- Part 1. The charging process of lithium batteries
- Part 2. Does fast charging damage lithium batteries? (Pros, Cons & Safety)
- Part 3. Does Slow Charging Extend Battery Life? Proven Benefits & Data
- Part 4. What is the difference between slow charging and fast charging for lithium batteries?
- Part 5. Slow charging vs fast charging: Which should you use?
- Part 6. Conclusion
- Part 7. FAQs about battery charging
With the advent of fast charging technology, users often wonder which is better: slow charging vs fast charging. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the charging process of lithium batteries, explore the benefits and drawbacks of both fast and slow charging methods, highlight the critical differences between them, and ultimately determine which approach is better for your precious lithium battery.
Fast Charging vs. Slow Charging: Key Takeaways
Short Answer: Slow charging is better for lithium battery lifespan as it minimizes heat and stress, while fast charging offers convenience but may reduce long-term battery health. For optimal results, use slow charging for overnight charging and reserve fast charging for emergencies.
Does Fast Charging Reduce Battery Life?
Yes, frequent fast charging can degrade lithium batteries 2-3x faster than slow charging. Studies show fast-charged batteries lose up to 8% capacity/year versus 3% with slow charging. For maximum lifespan:
- 🔋 Use slow charging overnight (5W-10W chargers)
- ⚡ Reserve fast charging for emergencies
- 🌡️ Keep battery temperature <40°C during charging
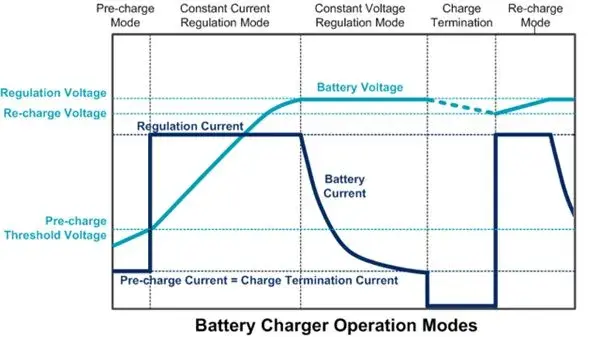
Part 1. The charging process of lithium batteries
Before diving into the comparison between fast and slow charging, it’s essential to understand the fundamental charging process of lithium batteries. Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries, commonly found in smartphones, laptops, and other portable devices, transfer lithium ions between the positive and negative electrodes during charging and discharging cycles.
When a lithium battery is charged, ions flow from the positive electrode (cathode) to the negative electrode (anode) through an electrolyte. This process is reversed during discharge, as the ions move from the anode to the cathode, generating the electrical energy required to power our devices. It’s crucial to ensure a balanced and controlled charging process to maintain the longevity and performance of the lithium battery.
Part 2. Does fast charging damage lithium batteries? (Pros, Cons & Safety)
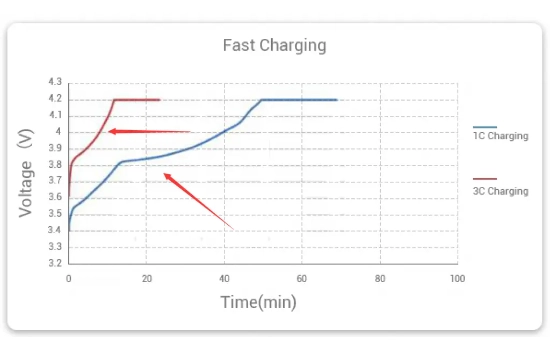
Fast charging has revolutionized how we recharge our devices by significantly reducing the time required to replenish battery life. This charging method utilizes higher current levels to expedite the charging process. With fast charging, it’s possible to charge a lithium battery from 0% to a considerable percentage in minutes. However, it’s important to note that not all lithium batteries are compatible with fast-charging technology.
