energy in a smaller space, making them ideal for devices where size and weight are critical.
- Voltage Stability: They maintain a stable voltage throughout their discharge cycle, providing consistent performance.
- Temperature Sensitivity: LCO batteries are sensitive to high temperatures, which can lead to thermal runaway. In this condition, the battery overheats and potentially catches fire.
Advantages of LCO Batteries
- Compact Size: Their high energy density allows for smaller and lighter battery designs, essential for portable devices.
- Performance: LCO batteries provide excellent power output and efficiency performance, making them suitable for high-demand applications.
- Voltage Stability: They maintain a consistent voltage throughout their discharge cycle, which is beneficial for electronic devices.
Disadvantages of LCO Batteries
- Safety Concerns: The risk of thermal runaway makes LCO batteries less safe, especially in high-temperature environments.
- Shorter Lifespan: LCO batteries typically have a shorter cycle life, requiring more frequent replacements.
- Environmental Impact: The reliance on cobalt raises ethical and environmental concerns related to mining practices.
Part 2. What is an LFP battery?
LFP battery utilize lithium iron phosphate as their cathode material. They are recognized for their safety and longevity, making them popular in applications like electric vehicles and renewable energy storage. While LFP batteries generally have a lower energy density than LCO batteries, their advantages in safety and lifespan make them a compelling choice for many applications.
Characteristics of LFP Batteries
- Safety: LFP batteries are less prone to thermal runaway and are considered safer than LCO batteries, especially in high-temperature environments.
- Long Cycle Life: They can endure more charge and discharge cycles, often lasting up to 10 years or more.
- Lower Energy Density: While safer, LFP batteries typically offer lower energy density, requiring more space for the same energy storage.
Advantages of LFP Batteries
- Safety: LFP batteries are inherently safer, with a lower risk of overheating and combustion.
- Longevity: They offer a longer lifespan, making them more cost-effective.
- Environmental Benefits: The materials used in LFP batteries are more abundant and less harmful to the environment compared to cobalt.
Disadvantages of LFP Batteries
- Lower Energy Density: LFP batteries require more space for the same energy output, which can be a limitation in compact applications.
- Cost: While LCO batteries are generally less expensive, the initial investment can still be significant for large-scale applications.
- Performance: They may deliver a different high performance than LCO batteries in specific applications, particularly those requiring rapid energy release.
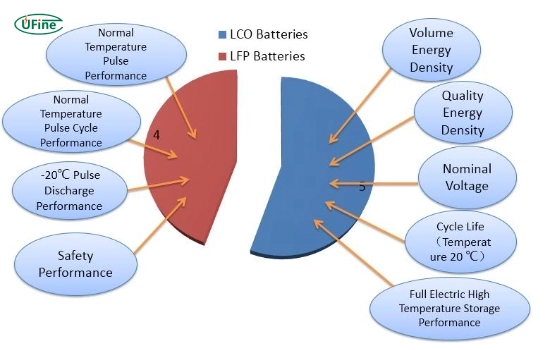
Part 3. Differences between LCO and LFP batteries
Consider several vital aspects when comparing LCO and LFP batteries:
- Energy Density: LCO batteries have a higher energy density, making them suitable for compact devices. In comparison, LFP batteries have a lower energy density.
- Safety: LFP batteries are generally safer, with a lower risk of thermal runaway than LCO batteries.
- Cycle Life: LFP batteries typically have a longer cycle life, lasting up to 10 years, whereas LCO batteries usually last 2-3 years.
- Cost: LCO batteries tend to be more expensive due to the high cost of cobalt. In contrast, LFP batteries are generally less costly.
- Temperature Sensitivity: LCO batteries are more sensitive to high temperatures, increasing the risk of overheating.
- Environmental Impact: Compared to cobalt used in LCO batteries, the materials used in LFP batteries are more sustainable and less environmentally harmful.
- Applications: Manufacturers primarily use LCO batteries in portable electronics, while they prefer LFP batteries for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage.
Comparison Table
| Feature | LCO Battery | LFP Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | High | Moderate |
| Safety | Moderate risk of thermal runaway | High safety |
| Cycle Life | Shorter (2-3 years) | Longer (up to 10 years) |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Generally less expensive |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Sensitive to high temperatures | More stable in high temperatures |
| Environmental Impact | Higher due to cobalt mining | Lower, more sustainable materials |
| Applications | Portable electronics | Electric vehicles, storage systems |
Part 4. Cost comparison between LCO and LFP
LCO batteries tend to be more expensive due to the high cost of cobalt. However, LFP batteries, while generally cheaper, can still represent a significant investment, especially in large-scale applications. Consider the total cost of ownership, including lifespan and maintenance costs.
Part 5. FAQs
-
What is the lifespan of an LCO battery?
Depending on usage and environmental conditions, LCO batteries typically have a 2-3 year lifespan. -
How do LFP batteries compare in safety?
LFP batteries are generally considered safer due to their thermal stability and lower risk of thermal runaway. -
Can LCO batteries be recycled?
Yes, LCO batteries can be recycled, but the process can be complex due to the cobalt content. -
What are the energy densities of LCO vs LFP batteries?
LCO batteries usually have a higher energy density than LFP batteries, making them suitable for compact devices. -
Which battery type is best for electric vehicles?
Manufacturers prefer LFP batteries for electric vehicles due to their longevity and safety features.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.