- Key Takeaways
- Part 1. Why weight actually matters
- Part 2. Inside a car battery: why they’re heavy
- Part 3. Types of car batteries and how much they weigh
- Part 4. Vehicle type vs battery weight(quick reference)
- Part 5. Why this matters: performance & efficiency
- Part 6. How to calculate car battery weight and choose the right one
- Part 7. FAQs
Key Takeaways
If you’re in a hurry, here’s the gist: a standard lead-acid car battery weighs 30–50 lbs (13.6–22.7 kg), a lithium-ion 12V battery is much lighter at 10–20 lbs (4.5–9.1 kg), and heavy-duty SUV or truck batteries can hit 80 lbs (36 kg). Full EV battery packs? They’re monsters, weighing 900–1,500 lbs (408–680 kg) depending on the car and range.
Part 1. Why weight actually matters
You might think, “It’s just a battery, right?” Not quite. Battery weight affects almost everything about your ride:
- Performance: A heavier battery slows down acceleration and can make handling feel a bit sluggish.
- Fuel or Energy Efficiency: More pounds = more work for your engine or motor. For EVs, this can mean a shorter range.
- Safety: Battery weight changes the vehicle’s center of gravity. A properly mounted heavy battery can improve stability, but it also needs strong crash protection.
- Durability: Extra weight stresses suspension components and chassis over time.
- Installation: Knowing the exact weight keeps you (and your back) safe when swapping batteries.
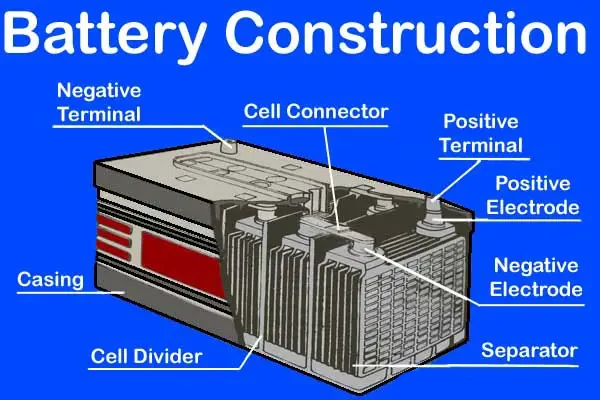
Part 2. Inside a car battery: why they’re heavy
Let’s break down what actually makes a battery heavy.
- Lead Plates: Dense, energy-storing metal. Lead is heavy, but it’s what gives lead-acid batteries their power.
- Electrolyte Solution: Usually a mix of sulfuric acid and water. Adds volume and weight.
- Casing: Plastic or metal shell protects everything. It’s not super heavy, but it counts.
- Connectors & Terminals: Small metal parts, minor weight contribution, but essential.
Part 3. Types of car batteries and how much they weigh
Not all car batteries are created equal—some are heavy, some are feather-light, and each comes with its own pros and cons. Let’s break it down.
1 Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are the classic choice for most traditional cars. They usually weigh 30–50 lbs (13.6–22.7 kg). That extra heft comes from lead plates and sulfuric acid inside.
Why choose them? They’re reliable, affordable, and can handle high power demands.
The downside: their weight can slightly impact acceleration, handling, and fuel efficiency.
So if you’re aiming for a lighter, more nimble ride, lead-acid batteries aren’t the lightest option—but they sure get the job done.
2 Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are the modern lightweight champs, averaging 10–20 lbs (4.5–9.1 kg). That’s often less than half the weight of a standard lead-acid battery.
Why are they so light?
- They use advanced lithium compounds instead of heavy lead.
- Their design focuses on maximizing energy storage while minimizing bulk.
Benefits: lighter weight improves fuel efficiency, makes your car handle better, and they tend to last longer than standard lead-acid batteries.
| Battery Type | Weight Range |
|---|---|
| AGM | 44–66 lbs (20–30 kg) |
| Lead-Acid | 55–88 lbs (25–40 kg) |
If you’ve been wondering “how much do car batteries weigh?”, lithium-ion batteries are the clear winner for lightness.
3 AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) Batteries
AGM batteries are a modern twist on lead-acid technology. They’re a bit heavier than standard lead-acid batteries, usually 44–66 lbs (20–30 kg), thanks to their improved construction.
Why go AGM?
They offer better vibration resistance, longer lifespan, and more consistent performance. They sit right in the middle—heavier than lithium but lighter than some traditional lead-acid batteries.
| Battery Type | Weight Range |
|---|---|
| AGM | 44–66 lbs (20–30 kg) |
| Lead-Acid | 55–88 lbs (25–40 kg) |
AGM batteries are a solid choice if you want a balance between weight and durability.
4 Electric Vehicle (EV) Batteries
EV batteries are in a league of their own—they are massive.
Depending on the model, they can weigh anywhere from 550 to 2,000 lbs (250–900 kg).
That’s because they need to store enough energy to cover long distances.
