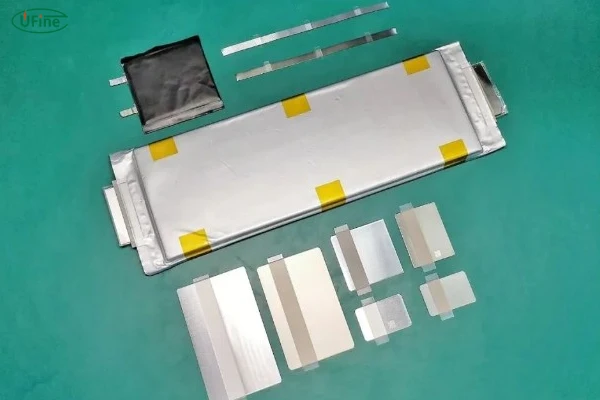
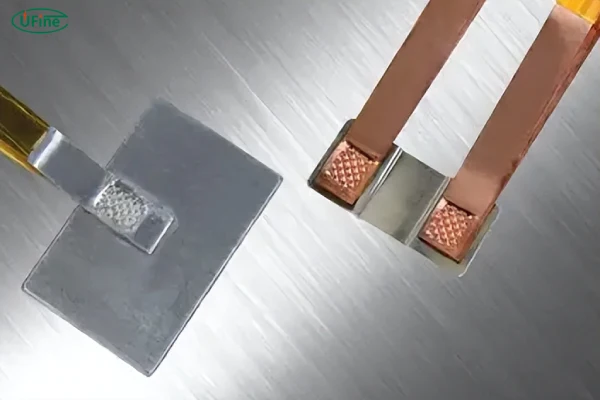
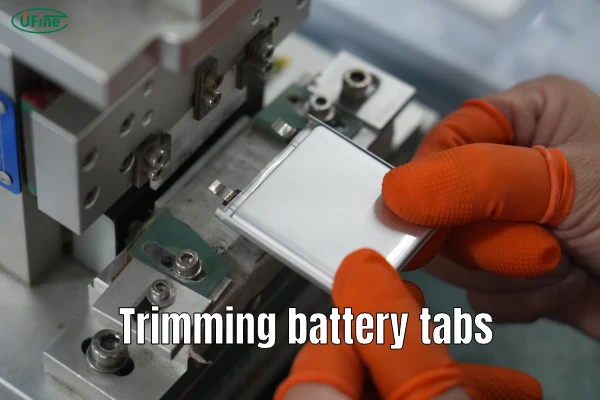
Batteries power our modern world, from smartphones to electric vehicles. Yet, one small component often goes unnoticed—the battery tab. While tiny in size, this piece is a powerhouse when it comes to energy transfer and efficiency. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of battery tabs, uncovering their importance, materials, types, and even how the revolutionary tabless cell technology is reshaping the industry.
Part 1. What is a battery tab?
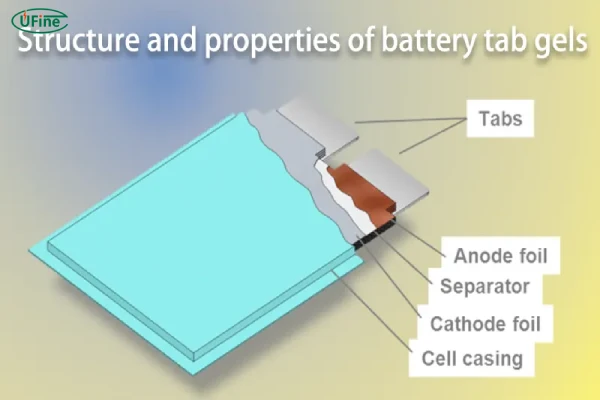
To understand battery tabs, let’s start with the basics. A battery tab is a thin, conductive strip that connects the internal components of a battery to its external circuits. Think of it as a bridge that ensures electrical energy flows smoothly from the electrodes inside the battery to the device it powers.
Structure and Principle
Battery tabs typically come in two main types:
- Positive tabs: Made of materials like aluminum, they connect to the positive electrode (cathode).
- Negative tabs: Often made of copper, they connect to the negative electrode (anode).
The principle is straightforward. The tab acts as a conduit, transferring electrons generated during the chemical reaction within the battery to the external circuit. Without it, there’s no way for electricity to travel from the battery to power your device.
But don’t let its simplicity fool you. The design and material of a battery tab play a pivotal role in determining the battery’s overall performance.
Part 2. What is the function of a battery tab?
Now that we know what a battery tab is, let’s explore its functions.
