In the quest for better energy storage solutions, flow, and lithium-ion batteries have emerged as two of the most promising technologies. Each type has its own unique set of characteristics, advantages, and limitations. This article will delve into the differences between these two battery technologies, helping you understand which might be best suited for various applications.
Part 1. Battery technologies
Energy storage is a critical component of modern technology, impacting everything from consumer electronics to renewable energy integration. Understanding the nuances of different battery technologies can inform decisions regarding their use in various applications.
Part 2. What are flow batteries?
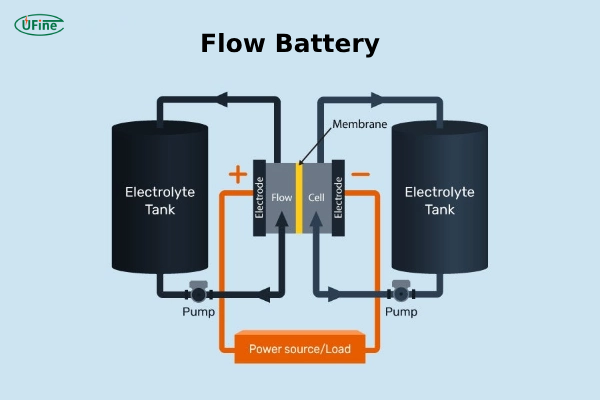
Redox flow batteries store energy in liquid electrolyte solutions that flow through an electrochemical cell. The most common types are vanadium redox flow batteries and zinc-bromine flow batteries.
How Flow Batteries Work?
Flow batteries operate by circulating liquid electrolytes through a cell stack, where electrochemical reactions occur to store or release energy. Store the electrolytes in external tanks and adjust their flow rate to scale the power output.
Advantages of Flow Batteries
- Scalability: Power and energy capacity can be scaled independently by adjusting the cell stack’s size and the electrolyte tanks’ volume.
- Long Lifespan: They can endure many charge/discharge cycles without significant degradation.
- Safety: The risk of thermal runaway is minimal compared to lithium-ion batteries.
Part 3. What are lithium-ion batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries are the most prevalent rechargeable batteries in use today. They exist in everything from smartphones to electric vehicles and grid storage systems.
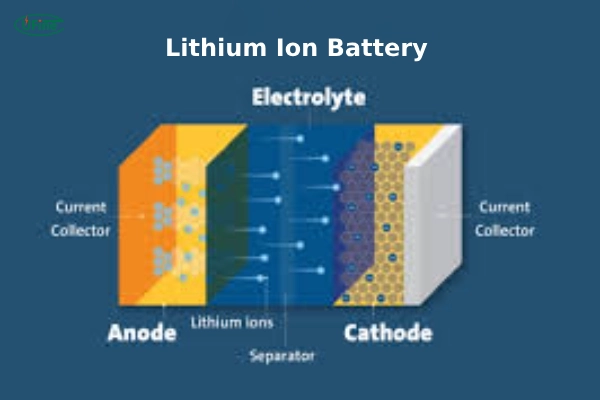
How Lithium-Ion Batteries Work?
Lithium-ion batteries consist of an anode, a cathode, and an electrolyte that facilitates the movement of lithium ions between the electrodes during charging and discharging.
Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries
- High Energy Density: They store much energy compactly, making them ideal for portable electronics.
- Efficiency: They have high charge/discharge efficiency, reducing energy loss.
- Mature Technology: Extensive research and development have made them reliable and relatively cost-effective.
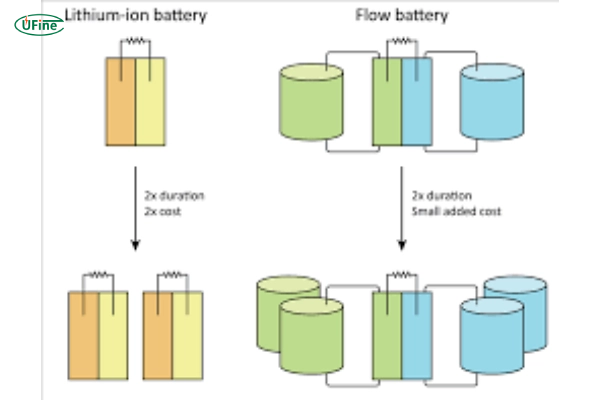
Part 4. Flow batteries vs. lithium-ion batteries
1. Energy Density and Efficiency
Flow Batteries
Flow batteries typically have lower energy density compared to lithium-ion batteries. This makes them less suitable for applications where space is a critical factor. However, their efficiency can be relatively high, typically from 70% to 85%.
Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries boast a high energy density, often exceeding 200 Wh/kg, so many favor them for applications like electric vehicles and portable devices. Their efficiency generally falls between 85% and 95%.
2. Lifespan and Durability
Flow Batteries
Flow batteries are known for their long lifespan, often exceeding 20 years with minimal degradation. They can handle over 10,000 cycles, making them highly durable and cost-effective over the long term.
Lithium-ion Batteries
While lithium-ion batteries have a shorter lifespan, typically 5 to 10 years, technological advances are continually improving their durability. They usually endure 500 to 1,500 charge cycles before a significant capacity loss occurs.
