Battery certification plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and performance of battery products across various industries. In this guide, we’ll break down the essential certifications you need to know, including the types of certifications, the costs involved, expected timeframes, and the standards that govern them. Whether you’re a manufacturer or a consumer, this guide will help you navigate the certification process with ease.
Part 1. What is battery certification?
Battery certification involves testing and verifying batteries to meet specific safety, performance, and environmental standards. These certifications ensure that batteries are safe and comply with regulatory requirements. They help manufacturers demonstrate that their products are reliable and secure for consumers, enhancing marketability and consumer trust.
Why is Battery Certification Important?
- Safety Assurance: Certification helps to ensure that batteries do not pose safety risks, such as overheating or exploding.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many regions have legal requirements for battery certification, particularly lithium-ion batteries.
- Market Access: Certain certifications are required to sell batteries in specific markets, especially in the European Union and North America.
- Consumer Confidence: Certifications assure consumers of the product’s quality and safety.
Part 2. Types of battery certifications
Batteries may require several key certifications depending on their chemistry, intended use, and market. Here are some of the most common types:
UL Certification
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) is a global safety certification organization that tests and certifies batteries for safety and performance. Essential UL standards include:
- UL 1642: Tests lithium cells for safety.
- UL 2054: Covers battery packs for portable applications.
- UL 1973: Pertains to stationary batteries used in energy storage systems.
IEC Certification
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) develops international standards for electrical and electronic devices, including batteries. Necessary IEC standards include:
- IEC 62133: Safety requirements for portable sealed secondary cells.
- IEC 62619: Safety requirements for lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles.
CE Marking
The CE Mark indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA). This marking is essential for batteries sold in Europe.
UN38.3 Certification
This certification applies specifically to lithium batteries, which are needed for transportation. It ensures that shippers can safely transport the batteries without risking public safety.
ISO Certifications
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides several standards that can apply to battery manufacturers, including:
- ISO 9001: Quality management systems.
- ISO 14001: Environmental management systems.
KC Certification
The KC mark is a certification required in South Korea. It ensures that products meet safety and quality standards, which is crucial for battery market access in South Korea.
CB Scheme
The CB Scheme facilitates international trade by providing a single certification recognized in multiple countries. It covers battery safety standards, making it easier for manufacturers to access global markets.
PSE Certification
In Japan, the PSE (Product Safety Electrical Appliance & Material) certification is mandatory for electrical products, including batteries. This certification ensures that products meet safety standards set by the Japanese government.
RoHS Compliance
The Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive restricts the use of specific hazardous materials in electrical and electronic products. Compliance with RoHS is essential for manufacturers aiming to sell batteries in the European Union.
MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
While not a certification, the MSDS provides essential safety information about the materials used in batteries. Manufacturers must provide this documentation to ensure their products’ safe handling and use.
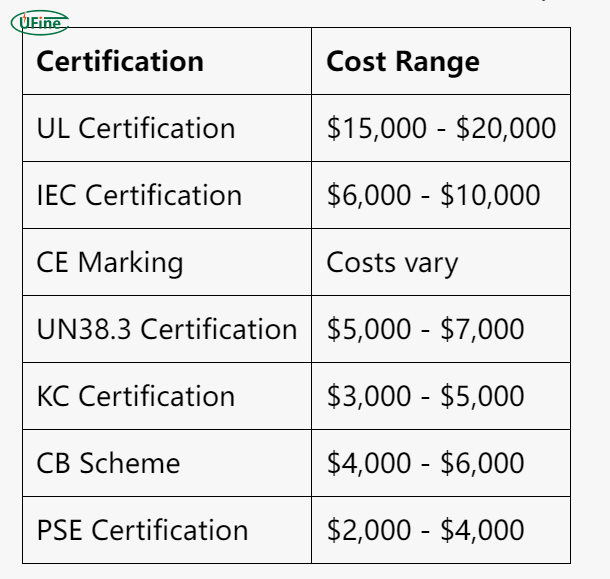
Part 3. Costs associated with battery certification
The costs of obtaining battery certifications can vary widely based on several factors, including the type of battery, the complexity of the tests, and the certification body. Here’s a general overview of costs associated with standard certifications:
- UL Certification: $15,000 – $20,000
- IEC Certification: $6,000 – $10,000
- CE Marking: Costs vary; often involves self-declaration but may require testing.
- UN38.3 certification: $5,000 – $7,000
- KC Certification: $3,000 – $5,000
- CB Scheme: $4,000 – $6,000
- PSE Certification: $2,000 – $4,000
These costs can fluctuate based on the specific requirements of the battery design and the testing agency’s fees.
