In the ever-evolving world of technology and energy storage, 24V batteries have emerged as a significant player. These batteries offer a remarkable combination of efficiency, versatility, and reliability, making them ideal for various applications. This comprehensive guide will explore the world of 24V batteries, their benefits, applications, and why they might be the perfect solution for your power needs.
Part 1. What are 24V batteries?
24V batteries are energy storage devices with a nominal voltage of 24 volts. They comprise multiple smaller cells connected in series or parallel to achieve the desired voltage and capacity. These batteries are commonly used in applications that require a higher voltage than the standard 12V batteries, providing more power and efficiency.
Part 2. Types of 24V batteries
Several types of 24V batteries are available, each with advantages and disadvantages. The most common types include:
1. Lead-acid batteries
Lead-acid batteries are one of the oldest and most widely used battery technologies. They are known for their reliability and affordability. However, they are relatively heavy and require regular maintenance.
2. Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are popular due to their high energy density, lightweight, and long lifespan. They are more expensive than lead-acid batteries but offer superior performance and efficiency.
3. Nickel-cadmium (NiCd) Batteries
NiCd batteries are known for their durability and ability to perform well in extreme temperatures. However, they suffer from a memory effect, which can reduce their overall capacity over time.
4. Nickel-metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries
NiMH batteries are an improvement over NiCd batteries, offering higher energy density and less susceptibility to memory effect. They are commonly used in consumer electronics and portable devices.
Part 3. Advantages of 24V batteries
1. Higher Efficiency
One of the primary advantages of 24V batteries is their higher efficiency compared to lower-voltage batteries. They can deliver more power with less energy loss, making them ideal for high-demand applications.
2. Versatility
24V batteries are incredibly versatile and can be used in various applications, from renewable energy systems to electric vehicles and backup power supplies.
3. Longer Lifespan
Many 24V batteries, especially lithium-ion types, offer a longer lifespan than their 12V counterparts. This means fewer replacements and lower long-term costs.
4. Compact Size
Despite their higher voltage, 24V batteries are often compact and lightweight, making them easier to install and transport.
5. Reduced Wiring Complexity
A higher voltage battery can reduce the wiring complexity in specific applications, leading to more straightforward and cost-effective installations.
Part 4. Applications of 24V batteries
1. Renewable Energy Systems
24V batteries are commonly used in solar and wind energy systems. They store the energy generated by these renewable sources and provide a reliable power supply when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing.
2. Electric Vehicles
Many electric vehicles (EVs) utilize 24V batteries for their power systems. These batteries provide the necessary voltage to drive electric motors efficiently.
3. Marine and RV Applications
Boats, yachts, and recreational vehicles (RVs) often use 24V batteries for their electrical systems. These batteries power everything from lighting to appliances, ensuring a comfortable and functional living space.
4. Backup Power Supplies
24V batteries are used in uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems to provide backup power during outages. They ensure critical systems and devices remain operational when the main power fails.
5. Industrial and Commercial Use
In industrial and commercial settings, 24V batteries power equipment, machinery, and emergency systems. Their reliability and efficiency make them a preferred choice in these demanding environments.
Part 5. How do you choose the correct 24V battery?
1. Determine Your Power Requirements
Before selecting a 24V battery, assess your power needs. Consider your specific application’s voltage, capacity, and discharge rate.
2. Consider Battery Type
Choose the type of 24V battery that best suits your needs. For high efficiency and long lifespan, lithium-ion batteries are an excellent choice. Lead-acid batteries may be more suitable for cost-effective solutions.
3. Evaluate Environmental Conditions
Consider the operating environment of the battery. If the battery is exposed to extreme temperatures or harsh conditions, opt for a battery that can withstand these challenges.
4. Check Compatibility
Ensure that the 24V battery you choose is compatible with your existing equipment and systems. Check for voltage compatibility, connectors, and other specifications.
5. Factor in Maintenance
Some batteries require regular maintenance, while others are virtually maintenance-free. Choose a battery that aligns with your maintenance capabilities and preferences.
Part 6. Caring for your 24V battery
1. Regular Inspections
Perform regular inspections of your 24V battery to check for any signs of damage or wear. Look for corrosion, leaks, or swelling.
2. Proper Charging
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for charging your 24V battery. Avoid overcharging or deep discharging, as these can reduce the battery’s lifespan.
3. Storage Conditions
Store your 24V battery in a cool, dry place when not in use. Extreme temperatures and humidity can negatively impact battery performance and longevity.
4. Use the Right Charger
Always use a charger that is compatible with your 24V battery. Using the wrong charger can damage the battery and pose safety risks.
