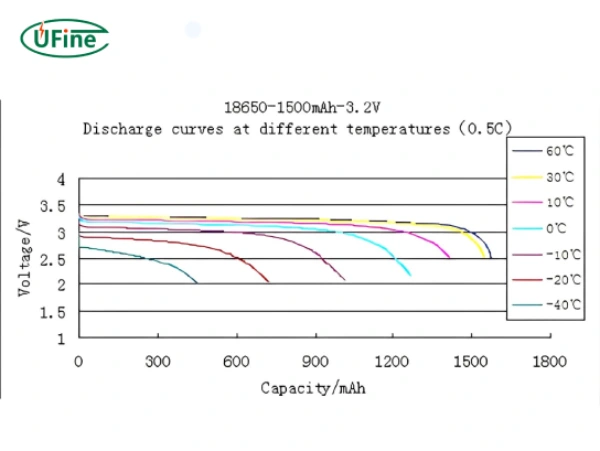
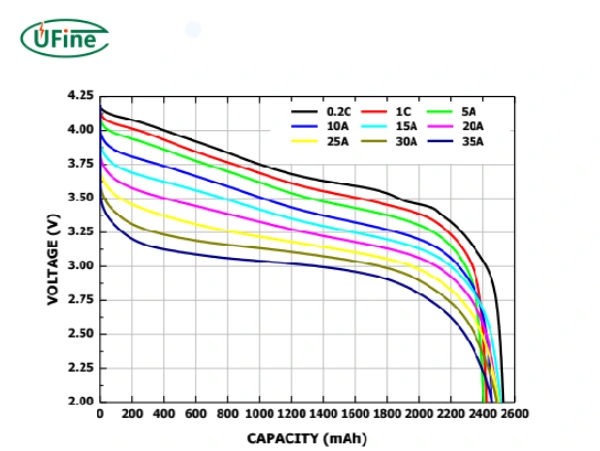
18650 battery voltage is one of the important parameters of the 18650 battery. Mastering the basic knowledge of 18650 battery voltage is important for correctly charging, discharging, and protecting the 18650 battery.
Part 1. 18650 battery voltage analysis
The voltage of 18650 batteries is generally above 3.6 V or 3.7V. This is much higher than the 1.2V voltage of nickel-cadmium and nickel-metal hydride batteries.
The voltage of a single 18650 cell is as follows:
1. 18650 battery nominal voltage
The core of the 18650 battery voltage is the working voltage, also called the nominal voltage, which is 3.7V. Some battery manufacturers have designed 18650 battery voltages to be 3.6V.
2. 18650 battery charging limit voltage
This is the maximum limit for the 18650 battery voltage, which is 4.2V. The 18650 battery charging process increases the 18650 battery voltage from 3.7V during operation to 4.2V. The process ends, indicating that the battery is fully charged. 18650 battery voltage exceeds 4.2V, which means it is overcharged. Overcharging can cause damage to 18650 batteries.
3. 18650 battery discharge termination voltage
This is the lowest working voltage at which the 18650 battery voltage drops to the point where it is no longer suitable to continue discharging, which is 2.75V. If the 18650 battery is discharged below the cut-off voltage, it is over-discharged.
Part 2. The 18650 battery voltage of different materials
18650 batteries can be divided into four types: lithium cobalt oxide, lithium manganate, ternary, and lithium iron phosphate due to different positive electrode materials. Except for LiFePo4 batteries, the remaining three materials can replace each other.
Therefore, the voltages of the lithium cobalt oxide 18650 battery and LiFePo4 18650 battery are introduced here.
Lithium cobalt oxide 18650 battery voltage
- Nominal voltage: 3.7V;
- Charging limit voltage: 4.20V;
- Minimum discharge termination voltage: 2.75V;
- Diameter: 18±0.2mm;
- Height: 65±2.0mm;
- Capacity: above 1000mAh
LiFePo4 18650 battery voltage
- The nominal voltage of a single cell: 3.2V;
- Charging limit voltage: 3.6V;
- Minimum discharge termination voltage: 2V;
- Diameter: 18±0.2mm;
- Height: 65±2.0mm;
- Capacity: smaller than the capacity of lithium cobalt oxide 18650 battery, the common capacity is 1500 mah.
Part 3. 18650 voltage chart
| State of Charge (%) | Voltage (V) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 2.5 |
| 10 | 3.0 |
| 20 | 3.2 |
| 30 | 3.4 |
| 40 | 3.5 |
| 50 | 3.6 |
| 60 | 3.7 |
| 70 | 3.8 |
| 80 | 3.9 |
| 90 | 4.0 |
| 100 | 4.2 |
Part 4. What is the 18650 battery voltage range?
The 18650 battery voltage range depends on various factors, including its state of charge, load, temperature, battery model, quality, application requirements, and specific battery chemistry.
However, there are some general guidelines regarding the 18650 battery voltage range.
- Nominal Voltage: The nominal voltage of an 18650 battery is typically 3.7 volts per cell (1S). This means that when a single 18650 cell is fully charged, it will have a voltage of approximately 4.2 volts. However, it’s important to note that the nominal voltage is an average value, and the actual voltage can vary depending on the battery’s specific characteristics.
