- What is the difference between a lithium-sulfur battery and a lithium-ion battery?
- Part 1. What are lithium-sulfur batteries?
- Part 2. What are lithium-ion batteries?
- Part 3. Core differences between lithium-metal and lithium-ion batteries
- Part 4. Advantages and limitations of lithium sulfur and lithium ion batteries
- Part 5. Challenges and Future Outlook of lithium sulfur and lithium ion batteries
- Part 6. Scenario-based recommendations lithium sulfur and lithium ion batteries
- Part 7. FAQs about lithium sulfur and lithium ion batteries
What is the difference between a lithium-sulfur battery and a lithium-ion battery?
Lithium-sulfur batteries deliver higher energy density (400–500 Wh/kg) and use low-cost sulfur, while lithium-ion batteries offer longer cycle life, stable power output, and mature safety systems. Li-S suits weight-critical devices; Li-ion suits EVs and consumer electronics.
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries deliver 5X higher energy density than lithium-ion (Li-ion) but face shorter lifespans. This definitive guide compares lithium-sulfur and lithium-ion batteries across 5 key factors: energy density, cost, cycle life, safety, and environmental impact. Discover which battery technology wins for your application.
Part 1. What are lithium-sulfur batteries?
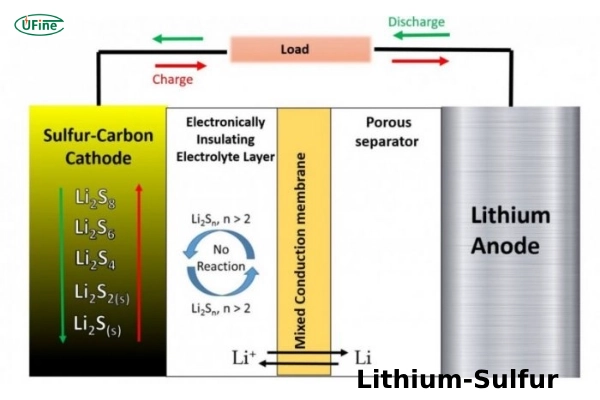
Lithium-sulfur batteries are rechargeable batteries that use lithium metal as the anode and sulfur as the cathode. They are best known for their exceptionally high energy density and the use of low-cost, abundant sulfur, which also reduces environmental impact compared with cobalt-based batteries.
How Do Lithium-Sulfur Batteries Work?
Lithium-sulfur batteries operate through a redox reaction between lithium and sulfur. During discharge, lithium ions travel from the lithium-metal anode to the sulfur cathode, forming lithium sulfide. During charging, the reaction reverses. The process involves intermediate lithium polysulfides, which directly impact Li-S battery lifespan and stability.
What are the Advantages of Lithium-Sulfur Batteries?
- Higher Energy Density: Li-S batteries can reach 400–500 Wh/kg, about five times the energy density of standard Li-ion cells.
- Lower Material Cost: Sulfur is abundant, low-cost, and non-toxic, reducing overall battery production cost.
- Environmental Advantages: Li-S batteries avoid heavy metals like cobalt, reducing ethical and ecological concerns.
What are the Disadvantages of Lithium-Sulfur Batteries?
- Shorter Lifespan: Li-S batteries typically last 300–500 cycles due to polysulfide shuttle effects causing capacity fade.
- Poor Conductivity: Sulfur and lithium sulfide have low conductivity, requiring carbon additives that reduce practical energy density.
- Volume Expansion: Up to 80% volume change during cycling can cause mechanical stress and early degradation.
Current Breakthroughs in Lithium-Sulfur Technology
Recent Nature Energy 2023 research shows that graphene-coated sulfur cathodes can extend cycle life to 800+ cycles. Companies such as Oxis Energy and Sion Power continue developing Li-S cells for aerospace and high-altitude platforms where weight dominates lifespan requirements.