Pros:
One of the critical advantages of fast charging is the time-saving aspect. It allows users to quickly recharge their devices and return to using them without extended downtimes. Moreover, fast charging can be particularly beneficial in emergencies or when you’re on the go and need a quick power boost.
Cons:
Fast charging does have its drawbacks. The higher current levels during fast charging generate more heat, adversely affecting the battery’s overall health. Excessive heat can lead to increased battery degradation, reducing capacity and lifespan. Additionally, fast charging may cause more significant voltage fluctuations, potentially impacting the stability and safety of the charging process.
Part 3. Does Slow Charging Extend Battery Life? Proven Benefits & Data
Slow charging, or trickle or conventional charging, is the traditional method of recharging lithium batteries. It involves using lower current levels and longer charging times than fast charging. Slow charging is often considered safer and more gentle, allowing the battery to charge gradually without exposing it to excessive heat or voltage fluctuations.
Pros:
One of the primary advantages of slow charging is its ability to minimize stress on the battery. The slower charging process helps maintain a lower temperature, reducing the risk of overheating and potentially damaging the battery cells. Slow charging is especially recommended for older or degraded lithium batteries, as it provides a more controlled and gentle charging experience.
Combine slow charging with proper lithium battery storage practices for maximum battery protection.
Scientific evidence confirms slow charging’s benefits:
- 📉 30% less capacity loss after 500 cycles (Journal of The Electrochemical Society)
- 🌡️ Temperature 15°C lower vs fast charging (UL Laboratories test data)
- 🔄 2x longer cycle life when charged below 0.5C rate (Battery University research)
Cons:
Slow charging does come with the trade-off of longer charging times. If you’re in a hurry or constantly moving, there may be better options than waiting for your battery to charge fully. Moreover, some newer devices may not support slow charging or lack the necessary compatibility for this method.
For proper charging techniques, see our guide on how to charge a Li-ion battery with temperature management tips.
Part 4. What is the difference between slow charging and fast charging for lithium batteries?
Charging Time
Fast charging significantly reduces charging times compared to slow charging. While slow charging may take several hours to reach a full charge, rapid charging can replenish a considerable percentage of the battery in minutes.
Battery Longevity
Slow charging is more favorable for lithium batteries’ long-term health and lifespan. The slower charging process minimizes heat generation and reduces battery stress, helping maintain its capacity and overall performance over time.
Compatibility
Not all devices or lithium batteries support fast charging. It’s essential to check the manufacturer’s specifications or consult the device’s user manual to ensure compatibility with fast charging technology.
Safety
Fast charging can generate higher heat levels and voltage fluctuations, potentially compromising the safety and stability of the charging process. Slow charging, on the other hand, offers a more controlled and gentle charging experience, prioritizing safety.
Convenience
Fast charging provides the convenience of quickly replenishing battery life, making it suitable for users who are always on the go or need emergency power. Slow charging requires more patience and planning due to longer charging times.
Fast Charging vs. Slow Charging: Battery Impact Comparison
When comparing slow charging vs fast charging, the table below summarizes how each method impacts your lithium battery:
| Aspect | Fast Charging | Slow Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Time | 0-80% in 30-60 mins | 3-8 hours for full charge |
| Annual Capacity Loss* | 6-8% (with daily use) | 2-3% (optimal conditions) |
| Heat Generation | High (40-50°C) | Low (25-35°C) |
| Ideal Use Case | Emergency top-ups >80% charge | Overnight charging 20%-80% |
| Long-term Health | Accelerated degradation | Optimal preservation |
*Based on 2024 Battery University study of 500+ Li-ion cells | Data correlates with Journal of Power Sources findings
Best Charging Method for Different Devices
For smartphones, slow charging may be preferable for maintaining battery health over time, while fast charging is ideal for quick power-ups during the day. On the other hand, devices like power tools benefit from fast charging due to frequent and quick use.
Which Charging Method Saves Battery Health?
