- Part 1. What are solid-state batteries?
- Part 2. How do solid-state batteries differ from lithium-ion batteries?
- Part 3. Do solid-state batteries use lithium?
- Part 4. Why is lithium important for solid-state batteries?
- Part 5. Are there solid-state batteries without lithium?
- Part 6. Advantages of lithium-based solid-state batteries
- Part 7. Challenges facing solid-state batteries
- Part 8. Applications of solid-state batteries
- Part 9. Are solid-state batteries the future of energy storage?
- Part 10. FAQs
Solid-state batteries have emerged as one of the most promising advancements in energy storage technology. Experts often tout them as the future of batteries, with their potential to revolutionize industries such as electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy, and portable electronics. However, a common question arises: Do solid-state batteries use lithium?
In this article, we’ll explore the composition of solid-state batteries, how they differ from traditional batteries, and whether lithium remains an essential component. By the end of this guide, you’ll clearly understand the role lithium plays in this cutting-edge technology.
Part 1. What are solid-state batteries?
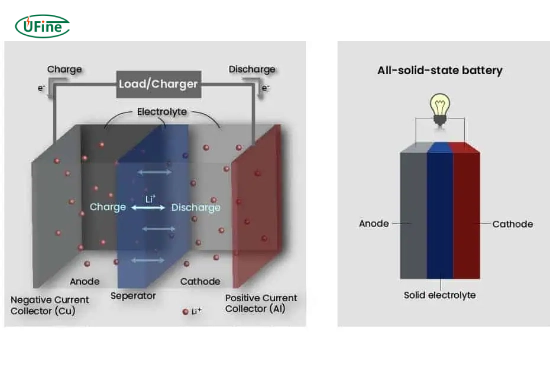
Solid-state batteries are a type of rechargeable battery that replaces the liquid or gel electrolyte found in traditional lithium-ion batteries with a solid electrolyte. This key difference makes them safer, more energy-dense, and longer-lasting than conventional battery technologies.
The solid electrolyte in these batteries can be made from various materials, such as ceramics, glass, or specific polymers. This innovation eliminates the flammable nature of liquid electrolytes, reducing the risk of thermal runaway and fires.
Part 2. How do solid-state batteries differ from lithium-ion batteries?
Solid-state and lithium-ion batteries may seem similar because both can use lithium as a key component. However, the differences lie in their internal structure and performance.
- Electrolyte material: Lithium-ion batteries use a liquid electrolyte, while solid-state batteries use a solid one.
- Energy density: Solid-state batteries generally have a higher energy density, meaning they can store more energy in a smaller space.
- Safety: Solid electrolytes in solid-state batteries are non-flammable, making them significantly safer.
- Durability: Solid-state batteries are less prone to degradation, offering longer lifespans.
Solid State Battery vs Lithium Ion: A Comparative Analysis
Part 3. Do solid-state batteries use lithium?
Yes, most solid-state batteries use lithium as a core component. Lithium remains a critical material because of its excellent electrochemical properties, high energy density, and lightweight structure. However, the exact role of lithium can vary depending on the battery’s design.
Lithium is used as lithium metal anodes or lithium-based compounds in many solid-state batteries. These components allow efficient energy transfer and storage, which is essential for high-performance applications like electric vehicles.
That said, researchers are also exploring alternatives to lithium for solid-state batteries. These include materials like sodium, magnesium, and aluminum, which offer similar performance at a lower cost or greater abundance.
Part 4. Why is lithium important for solid-state batteries?
Lithium plays a crucial role in solid-state batteries for several reasons:
- High energy density: Lithium is one of the lightest metals, offering unmatched energy density compared to other materials.
- Fast ion conductivity: Lithium ions move quickly through electrolytes, enabling rapid charging and discharging cycles.
- Compatibility with solid electrolytes: Lithium works well with many solid-state electrolyte materials, making it a natural fit for this technology.
While researchers study alternatives, lithium’s unique properties make it the material of choice for most current solid-state battery designs.
Part 5. Are there solid-state batteries without lithium?
There are non-lithium solid-state batteries, though they are less common and still under development. Researchers are exploring alternatives like:
- Sodium-ion solid-state batteries: Sodium is more abundant and cheaper than lithium, but its energy density is lower.