Quick Facts: Lithium-Sulfur Battery (Li-S)
- Best for: drones, aerospace, high-altitude systems
- Energy density: 400–500 Wh/kg
- Cycle life: 300–500 cycles (800+ in lab prototypes)
- Key advantages: high energy density, low-cost sulfur, eco-friendly materials
- Key limitations: polysulfide shuttle, volume expansion, shorter lifespan
Part 2. What are lithium-ion batteries?
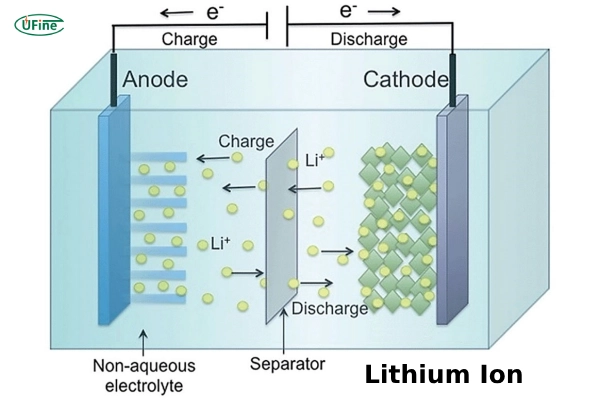
Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable batteries that store and release energy by moving lithium ions between a graphite anode and a metal-oxide cathode. As the most commercially mature technology, Li-ion powers smartphones, laptops, power tools, and nearly all modern electric vehicles.
How Do Lithium-ion Batteries Work?
Lithium-ion batteries function through ion shuttle between two electrodes: a graphite anode and a metal-oxide cathode (commonly nickel, manganese, or cobalt-based). During discharge, lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode through a non-aqueous electrolyte, producing electrical energy. Charging reverses the reaction. Modern Li-ion uses BMS systems to maintain thermal stability and extend lifespan.
What are the Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries?
- Longer Lifespan: Typical Li-ion cells provide 1000–3000 cycles, outperforming lithium-sulfur and many other chemistries.
- High Efficiency: Coulombic efficiency exceeds 99%, meaning minimal charging losses.
- Stable Voltage Output: Li-ion delivers flat voltage curves, ideal for electronics and EV applications requiring consistent power delivery.
What are the Disadvantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries?
- Higher Cost: The use of cobalt and nickel raises material cost compared with sulfur-based Li-S batteries.
- Safety Risks: Organic electrolytes are flammable and may cause thermal runaway if cells are damaged or mismanaged.
- Environmental Impact: Mining and refining cobalt, nickel, and lithium have significant environmental footprints.
For further chemistry comparisons, see our guide: Li-ion vs Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries.
Quick Facts: Lithium-Ion Battery (Li-ion)
- Best for: EVs, laptops, smartphones, power tools
- Energy density: 150–250 Wh/kg
- Cycle life: 1000–3000 cycles
- Main advantages: long lifespan, high efficiency, stable output, commercial maturity
- Main disadvantages: higher cost, cobalt mining impact, overheating/thermal runaway risks
Part 3. Core differences between lithium-metal and lithium-ion batteries
Lithium-metal and lithium-ion batteries differ fundamentally in their anode materials, safety behavior, cycle life, and commercial readiness. Lithium-metal cells use a pure lithium metal anode, which delivers exceptionally high theoretical energy density but introduces dendrite formation risks. In contrast, lithium-ion batteries use intercalation-based graphite or silicon–graphite anodes, enabling stable cycling, mature manufacturing, and widespread deployment across consumer and industrial applications.
From an engineering perspective, lithium-metal batteries pursue extreme gravimetric energy density and next-generation performance, whereas lithium-ion batteries prioritize safety, durability, and reliable mass production. These differences shape suitability across EVs, wearables, aviation, and specialty devices.
Lithium-Metal vs. Lithium-ion: What Is the Main Difference?
The main difference is that lithium-metal batteries use a pure lithium metal anode for higher energy density, while lithium-ion batteries use graphite/Silicon–graphite anodes for safer, longer-lasting, and more commercially mature performance.
- Energy density: Lithium-metal is significantly higher.
- Safety: Lithium-ion is more stable, lower dendrite risk.