- Voltage Range during Discharge: As the 18650 battery discharges, its voltage gradually decreases. A discharged 18650 battery typically reaches a voltage of around 3.0-3.2 volts.
- Voltage Range during Charging: When an 18650 battery is being charged, its voltage increases. The charging voltage for an 18650 battery is typically around 4.2 volts per cell.
- Operating Voltage Range: The 18650 battery operating voltage range is typically between 3.0 and 4.2 volts per cell.
Part 5. What is the 18650 battery low voltage?
The 18650 battery low voltage typically refers to the voltage level at which the battery is considered to have reached the end of its usable capacity and should be recharged to prevent over-discharge.
While the nominal voltage of an 18650 battery is typically 3.7 volts per cell (1S), the low voltage threshold is generally considered below 3.0 volts per cell. This means that when the voltage of an individual 18650 cell drops below 3.0 volts, it is considered to have reached the 18650 battery low voltage.
The specific 18650 battery low voltage threshold may vary depending on the battery’s characteristics and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
The 18650 battery low voltage can lead to over-discharge, which can damage the battery.
How to prevent the 18650 battery from low voltage?
Various methods can be employed to monitor battery voltage, such as using a LiPo voltage checker, multimeter, or battery voltage alarm. These devices can indicate the voltage level of the battery and help identify when it reaches the 18650 battery low voltage.
In addition, when the voltage of an 18650 battery drops below the recommended low voltage threshold, it is essential to recharge the battery promptly. Recharging the battery before it reaches a critically low voltage level helps maintain its lifespan, capacity, and overall performance.
Part 6. What affects the 18650 battery voltage?
Several factors can affect the 18650 battery voltage:
- State of Charge (SOC): The 18650 battery voltage is directly related to its state of charge. A fully charged battery will have a higher voltage, while a discharged battery will have a lower voltage.
- Load: The load applied to the 18650 battery voltage can be influenced by the load. Higher loads can cause the battery’s voltage to drop more quickly, while lighter loads may result in a slower voltage decrease.
- Temperature: The temperature of an 18650 battery can impact the 18650 battery voltage. Higher temperatures can lead to a slight increase in voltage, while lower temperatures can cause a slight decrease.
- Battery Chemistry: The specific chemistry of the 18650 battery can affect its voltage characteristics. Different chemistries like Li-ion, LiPo, or LiFePO4 have varying voltage profiles.
- Internal Resistance: The battery’s internal resistance affects its voltage. Higher internal resistance can lead to more significant voltage drops under load conditions and reduced overall voltage stability.
- Chemistry and Design: The specific chemistry and design of the 18650 battery can influence its voltage characteristics. Different lithium-ion chemistries have varying voltage profiles, and design factors such as electrode materials and cell construction can impact 18650 battery voltage stability.
- Age and Cycle Life: Over time and with repeated charge-discharge cycles, the voltage characteristics of an 18650 battery may change. Aging effects such as capacity loss, increased internal resistance, and changes in electrode structure can alter 18650 battery voltage.
- Charging and Discharging Rate: The rate at which an 18650 battery is charged or discharged can affect its voltage. Rapid charging or discharging can lead to voltage spikes or drops, respectively, due to kinetic limitations within the battery.
It is important to note that these factors can interact, and the 18650 battery voltage is not solely determined by one factor alone.
Part 7. FAQs
-
How does temperature affect the 18650 battery voltage?
Lower temperatures decrease voltage, while higher temperatures increase it. -
Why does the voltage drop under heavy loads?
Due to internal resistance within the battery. -
Can over-discharging harm an 18650 battery?
Yes, it can lead to irreversible damage. -
How does the charging rate affect the 18650 battery voltage?
Rapid charging can cause voltage spikes. -
What is the operational voltage range of an 18650 battery?
Typically from 4.2 volts (fully charged) to around 2.5 volts (fully discharged). -
How often should I monitor the voltage of my 18650 battery?
Regularly, especially during use and charging. -
Why is it essential to prevent over-discharge?
To avoid damage, capacity loss, and safety hazards.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Battery Load Test: A Comprehensive Guide
Step-by-step battery load test guide for car, solar & industrial use. Learn how to load test a battery, interpret voltage charts, and avoid common mistakes.
The Comprehensive Guide to Battery Balancing and Battery Balancer
Discover how battery balancers improve lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety. Learn types, functions, and tips to choose the right balancer.
What Is the Best Voltage for a Chainsaw Battery?
Compare 12V-80V chainsaw batteries for light pruning, medium firewood, and professional cutting. See best battery chainsaw with runtime charts and safety tips.
Lithium VS. Alkaline Batteries: A Comprehensive Comparison
Lithium batteries last 3–7× longer than alkaline and perform better in cold weather. Compare lifespan, cost, safety, and best uses to choose the right battery.
Comparing Lithium-Sulfur and Lithium-Ion Batteries: Which is Right for You?
Compare lithium-sulfur (Li-S) and lithium-ion batteries on energy, lifespan, cost, safety, and applications. Best choice for drones, EVs, and electronics.