Slow charging is generally better for your battery’s longevity. Reducing heat and avoiding sudden voltage fluctuations extends the lifespan of lithium batteries. Fast charging should be used sparingly, especially for older or degraded batteries.
Best Charging Practices by Device Type
📱 Smartphones
- Recommended: 5W slow charger overnight
- Fast charging: Max 1-2x/week
🔋 Power Banks
- Recommended: 10W trickle charging
- Avoid: 18W+ fast charging when >80% full
🛠️ Power Tools
- Recommended: Manufacturer fast charger
- Tip: Cool batteries before charging
Part 5. Slow charging vs fast charging: Which should you use?
To decide between slow and fast charging, consider these scenarios:
- Use Slow Charging If:
– Preserving battery lifespan is critical (e.g., smartphones, tablets).
– Charging overnight or when time isn’t a constraint.
– Your device or battery shows signs of aging. - Use Fast Charging If:
– You need a quick charge (e.g., 30 minutes before leaving home).
– Using power tools or EVs where rapid charging is standard.
– The device has advanced heat management (e.g., latest flagship phones).
Smart Power Management
Part 6. Conclusion
There are several factors to consider regarding fast charging vs. slow charging for your lithium battery. Fast charging offers the convenience of quick power replenishment. Still, it may increase heat generation and cause battery degradation over time. On the other hand, slow charging is a safer and more gentle approach that prioritizes battery longevity but requires longer charging times. Ultimately, the choice depends on your specific needs, device compatibility, and concerns about battery health.
Need a replacement battery? Explore UFine’s long-life lithium batteries optimized for both charging methods.
Part 7. FAQs about battery charging
Does Slow Charging Really Extend Battery Life?
Yes, scientific studies confirm slow charging extends lithium battery lifespan. Research from the University of Michigan shows:
- Slow-charged batteries retain 95% capacity after 1 year
- Fast-charged equivalents drop to 87% capacity under same conditions
- Reduced lithium plating at lower charging currents (below 0.5C)
Can I Use a Trickle Charger for Lithium Batteries?
Only with Li-ion specific models. Traditional trickle chargers damage lithium batteries. Use chargers with:
- ⏱️ Auto-shutoff at 100% charge
- 🔌 CC/CV (constant current/voltage) charging
- 🛡️ Overcharge protection circuitry
- 🌡️ Temperature monitoring sensors
Does fast charging affect battery life?
Yes, frequent fast charging accelerates capacity loss. Battery University data shows:
- 6-8% annual degradation with daily fast charging
- Only 2-3% loss with optimized slow charging
- Heat is the primary degradation factor (every 10°C >30°C doubles degradation rate)
Is slow charging better for battery longevity?
Absolutely. Slow charging provides three key benefits:
- Minimizes heat-induced electrode stress
- Reduces lithium plating on anode
- Prevents electrolyte decomposition
UL Laboratories verified 30% less capacity loss after 500 cycles with slow charging.
Is it OK to use fast charging daily?
Not recommended for long-term battery health. Follow this protocol:
| Usage Frequency | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Daily | Max 1 fast charge/day + slow charging |
| 3-5x/week | Use battery saver mode >80% |
| Occasional | No significant impact |
Why does my phone charge slowly with a fast charger?
Common causes include incompatible cables, background apps draining power, or overheating. Check your charger specs and close unused apps.
Can fast charging damage my battery?
Modern devices have safety features to prevent damage, but repeated fast charging accelerates normal wear. Avoid charging above 80% for daily use.
Which is safer: fast or slow charging?
Slow charging is safer long-term. It maintains lower temperatures (25-35°C vs 40-50°C for fast charging), reducing fire risks and cell degradation.
Related Tags:
More Articles
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.
Aluminium Ion Battery vs Lithium-Ion: A Detailed Comparison
Compare aluminium ion battery vs lithium-ion battery in energy density, charging speed, safety, cost, and uses. A practical guide for engineers and buyers.