Part 7. The importance of choosing a suitable 24V battery charger
A high-quality charger optimizes charging by delivering the correct voltage and current. This precision prevents damage to the battery cells and maintains their performance. Additionally, a good charger includes safety features such as overcharge protection, temperature monitoring, and short-circuit prevention, enhancing safety and efficiency.
Compatibility and Efficiency
Using a charger specifically designed for your battery type is essential. Different batteries—like lead-acid or lithium-ion—have unique charging requirements. A compatible charger ensures the battery receives the appropriate charge profile, maximizing efficiency and life expectancy.
Smart Chargers
Investing in a smart charger can bring significant benefits. Smart chargers automatically adjust the charging rate based on the battery’s state, preventing overcharging and extending the battery’s life. They can also diagnose and address minor issues before they escalate, ensuring your battery remains in optimal condition.
The Ultimate Guide to Charging 24V Lithium Battery
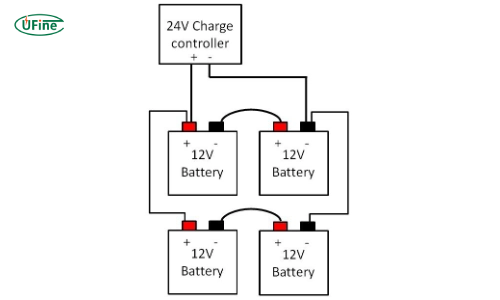
Part 8. How do you connect 4 12v batteries to make 24v?
Step-by-Step Guide
Identify and Prepare the Batteries: Ensure all four 12V batteries have the same type and capacity to ensure consistent performance and prevent imbalances.
Connect in Series to Form Pairs:
- First Pair: Connect the positive terminal of the first battery to the negative terminal of the second battery.
- Second Pair: Connect the positive terminal of the third battery to the negative terminal of the fourth battery.
- Check Voltage of Pairs: Each pair should now read 24V. You can verify this using a multimeter.
Connect Pairs in Parallel:
- Connect the positive terminal of the first pair (first battery) to the positive terminal of the second pair (third battery).
- Connect the negative terminal of the first pair (second battery) to the negative terminal of the second pair (fourth battery).
- Final Voltage Check: A multimeter measures the voltage across the combined setup. It should read 24V but with increased capacity due to the parallel configuration.
- Connect to Your System: Attach the free terminals (approving of the first battery in the first pair and negative of the second battery in the second pair) to your 24V system. Ensure all connections are secure to avoid any power loss or safety risks.
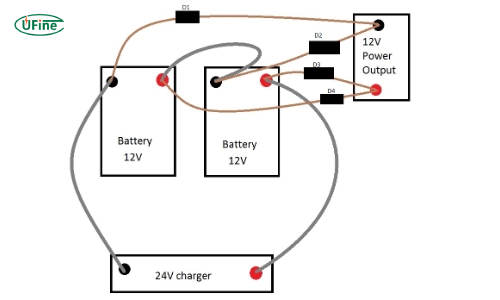
Part 9. How do you make 2 12v batteries 24v?
Step-by-Step Guide
Prepare the Batteries: Ensure both 12V batteries are identical in type and capacity to maintain balance and efficiency.
Connect in Series:
- Connect the positive terminal of the first battery to the negative terminal of the second battery. This series connection will combine their voltages.
- Check the Voltage: Use a multimeter to measure the voltage across the free positive terminal of the first battery and the free negative terminal of the second battery. It should read 24V.
- Connect to Your System: Attach the free terminals (approving of the first battery and negative of the second) to your 24V system. Ensure all connections are secure to avoid any power loss or safety risks.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Lithium 24V Batteries for Golf Carts: Why They’re Becoming the New Standard
Lithium 24V batteries are replacing lead-acid in golf carts, offering better performance and numerous advantages over older technologies.
Double A Lithium Batteries for Camera Gear: A Smart Choice for Photographers
Double-A lithium batteries offer photographers durability, efficiency, and convenience, improving workflow and reliability for camera gear.
Why You Need a Lithium Battery Heater for Cold Weather Performance and Longevity
Cold weather can reduce lithium battery performance. This article explores how lithium battery heaters work and their benefits for cold weather use.
Why Does a Battery Inflate? Common Causes and How to Prevent It
Swollen batteries are a common issue in devices like smartphones and laptops. This guide explores the causes, risks, and prevention tips.
What is a VRB Battery and How Does It Compare to Lithium Ion Batteries?
As the world shifts to sustainable energy, VRB and Lithium-Ion batteries play a key role. This article compares their features and benefits.