- Cycle life: Lithium-ion lasts much longer.
- Commercial maturity: Lithium-ion is mass-produced and widely available.
Lithium-Metal vs Lithium-ion Battery Comparison Table
| Parameter | Lithium-Metal Battery | Lithium-ion Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Anode Material | Pure lithium metal | Graphite / Silicon–graphite |
| Energy Density (Gravimetric) | 400–500+ Wh/kg (potential up to 700 Wh/kg) | 180–285 Wh/kg |
| Energy Density (Volumetric) | ~900–1,200 Wh/L | ~500–750 Wh/L |
| Cycle Life | 150–300 cycles (current prototypes) | 500–3,000+ cycles depending on chemistry |
| Safety Profile | Higher dendrite risk; requires advanced electrolytes/separators | Stable, lower dendrite risk, mature BMS ecosystem |
| Charging Speed | Currently slower due to dendrite constraints | Wide range; some chemistries support fast charging |
| Operating Temperature Range | Moderate; sensitive to high temperatures | Broad; varies by chemistry but generally robust |
| Commercial Availability | Prototype and pre-commercial stage | Fully commercial, global supply chain |
| Typical Applications | Next-gen EVs, aerospace, UAVs, defense | Consumer electronics, EVs, energy storage, power tools |
Quick Comparison Summary
Lithium-metal batteries deliver far greater energy density but lack the safety stability and cycling durability required for mainstream adoption. Lithium-ion batteries remain the industry standard due to predictable performance, long cycle life, and advanced manufacturing maturity. For high-specific-energy missions, lithium-metal is a developing frontier, while lithium-ion continues to dominate commercial applications.
Part 4. Advantages and limitations of lithium sulfur and lithium ion batteries
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of lithium-metal and lithium-ion batteries helps users, engineers, and product designers determine the best fit for specific applications. The following sections outline the performance trade-offs across energy density, safety, cycle longevity, cost, and manufacturability.
Lithium-Metal Battery Advantages
- Exceptional Energy Density: Pure lithium metal anodes enable significantly higher gravimetric and volumetric energy density, making them suitable for weight-critical applications.
- High Specific Power Potential: With advanced electrolytes or solid-state designs, lithium-metal cells can deliver higher peak discharge capabilities.
- Long-Term Path to Solid-State Integration: Lithium-metal chemistry aligns with next-generation solid-state technologies, supporting ultra-safe and compact architectures.
- Extended Range for EVs and Aviation: Higher energy density directly translates to longer driving range or extended flight duration for electric aircraft and UAVs.
Lithium-Metal Battery Limitations
- Dendrite Formation Risk: Lithium-metal anodes are prone to dendritic growth, which can cause internal short circuits and thermal events.
- Lower Cycle Life: Compared with lithium-ion, current lithium-metal prototypes exhibit significantly shorter cycle life due to unstable lithium plating/stripping.
- Manufacturing Complexity: Requires strict moisture control, advanced electrolytes, and specialized production equipment.
- Higher Cost at Present: Limited scale and specialized materials contribute to higher cost per kWh.
- Not Yet Commercialized: Most lithium-metal designs remain in pilot or early validation stages.
Lithium-ion Battery Advantages
- High Safety and Stability: Mature intercalation anodes minimize dendrite growth and reduce short-circuit risks.
- Long Cycle and Calendar Life: Chemistries such as NMC, NCA, and especially LFP deliver excellent long-term durability.
- Fast Charging Capability: Advanced graphite and silicon–graphite systems support rapid charging while maintaining stability.
- Global Supply Chain Maturity: Standardized cell formats, BMS compatibility, and well-established production ecosystems reduce cost and variability.
- Cost-Effective: Economies of scale allow lithium-ion batteries to achieve the lowest cost per kWh among lithium-based chemistries.
Lithium-ion Battery Limitations
- Lower Energy Density Compared with Lithium-Metal: Graphite-based anodes limit maximum theoretical energy density.
- Thermal Runaway Risk Under Abuse: Although safer than lithium-metal, Li-ion cells still require robust BMS and thermal design.