- Magnesium solid-state batteries: Magnesium offers higher energy density and safety, but its ion conductivity is more challenging to optimize.
- Aluminum solid-state batteries: Aluminum is abundant and stable but faces similar conductivity challenges as magnesium.
These alternatives could become viable, especially if lithium resources become scarce or too expensive.
Part 6. Advantages of lithium-based solid-state batteries
Lithium-based solid-state batteries offer several benefits over traditional lithium-ion batteries:
- Increased safety: The solid electrolyte reduces the risk of leaks, fires, and explosions.
- Higher energy density: They can store more energy in less space, making them ideal for EVs and portable devices.
- Longer lifespan: These batteries degrade more slowly, allowing for more charge cycles.
- Faster charging: Lithium-based solid-state batteries can support rapid charging without overheating.
These advantages make them highly attractive for industries looking to improve performance and safety.
Part 7. Challenges facing solid-state batteries
Despite their potential, solid-state batteries face several challenges:
- Cost: Solid-state batteries’ materials and manufacturing processes are more expensive than lithium-ion batteries.
- Scalability: Producing solid-state batteries at a large scale remains a technical challenge.
- Material limitations: While lithium is effective, its scarcity and price volatility could hinder widespread adoption.
- Compatibility issues: Finding solid electrolytes compatible with lithium metal anodes is an ongoing area of research.
Overcoming these challenges is crucial for solid-state batteries to become mainstream.
Part 8. Applications of solid-state batteries
Solid-state batteries have a wide range of potential applications:
- Electric vehicles (EVs): Higher energy density and faster charging make them ideal for EVs.
- Consumer electronics: Devices like smartphones and laptops could benefit from longer battery life and improved safety.
- Renewable energy storage: Solid-state batteries can store energy from solar and wind power more efficiently.
- Medical devices: Their safety and reliability suit critical applications like pacemakers.
Solid-state batteries will play a more significant role as technology improves in these industries.
Part 9. Are solid-state batteries the future of energy storage?
Many experts believe that solid-state batteries represent the future of energy storage. Their superior performance, safety, and longevity make them an attractive option for replacing traditional lithium-ion batteries. However, widespread adoption will depend on overcoming cost and manufacturing challenges.
Research is progressing rapidly, and many major companies are investing heavily in solid-state battery development. This suggests that these batteries will become commercially viable soon.
Part 10. FAQs
-
Do solid-state batteries still use lithium?
Most solid-state batteries still use lithium due to its exceptional electrochemical properties. However, researchers are exploring alternatives like sodium and magnesium. -
Are solid-state batteries safer than lithium-ion batteries?
Solid-state batteries are safer because they use a non-flammable solid electrolyte, reducing the risk of fires and thermal runaway. -
When will solid-state batteries become widely available?
Solid-state batteries are still in the development phase. Still, many experts predict they will become commercially available within the next decade. -
Can solid-state batteries improve EV performance?
Absolutely. Solid-state batteries offer higher energy density and faster charging, making them ideal for electric vehicles. -
Are there any downsides to solid-state batteries?
The main downsides are their high cost and the technical challenges of scaling up production. However, these issues are likely to be resolved over time.
Related Tags:
More Articles

What are Watts and Watt Hours in Battery?
Understand watt vs watt-hour in batteries, how to calculate battery watt hours, and what Wh means for car batteries, devices, and energy storage.
A Complete Guide to the Best Batteries for Flashlights
Compare the best batteries for flashlights, including AA, AAA, 18650, 21700, CR123A. See which battery offers the best brightness, runtime, and reliability.
How Long Do Rechargeable AA Batteries Last?
How long do rechargeable AA batteries last? Compare NiMH and lithium AA lifespan, recharge cycles, key factors, and performance vs alkaline batteries.
How Much Current Can a 9V Battery Really Supply?
Discover how many amps a 9V battery can supply, its actual current output, discharge rate, and capacity for alkaline, lithium, and rechargeable 9V batteries.
12V STD vs 12V AGM: Meaning, Differences, and Which Is Better
Understand what STD and AGM batteries mean, their key differences, and which 12V battery fits your needs best in 2026.