Part 4. Timeframes for battery certification
The time it takes to obtain battery certification can also vary significantly. Here’s an estimated timeframe for some standard certifications:
- UL Certification: 10 – 12 weeks
- IEC Certification: 6 – 8 weeks
- CE Marking: Varies; can be quicker if self-declared.
- UN38.3 Certification: 4 – 6 weeks
- KC Certification: 4 – 8 weeks
- CB Scheme: 6 – 10 weeks
- PSE Certification: 4 – 6 weeks
These timeframes depend on the battery design’s complexity and the testing agency’s efficiency.
Part 5. Understanding battery standards
Battery standards are essential guidelines that ensure safety and performance. Various organizations develop them, and they are crucial for manufacturers to understand. Here are some key standards:
Safety Standards
- UL 1642: Focuses on the safety of lithium batteries, ensuring they do not pose a risk of fire or explosion.
- IEC 62133: Provides safety requirements for portable batteries, addressing risks associated with misuse.
Performance Standards
- UL 2054: Evaluates the performance of battery packs in real-world applications.
- IEC 61960: Covers performance specifications for lithium batteries in consumer electronics.
Environmental Standards
- ISO 14001 Ensures manufacturers minimize their environmental impact throughout the battery’s lifecycle.
Part 6. The certification process
The certification process typically involves several key steps:
- Preliminary Assessment: Manufacturers assess which certifications are necessary for their products based on market requirements.
- Testing: Batteries undergo rigorous testing by certified laboratories to ensure compliance with relevant standards.
- Documentation: Manufacturers must compile detailed documentation demonstrating safety and performance standards compliance.
- Certification Issuance: Upon successful testing and documentation review, the certification body issues the necessary certifications.
- Ongoing Compliance: Manufacturers must maintain compliance and may undergo periodic audits to ensure continued adherence to standards.
Part 7. Challenges in battery certification
Obtaining battery certification can be fraught with challenges, including:
- Complex Regulations: Navigating the various regulations across different markets can be daunting.
- Cost Implications: The high costs associated with testing and certification can be a barrier for smaller manufacturers.
- Time Delays: Lengthy testing and approval processes can delay product launches.
Part 8. FAQs
-
What is the purpose of battery certification?
Battery certification ensures that batteries meet safety, performance, and environmental standards, assuring consumers and regulatory bodies. -
How long does it take to get a battery certified?
The timeframe for battery certification can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the type of certification and the complexity of the tests. -
What are the costs associated with battery certification?
Costs can vary widely, with UL certification ranging from $15,000 to $20,000, while UN38.3 certification may cost between $5,000 and $7,000. -
What are the critical certifications for lithium-ion batteries?
Key certifications include UL, IEC, CE Marking, UN38.3, KC, CB, PSE, and RoHS, each addressing different aspects of safety and compliance. -
Why is ISO certification important for battery manufacturers?
ISO certification helps manufacturers establish quality management and environmental systems, ensuring consistent product quality and compliance with regulations. -
How does battery certification vary by region?
Battery certification requirements vary by region. In Europe, for example, CE marking is mandatory, while UL certification is critical for the US market. Each region has its own set of regulations and standards for battery safety and performance. -
What are the specific requirements for lithium-ion batteries in Europe?
In Europe, lithium-ion batteries must meet CE Marking requirements for safety, health, and environmental standards. Additional certifications like IEC 62133 or UN38.3 may be needed for transport and use. -
What to consider when choosing a certification body?
When selecting a certification body, consider its reputation, recognized standards, and the cost and time involved. Ensure it’s accepted in your target markets for certification validity.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Paper Battery vs. Flexible Battery: What’s the Difference and Which Is Better?
Paper vs. flexible batteries: learn the key differences, benefits, and which power source fits best for wearables, sensors, and smart tech.
What to Know Before Buying a Tiny LiPo Battery for Your Project
Tiny LiPo batteries are powerful and compact. Learn how to choose the right one for your project with specs, safety, and charging tips.
Bloated LiPo Battery: Will It Explode?
Will a bloated LiPo battery explode? Discover the causes, risks, safety steps, and expert tips to avoid disaster and protect your gear. Must-read safety guide!
12V 100Ah Lithium Ion Battery Price: Full Guide
Learn about 12V 100Ah lithium-ion battery price, from cost ranges to best brands, hidden fees, and how to get the best deal. A must-read for smart buyers!
Resistance and Conductivity: What It Means for Your Lithium Batteries
Resistance and conductivity impact lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety—learn how they work and why they matter.