3. Safety Concerns
Flow Batteries
Flow batteries are generally considered safer than lithium-ion batteries. The risk of thermal runaway is low, and they are less prone to catching fire or exploding.
Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries ‘ safety is a significant concern due to their susceptibility to thermal runaway, which can lead to fires or explosions. However, modern safety features and battery management systems have mitigated many risks.
4. Cost Considerations
Flow Batteries
The initial cost of flow batteries can be higher due to the need for large tanks and complex systems to manage the flow of electrolytes. However, their long lifespan and low maintenance costs can make them more cost-effective in the long run.
Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries have become more affordable due to mass production and technological advancements. However, their shorter lifespan and potential recycling costs can offset their lower initial price.
5. Environmental Impact
Flow Batteries
Flow batteries use materials like vanadium and bromine, which can be recycled and reused, reducing their environmental impact. Additionally, their long lifespan means fewer replacements and less waste.
Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries rely on materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which have significant environmental and ethical implications due to mining practices. Recycling lithium-ion batteries is possible but challenging, and the ecological impact of mining and disposal remains a concern.
6. Applications
Flow Batteries
Flow batteries are particularly well-suited for large-scale energy storage applications, including:
- Grid Storage: Their ability to scale quickly makes them ideal for stabilizing power grids and integrating renewable energy sources.
- Backup Power Systems: They provide reliable backup power for critical infrastructure, such as hospitals and data centers.
- Industrial Use: Because of their long lifespan and durability, flow batteries are useful in industrial settings where consistent and reliable power is essential.
Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are versatile and used in a wide range of applications, such as:
- Consumer Electronics: Their high energy density makes them perfect for smartphones, laptops, and other portable devices.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): They are the preferred choice for EVs due to their efficiency and compact size.
- Residential Energy Storage: Home battery systems like the Tesla Powerwall utilize lithium-ion technology to store energy from solar panels.
7. Future Prospects
Flow Batteries
Experts expect flow batteries to play a crucial role in the future of renewable energy storage. Advances in technology may lead to reductions in cost and increases in energy density, making them more competitive with other types of batteries.
Lithium-ion Batteries
The future of lithium-ion batteries looks promising, with ongoing research focused on improving energy density, safety, and longevity. Innovations like solid-state batteries could address many current limitations, further solidifying their dominance in the market.
8. Maintenance and Management
Flow Batteries
Flow batteries require regular maintenance to ensure the proper functioning of pumps, tanks, and other components. However, their relatively simple design makes maintenance straightforward.
Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries require less maintenance than flow batteries but need careful management to prevent issues related to overheating and capacity degradation. Battery management systems (BMS) are crucial for monitoring and optimizing performance.
9. Performance in Extreme Conditions
Flow Batteries
Flow batteries perform well in a range of environmental conditions. Their ability to operate efficiently at various temperatures makes them suitable for diverse geographic locations.
Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries can be sensitive to extreme temperatures. High temperatures can accelerate degradation, while low temperatures can reduce their efficiency. Advances in thermal management systems are helping mitigate these issues.
Part 8. FAQs
-
What are the main problems with iron flow batteries?
Iron flow batteries face several challenges. One main problem is their size. They are large and bulky, making them hard to use in small spaces. Another issue is cost. They can be expensive to build and maintain. Efficiency is also a concern. They are not as efficient as some other types of batteries, meaning they lose more energy during use. -
What are the downsides of flow batteries?
Flow batteries have a few downsides. First, they take up a lot of space. They need big tanks to store the liquid electrolytes. Second, they can be costly. Building and maintaining them is expensive. Third, they have lower energy density. This means they store less energy per unit of volume compared to other batteries, like lithium-ion. -
What is the lifespan of a flow battery?
The lifespan of a flow battery is quite long. Typically, lithium-ion batteries can last between 10 to 20 years. This is because they have a unique design that reduces wear and tear. Replacing the electrolytes helps extend their life. Proper maintenance is critical to ensuring they last a long time. -
What battery will replace lithium-ion?
Several types of batteries could replace lithium-ion in the future. Solid-state batteries are one option. They use a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid one, which makes them safer and more efficient. Sodium-ion batteries are another option. They are cheaper to produce and use more abundant materials. Iron and other flow batteries could also play a role, especially for large-scale energy storage.
Related Tags:
More Articles

What are Watts and Watt Hours in Battery?
Understand watt vs watt-hour in batteries, how to calculate battery watt hours, and what Wh means for car batteries, devices, and energy storage.
A Complete Guide to the Best Batteries for Flashlights
Compare the best batteries for flashlights, including AA, AAA, 18650, 21700, CR123A. See which battery offers the best brightness, runtime, and reliability.
How Long Do Rechargeable AA Batteries Last?
How long do rechargeable AA batteries last? Compare NiMH and lithium AA lifespan, recharge cycles, key factors, and performance vs alkaline batteries.
How Much Current Can a 9V Battery Really Supply?
Discover how many amps a 9V battery can supply, its actual current output, discharge rate, and capacity for alkaline, lithium, and rechargeable 9V batteries.
12V STD vs 12V AGM: Meaning, Differences, and Which Is Better
Understand what STD and AGM batteries mean, their key differences, and which 12V battery fits your needs best in 2026.