-
Electrical Conduction
Battery tabs are the highway for electrical energy. They allow the current to flow between the electrodes and the external device, ensuring a stable energy supply. -
Heat Dissipation
During operation, batteries generate heat. A well-designed tab helps distribute and dissipate this heat, preventing overheating and ensuring the battery operates safely. -
Structural Support
Battery tabs also provide mechanical stability, keeping internal components securely connected. This stability is crucial for batteries used in high-vibration environments, such as electric vehicles.
Without battery tabs, the functionality and safety of batteries would be severely compromised.
Part 3. Does every battery have a tab?
The short answer is no. While traditional batteries like lithium-ion, lead-acid, and nickel-metal hydride rely on tabs, newer technologies are challenging this norm.
Tabless Batteries
In tabless designs, the traditional tab is replaced with a more integrated structure. For example, Tesla’s 4680 cells use a tabless approach where the entire electrode extends into the connection. This design reduces resistance and improves efficiency.
While not every battery has a traditional tab, most still rely on a conductive pathway, whether it’s a tab or an integrated structure.
Part 4. Tabless cell technology
The future of batteries is shifting towards tabless designs, which eliminate traditional tabs. This innovation has been popularized by companies like Tesla, especially with their 4680 cell.
Characteristics of Tabless Cells
- Lower resistance: Direct pathways reduce resistance.
- Better heat management: Uniform heat distribution.
- Improved energy density: More space for active materials.
Advantages
- Higher efficiency and longer lifespan.
- Better suited for fast charging.
Disadvantages
- More complex to manufacture.
- Higher initial costs.
Despite these challenges, tabless technology is gaining traction, especially in EVs and advanced storage systems.
Part 5. How do battery tabs affect battery performance?
The quality and design of battery tabs significantly impact the overall performance of a battery. Here’s how:
Electrical Efficiency
High-quality materials like copper and aluminum ensure excellent conductivity. Poor-quality tabs can increase electrical resistance, leading to energy loss and reduced performance.
Heat Management
Efficient tabs distribute heat evenly. Improperly designed tabs can cause hot spots, leading to thermal issues and reduced battery lifespan.
Durability
The welding process is critical. A poorly welded tab might disconnect under stress or vibrations, leading to battery failure. Precision and quality control during manufacturing are essential.
Energy Density
Well-designed tabs minimize space while maximizing efficiency, contributing to higher energy density in modern batteries.
In short, even the smallest flaws in tab design or manufacturing can have a ripple effect on battery performance.
Part 6. Types of battery tabs
Battery tabs come in various types, each suited for specific applications.
By Material
-
Aluminum Tabs
- Lightweight
- High conductivity
- Commonly used for the positive terminal
-
Copper Tabs
- Superior electrical conductivity
- Often used for the negative terminal
-
Nickel-Coated Tabs
- Corrosion-resistant
- Durable and suitable for harsh environments
By Design
- Flat Tabs: Simple and cost-effective, widely used in consumer electronics.
- Perforated Tabs: Allow better heat dissipation, used in high-performance batteries.
Choosing the right type depends on the battery’s application and required performance.
Part 7. What is the battery tab material?
The material of a battery tab can make or break its efficiency. Let’s dive deeper into the options:
-
Aluminum
- Lightweight and affordable.
- Ideal for applications where weight matters, like electric vehicles.
-
Copper
- Excellent conductivity and thermal performance.
- More expensive but necessary for high-performance batteries.
-
Nickel-Coated Materials
- Resistant to oxidation and corrosion.
- Often used in extreme environments.
Each material has pros and cons, and manufacturers often use a combination to optimize performance and cost.
Part 8. High-quality battery tabs: Key processes
At Ufine Battery, we understand that the smallest components often have the biggest impact. Here’s how we ensure top-notch battery tabs:
-
Material Selection
- We use only premium materials like high-purity copper and aluminum for optimal performance.
-
Precision Manufacturing
- Advanced cutting and welding techniques ensure consistent quality.
-
Rigorous Testing
- Every tab undergoes strict testing to meet safety and performance standards.
Our expertise allows us to deliver reliable, high-performance battery tabs for industries ranging from consumer electronics to electric vehicles.
Part 9. Conclusion
Battery tabs may be small, but they’re the backbone of modern batteries. From ensuring electrical conduction to supporting innovations like tabless technology, these components are vital to performance, safety, and efficiency.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Aluminum Air Battery Design: Materials, Assembly & Efficiency Tips
An aluminum air battery uses aluminum and air to generate power. Learn its materials, assembly steps, and tips to boost energy output and efficiency.
7 Advantages of a Heated Lithium Battery in Cold Climates
Looking to power batteries in freezing temps? Heated lithium batteries excel in cold climates. Here are 7 key benefits and how they work.
How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.