- Cathode Material Cost Fluctuations: Cobalt, nickel, and lithium price volatility affects certain chemistries.
- Degradation at High Temperatures: Elevated conditions accelerate SEI growth and capacity fade.
- Limited High-Altitude Performance: Some Li-ion chemistries require pressure compensation for aviation use.
Advantages & Limitations Summary
Lithium-metal batteries offer exceptional energy density but remain restricted by safety, cycle life, and manufacturing challenges. Lithium-ion batteries continue to dominate the market due to their stability, long service life, and proven industrial scalability. The choice depends on required energy density, safety demands, budget, and the stage of product development.
Part 5. Challenges and Future Outlook of lithium sulfur and lithium ion batteries
Challenges Facing Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
- Polysulfide Shuttle: Dissolution of lithium polysulfides into the electrolyte causes rapid capacity fade.
- Volume Expansion: Sulfur cathodes expand up to 80% during discharge, which stresses the cell structure.
- Electrical Conductivity: Sulfur and lithium sulfide have low conductivity, necessitating carbon or conductive additives.
- Limited Commercial Production: Li-S batteries are mostly in pilot or aerospace-focused applications.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Performance drops at low temperatures, challenging EV integration.
Challenges Facing Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Resource Dependence: Cobalt and nickel mining has environmental and ethical concerns.
- Thermal Runaway: Overcharge or mechanical damage can cause fire if BMS and cooling fail.
- Energy Density Limitation: Li-ion energy density peaks at ~250 Wh/kg for commercial cells.
- Calendar Aging: Even without cycling, Li-ion cells degrade over years.
Future Outlook
- Lithium-Sulfur: Mass adoption expected 2027–2030. Solid-state electrolytes and graphene cathodes may overcome lifespan and conductivity limits.
- Lithium-Ion: Continuous incremental improvements in anode/cathode chemistry, solid electrolytes, and battery management systems will increase energy density and safety.
- Hybrid Solutions: Some next-gen EVs and drones explore Li-S/Li-ion hybrid packs for weight and longevity optimization.
Part 6. Scenario-based recommendations lithium sulfur and lithium ion batteries
- High-Altitude Drones & Aerospace: Li-S batteries provide 30% longer flight time, short cycle life acceptable.
- Electric Vehicles: Li-ion batteries ensure 1500+ cycles and reliable daily usage.
- Environmentally Sensitive Projects: Li-S batteries preferred for low toxicity and sustainable material use.
- Consumer Electronics & Laptops: Li-ion batteries dominate due to long life and stable voltage delivery.
Part 7. FAQs about lithium sulfur and lithium ion batteries
How long do lithium-sulfur batteries last?
Current lithium-sulfur batteries last 300-500 cycles, about half of lithium-ion batteries’ 1000+ cycles. Advanced lab prototypes with graphene-coated cathodes achieved 800 cycles.
What are the main advantages of lithium-sulfur batteries?
Li-S batteries provide higher energy density (400–500 Wh/kg), lower material cost due to abundant sulfur, and enhanced safety with non-flammable cathodes.
Are lithium-sulfur batteries commercially available?
Companies like Oxis Energy and Sion Power are developing Li-S cells for aerospace and specialized EV applications. Mass-market adoption is projected by 2027–2030.
Why don’t electric vehicles use lithium-sulfur batteries yet?
EVs require long cycle life and stable power under daily charging. Li-S batteries currently face polysulfide dissolution and temperature sensitivity, limiting their daily-use practicality.
Can lithium-sulfur batteries replace lithium-ion?
Li-S batteries can replace Li-ion in weight-critical applications such as drones and satellites. For consumer electronics and long-life EVs, lithium-ion remains the preferred choice. Hybrid pack solutions are emerging to combine advantages.
Related Tags:
More Articles
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.
Aluminium Ion Battery vs Lithium-Ion: A Detailed Comparison
Compare aluminium ion battery vs lithium-ion battery in energy density, charging speed, safety, cost, and uses. A practical guide for engineers and buyers.