U.S. tariffs on Chinese lithium batteries have become a critical factor shaping the global battery market in 2025. These tariffs directly impact lithium-ion batteries’ cost, supply chain, and competitiveness, essential for electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy storage, and consumer electronics. This article comprehensively analyses U.S. tariffs on Chinese lithium batteries, exploring the latest tariff rates, their economic effects, and future implications for industries and consumers.
Part 1. What are U.S. tariffs on Chinese lithium batteries in 2025?
In April 2025, the U.S. government updated its tariff policy on lithium-ion batteries imported from China. The current tariff structure includes:
- A 3.4% global tariff on lithium-ion batteries, regardless of origin.
- A Section 301 tariff targeting Chinese imports, currently at 7.5%, is scheduled to rise to 25% by January 2026.
- Additional tariffs imposed under recent trade actions push the total tariff on Chinese lithium batteries to approximately 82% by 2026.
These tariffs are part of a broader strategy to reduce U.S. dependence on Chinese battery imports and encourage domestic production.
Part 2. Why are lithium batteries necessary in U.S.-China trade?
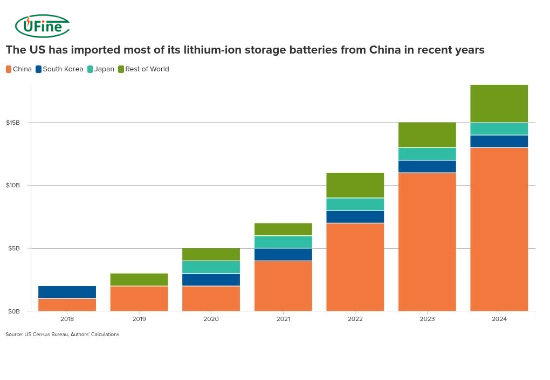
Lithium-ion batteries power various technologies, from smartphones to electric vehicles and grid storage. China dominates the global lithium battery supply chain, producing over 75% of the world’s lithium-ion battery cells. The U.S. imports nearly 70% of its lithium batteries from China, making tariffs on these products highly impactful.
The U.S. aims to build a resilient domestic battery industry to support its clean energy goals. Still, the current supply chain relies heavily on Chinese raw materials, components, and finished products.
Part 3. How do tariffs affect the U.S. battery market?
Tariffs increase the cost of imported batteries, which can:
- Raise prices for U.S. manufacturers who rely on Chinese batteries or components.
- Slow down the adoption of electric vehicles due to higher battery costs.
- Increase costs for renewable energy storage systems, affecting grid modernization efforts.
U.S. battery manufacturers face challenges despite tariffs because many components and raw materials still come from China or other countries with complex supply chains.
Part 4. What is the economic impact of tariffs on electric vehicles?
Electric vehicles depend heavily on lithium-ion batteries, which account for about 30-40% of an EV’s total cost. Tariffs that increase battery prices by up to 82% could add thousands of dollars to the cost of an EV. This price increase may slow consumer adoption, delaying the transition to cleaner transportation.
For example, if a battery pack costs $10,000, an 82% tariff could add $8,200 in costs, which manufacturers might pass on to consumers.
Part 5. How do tariffs influence renewable energy storage?
Energy storage systems, essential for integrating solar and wind power, rely on lithium-ion batteries. Tariffs increase the cost of these systems, potentially slowing renewable energy deployment.
The U.S. aims to install 30 GW of energy storage capacity by 2030, but higher battery costs could make this goal harder to achieve.
Part 6. What are the global trade shifts caused by these tariffs?
Many manufacturers are relocating battery production to Southeast Asia to avoid high tariffs, including Vietnam, Thailand, and Indonesia. These countries have become alternative hubs for battery assembly and component manufacturing.
However, the U.S. has also extended tariffs to some Southeast Asian countries to prevent tariff circumvention, complicating global supply chains further.
Part 7. What challenges do U.S. battery manufacturers face?
U.S. manufacturers struggle with:
- Raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel are often imported and subject to tariffs.
- High production costs compared to Chinese manufacturers benefiting from economies of scale.
- Supply chain complexity, as many components still come from China or countries affected by tariffs.
These challenges slow the growth of an entirely domestic battery supply chain.
Part 8. How is the U.S. government supporting domestic battery production?
The U.S. government has launched initiatives such as the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), which provides tax credits and subsidies for domestic battery manufacturing and critical mineral processing.
These policies aim to:
- Encourage investment in U.S. battery plants.
- Support research into alternative battery technologies.
- Reduce reliance on Chinese imports over the next decade.
Part 9. What are the potential alternatives to lithium-ion batteries?
Rising tariffs and supply chain risks have accelerated interest in alternative battery technologies, including:
- Lithium-sulfur batteries promise higher energy density and lower costs.
- Solid-state batteries offer improved safety and longevity.
- Sodium-ion batteries, which use more abundant materials.
These alternatives could reduce dependence on traditional lithium-ion batteries sourced from China.
Part 10. FAQs about U.S. tariffs on Chinese lithium batteries
What is the total tariff rate on Chinese lithium batteries in 2025?
The total tariff rate is approximately 82%, combining global tariffs, Section 301 tariffs, and additional trade measures.
How do tariffs affect the price of electric vehicles?
A: Tariffs can increase battery costs by up to 82%, potentially adding thousands of dollars to EV prices and slowing adoption.
Are there efforts to build U.S. battery manufacturing capacity?
Government incentives like the Inflation Reduction Act support domestic battery production and critical mineral processing.
Can manufacturers avoid tariffs by moving production outside China?
Some have shifted production to Southeast Asia, but the U.S. has extended tariffs to some countries to prevent circumvention.
What alternatives exist to lithium-ion batteries?
Emerging technologies like lithium-sulfur, solid-state, and sodium-ion batteries offer potential alternatives with different cost and performance profiles.
Data and sources
| Metric | Value | Source |
|---|---|---|
| China’s share of global lithium-ion battery production | 75% | Benchmark Mineral Intelligence |
| U.S. reliance on Chinese lithium battery imports | 70% | U.S. International Trade Commission |
| Tariff rate on Chinese lithium batteries (2025) | 82% | U.S. Trade Representative Office |
| Battery cost as % of EV price | 30-40% | BloombergNEF |
| U.S. energy storage target by 2030 | 30 GW | U.S. Department of Energy |
Note: Data sources are publicly available reports from Benchmark Mineral Intelligence, U.S. government agencies, and industry analysts.
Related Tags:
More Articles

What You Need to Know About AA 3.6V Lithium Battery
Learn all about AA 3.6V lithium batteries—voltage, size, capacity, uses, and the best replacements. Discover why they’re powerful, and highly reliable.
What Are Lithium Salts and Why They Matter in Battery Electrolytes
Lithium salts in electrolytes are key to battery performance, powering everything from phones to EVs and shaping the future of clean energy.
Lithium AAA Battery Guide: Power, Performance & Chargers
Explore lithium AAA batteries—voltage, capacity, weight, top brands, and more. Learn how to choose the best battery for your device and why it really matters.
How to Calculate Watts, Volts, and Amps (With Simple Formulas and Examples)
Learn how to calculate watts, volts, and amps for lithium batteries with simple formulas and examples, ideal for EVs, solar, and energy systems.
What Are Lithium Button Batteries?
Learn about lithium button batteries (CR2032, CR2025), their uses, safety tips, and how to replace them properly.