Connecting two batteries in parallel is a practical and efficient way to increase capacity and extend the runtime of your devices. Whether you’re working on a DIY project, powering an RC car, or setting up a solar energy system, understanding how to properly connect batteries in parallel is essential. This guide will walk you through the process step by step, providing detailed explanations, tips, and solutions to common problems. Let’s dive in and explore everything you need to know!
Part 1. Advantages and disadvantages of battery parallel connection
Before jumping into the technical details, it’s important to understand why you might want to connect two batteries in parallel and what challenges you might face.
Advantages:
-
Increased Capacity:
When you connect two batteries in parallel, their capacities add up. For example, two 2000mAh batteries will give you a total capacity of 4000mAh. This means your device will run longer without needing a recharge. -
Balanced Load:
In a parallel connection, both batteries share the load equally. This reduces the strain on each battery, potentially extending their lifespan. -
Simple Setup:
Parallel connections are relatively easy to set up, even for beginners. You don’t need advanced technical skills to get started.
Disadvantages:
-
Voltage Remains the Same:
Unlike series connections, parallel connections don’t increase voltage. If you’re using two 3.7V batteries, the combined output will still be 3.7V. -
Risk of Imbalance:
If the batteries aren’t perfectly matched, one may drain faster than the other. This can lead to inefficiencies and even damage over time. -
Space and Weight:
Using two batteries means more space and added weight, which might not be ideal for portable devices.
Despite these challenges, parallel connections are widely used because of their simplicity and effectiveness. With proper care and attention, you can avoid most of the pitfalls and enjoy the benefits.
Batteries In Series Vs Parallel:Which Is Better?
Part 2. What are the requirements for batteries?
Connecting two batteries in parallel isn’t as simple as just wiring them together. To ensure safety and efficiency, the batteries must meet certain requirements.
-
Same Voltage:
Both batteries must have the same nominal voltage. For example, if one battery is 3.7V, the other must also be 3.7V. Mixing voltages can cause one battery to overcharge or discharge the other, leading to potential damage. -
Same Capacity:
Ideally, the batteries should have the same capacity (measured in mAh). If one battery has a higher capacity, it will end up doing most of the work, which can lead to imbalances. -
Same Type:
Use the same type of battery (e.g., both LiPo, both LiFePO4, or both 18650). Different battery chemistries have different charging and discharging characteristics, which can cause problems in a parallel setup. -
Similar Age and Condition:
Avoid pairing a new battery with an old one. Older batteries often have reduced capacity and higher internal resistance, which can lead to imbalances.
If you’re unsure about which batteries to use or need custom solutions, Ufine Battery can help. As a leading manufacturer of custom lithium batteries, we can provide batteries tailored to your specific needs, ensuring perfect compatibility for parallel connections.
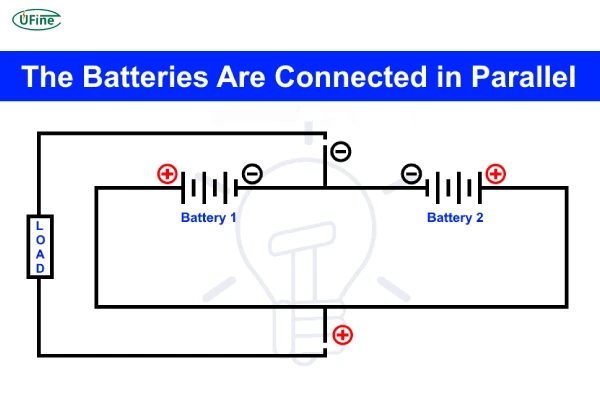
Part 3. 2 Batteries in parallel circuit diagram
Visualizing the connection can make the process much easier. Here’s a simple circuit diagram to help you understand how to connect two batteries in parallel:
-
The positive terminals of both batteries are connected together.
-
The negative terminals of both batteries are connected together.
-
The combined terminals are then connected to the device.
This configuration ensures that both batteries work together to power your device, sharing the load equally.
Part 4. Tools and materials Needed
Before you start, make sure you have the right tools on hand. Here’s what you’ll need:
-
Battery Connectors:
Use connectors that match your batteries and device (e.g., XT60, JST, or Deans connectors). -
Wires:
High-quality wires with proper insulation are essential for safe and efficient connections. -
Soldering Iron:
A soldering iron will help you create secure and durable connections. -
Heat Shrink Tubing:
Use heat shrink tubing to protect the connections and prevent short circuits. -
Multimeter:
A multimeter is crucial for checking voltage and ensuring everything is connected correctly.