Here’s a snapshot of some popular EVs:
| EV Model | Battery Capacity (kWh) | Approximate Battery Weight | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tesla Model 3 (82 kWh) | ~82 kWh | ~1,060 lbs (480 kg) | ~250–358 miles |
| Hyundai Ioniq 5 (77.4 kWh) | ~77.4 kWh | ~816–1,052 lbs (370–477 kg) | ~220–300 miles |
| Ford Mustang Mach‑E (91 kWh) | ~91 kWh | ~1,050 lbs (476 kg) | ~250–300 miles |
| Nissan Leaf (40–62 kWh) | ~40–62 kWh | ~668–903 lbs (303–410 kg) | ~150–226 miles |
EV batteries aren’t light by any means, but all that weight is necessary to store energy for long-range driving. In this case, heft equals performance and reliability.
Note: These battery weight ranges may vary depending on the specific vehicle model configuration, battery cell chemistry, and packaging design, but they generally reflect the battery weight levels of mainstream EVs in the real market.
If you’re curious about how AGM, lithium, and lead-acid batteries compare in performance, lifespan, and weight, check out our AGM VS Lithium VS Lead-Acid Battery: Comprehensive Comparison guide for a deeper dive.
Part 4. Vehicle type vs battery weight(quick reference)
Another quick reference:
| Vehicle Type | Typical Battery Weight | Chemistry Usually Used |
|---|---|---|
| Small cars | 25–35 lbs (11–16 kg) | Lead-acid, AGM |
| SUVs | 40–60 lbs (18–27 kg) | Lead-acid, AGM |
| Trucks | 50–80 lbs (23–36 kg) | Heavy-duty lead-acid |
| Electric Vehicles | 900–1,500 lbs (408–680 kg) | Lithium-ion pack |
Part 5. Why this matters: performance & efficiency
Think of it like this: a heavier battery might store more energy, but your car has to lug it around.
That’s extra work for your engine or motor. Lighter lithium-ion batteries are more efficient—they make acceleration snappier, improve handling, and in EVs, give you a longer range.
- Acceleration & Handling: Heavier batteries slow down 0–60 mph times and make cornering feel less responsive. Even a 10–20 lb difference can be noticeable in small or performance cars.
- Efficiency & Range: Extra weight increases energy consumption. In gas cars, MPG drops slightly; in EVs, range decreases. Lighter lithium-ion batteries offer similar or higher energy storage at a fraction of the weight.
- Safety & Dynamics: Heavier batteries influence the vehicle’s center of gravity. Heavier batteries can increase the damage caused during collisions. Properly placed EV packs improve stability, but mass increases braking distance and stresses suspension components.
It’s all a balancing act engineers have to juggle when designing a car.
Part 6. How to calculate car battery weight and choose the right one
1 Steps to Determine Battery Weight
- Step 1- Check the Battery Label: Most batteries list weight directly.
- Step 2-Use BCI Group Number: Batteries in the same group typically fall within a predictable weight range.
- Step 3-Consult Manufacturer Specs: OEM and aftermarket datasheets usually include weight and capacity.
- Step 4-Weigh It Yourself: Use a scale for exact measurement. Wear gloves and handle lead-acid batteries carefully.
- Step 5-Estimate by Chemistry & Capacity: Higher Ah or denser chemistry usually means more weight.
2 Tips for Selecting the Right Battery Weight
- Follow OEM Recommendations: Match group size, voltage, and CCA for reliable starting.
- Balance Weight & Performance: Lighter lithium batteries improve acceleration and handling without compromising power.
- Consider Efficiency: Lighter batteries reduce energy consumption over time.
- Match Driving Style & Climate: Aggressive driving or extreme temperatures may require slightly heavier, more robust batteries.
Key Takeaway: Battery selection isn’t about the lightest option—it’s about the right balance of weight, capacity, and chemistry for your vehicle’s performance, efficiency, and safety.
Part 7. FAQs
1. Does battery weight influence tire wear?
Indirectly. More weight increases overall vehicle mass, which can accelerate tire wear, especially on front-drive cars where the battery is front-mounted.
2. Are heavier batteries better for cold starts?
Not necessarily. Cold cranking ability matters more than weight. Some lightweight lithium batteries provide excellent cold-weather starting, despite being lighter than lead-acid.
3. Can I safely install a battery that’s slightly heavier than OEM specs?
Usually yes, but check mounting points and secure fasteners. Extra weight may require minor adjustments to brackets or support structures.
4. How do hybrid batteries compare in weight to standard and EV batteries?
Hybrid batteries are heavier than a standard 12V lead-acid but much lighter than full EV packs. This balance allows hybrids to support electric assist without overly affecting fuel economy.
5. Can battery weight affect towing capacity?
Yes. Heavier batteries reduce the available payload and towing capacity slightly. EVs and trucks often compensate with reinforced frames and suspension.
6. Are lightweight lithium batteries more eco-friendly?
Generally yes. Lighter batteries reduce energy consumption over the vehicle’s life and often use more recyclable materials, making them a greener option compared with traditional lead-acid batteries.
Related Tags:
More Articles
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.
Aluminium Ion Battery vs Lithium-Ion: A Detailed Comparison
Compare aluminium ion battery vs lithium-ion battery in energy density, charging speed, safety, cost, and uses. A practical guide for engineers and buyers.