Having the right tools not only makes the process easier but also ensures a safe and reliable setup.
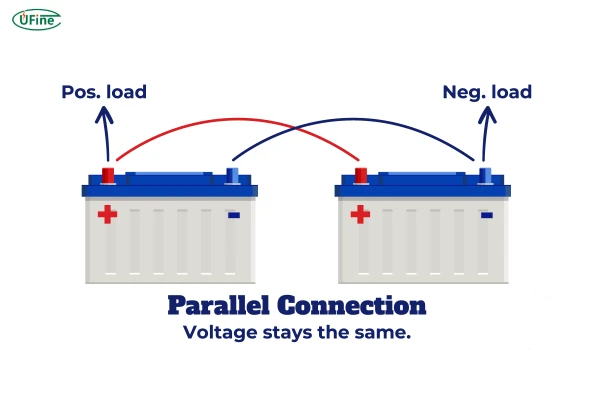
Part 5. How to connect 2 batteries in parallel?
Now that you have everything you need, let’s walk through the process step by step.
Step 1: Check Battery Voltage
Before connecting the batteries, use a multimeter to check their voltage. Both batteries should have the same voltage. If one battery has a significantly higher voltage, it could overcharge the other, leading to potential damage.
Step 2: Connect Positive Terminals
Take a wire and connect the positive terminal of Battery 1 to the positive terminal of Battery 2. Make sure the connection is secure. If you’re using a soldering iron, solder the wires to the terminals for a durable connection.
Step 3: Connect Negative Terminals
Next, connect the negative terminal of Battery 1 to the negative terminal of Battery 2 using another wire. Again, ensure the connection is secure.
Step 4: Connect to the Device
Once the batteries are connected in parallel, attach the combined positive and negative terminals to your device. Use connectors that match your device’s input.
Step 5: Secure the Connections
Use heat shrink tubing or electrical tape to protect the connections. This prevents short circuits and ensures the setup is safe to use.
Step 6: Test the Setup
Finally, use a multimeter to verify the voltage at the combined terminals. It should match the voltage of a single battery. If everything checks out, you’re ready to power your device!
Part 6. Common mistakes and how to fix them
Even with careful planning, mistakes can happen. Here are some common issues and how to avoid them:
Mistake 1: Mixing Different Batteries
Using batteries with different voltages, capacities, or chemistries can cause imbalances and damage.
Solution: Always use identical batteries. If you’re unsure, consult a professional or contact us for custom solutions.
Mistake 2: Poor Connections
Loose or poorly soldered connections can lead to power loss, overheating, or even fires.
Solution: Double-check all connections and use a soldering iron for secure joints.
Mistake 3: Ignoring Safety Precautions
Parallel connections can be dangerous if not done properly. Short circuits or overcharging can cause batteries to swell, leak, or even explode.
Solution: Use insulated tools, avoid short circuits, and monitor the setup during use.
Part 7. FAQ
1. Can I connect more than two batteries in parallel?
Yes, you can connect multiple batteries in parallel to further increase capacity. However, ensure all batteries have the same voltage, capacity, and type. The more batteries you add, the more critical it becomes to monitor the setup for imbalances.
2. What happens if one battery fails in a parallel connection?
If one battery fails (e.g., due to a short circuit or internal damage), the other battery will continue to power the device. However, the failed battery may drain the working battery, so it’s important to disconnect and replace the faulty battery as soon as possible.
3. Can I mix old and new batteries in parallel?
It’s not recommended. Older batteries often have reduced capacity and higher internal resistance, which can cause imbalances and reduce the overall performance of the parallel setup.
4. Do I need a balancing board for parallel connections?
Balancing boards are typically used for series connections, not parallel connections. In a parallel setup, the batteries naturally balance each other because they share the same voltage. However, you should still monitor the setup to ensure both batteries are functioning properly.
5. Can I use different brands of batteries in parallel?
While it’s possible, it’s not ideal. Different brands may have slight variations in performance, even if they have the same specifications. For the best results, use batteries from the same brand and batch.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.