Choosing the correct battery for your needs can be complex, especially when understanding the differences between high-voltage and low-voltage batteries. This article will guide you through the essential aspects of both types of batteries, helping you make an informed choice.
Part 1. What is a high-voltage battery?
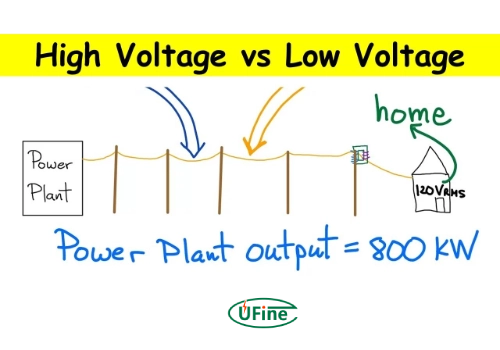
In some applications, a high-voltage battery typically operates at voltages above 12V, with typical voltage levels including 24V, 48V, and even up to 800V. These batteries handle more extensive power requirements and frequently suit applications where high energy density and efficiency are crucial.
Characteristics of High Voltage Batteries
- Higher Energy Density: High voltage batteries can store more energy in a smaller space, making them ideal for applications where space and weight are critical factors.
- Efficiency: These batteries are more efficient in transferring power due to lower current requirements, which reduces energy loss.
- Fast Charging: High-voltage systems can charge faster than low-voltage systems, which is beneficial for applications that require quick turnaround times.
- Applications: Commonly used in electric vehicles, industrial machinery, and large-scale energy storage systems.
Common Types of High Voltage Batteries
- Lithium-ion Batteries: Widely used in electric vehicles and portable electronics.
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries: Often found in hybrid vehicles.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Used in industrial applications and backup power systems.
Part 2. What is a low-voltage battery?
Low-voltage batteries operate below 12V, with typical levels including 1.2V, 6V, and 9V. They are generally used in applications that require less power and where safety and simplicity are more critical than high energy density.
Characteristics of Low Voltage Batteries
- Safety: Low-voltage batteries are generally safer to use and handle, making them suitable for consumer electronics and other low-power applications.
- Cost-Effective: These batteries are often less expensive to produce and maintain.
- Applications: Commonly used in household electronics, remote controls, and small appliances.
Common Types of Low Voltage Batteries
- Alkaline Batteries: People commonly use these in household electronics, such as remote controls and flashlights.
- Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) Batteries: Used in portable tools and small appliances.
- Zinc-carbon batteries: Found in low-drain devices like clocks and radios.
Part 3. High voltage battery vs low voltage battery: Advantages
High Voltage Batteries
Higher Efficiency
High-voltage batteries transfer power more efficiently, wasting less energy during operation.
Faster Charging
These batteries can be charged much faster than their low-voltage counterparts, making them ideal for applications that require quick turnaround times.
Compact Size
Due to their higher energy density, high-voltage batteries can pack more power into a smaller space, which is crucial for applications where space is limited.
Low Voltage Batteries
Safety
Low-voltage batteries are generally safer to use and handle, reducing the risk of electric shock and other hazards.
Cost-Effectiveness
These batteries are often less expensive to produce and maintain, making them a cost-effective solution for many applications.
Simplicity
Low-voltage batteries are more straightforward to manage and integrate into various systems, making them a versatile choice for many applications.
Part 4. High voltage battery vs low voltage battery: Disadvantages
High Voltage Batteries
Cost
High-voltage batteries are more expensive due to the advanced technology and materials required.
Safety Concerns
These batteries require more safety measures to prevent electric shock and other hazards, making them more complex.
Low Voltage Batteries
Lower Efficiency
Low-voltage batteries are less efficient in power transfer, leading to more energy loss during operation.
Slower Charging
These batteries take longer to charge, which can be a drawback for applications that require quick turnaround times.
Part 5. High voltage battery vs low voltage battery: Applications
High Voltage Batteries
Electric Vehicles
High-voltage batteries are the backbone of modern electric vehicles (EVs). They provide the necessary power to drive the car while ensuring efficiency and long-range capabilities.
Industrial Machinery
High-voltage batteries power heavy machinery and equipment in industrial settings, offering reliability and high performance.
Energy Storage Systems
High-voltage batteries are ideal for large-scale energy storage systems, helping to stabilize the grid and store renewable energy for later use.
Low Voltage Batteries
Consumer Electronics
Low-voltage batteries are commonly found in everyday consumer electronics like remote controls, flashlights, and small gadgets.
Medical Devices
Many medical devices, such as hearing aids and portable monitors, rely on low-voltage batteries for safe and reliable operation.
Portable Tools
Low-voltage batteries are also used in portable tools and equipment, balancing power and safety.
Part 6. High voltage battery vs low voltage battery: Key differences
Energy Density
- High Voltage: This has a higher energy density and is suitable for applications that require a lot of power in a compact form.
- Low Voltage: Lower energy density, suitable for applications where power requirements are minimal.
Efficiency
- High Voltage: More efficient due to lower current requirements, which reduces energy loss.
- Low Voltage: Less efficient but more straightforward, making managing them more accessible.
Safety
- High Voltage: More safety measures are required due to the higher risk of electric shock and other hazards.
- Low Voltage: Generally safer and easier to handle, with fewer risks.
Cost
- High Voltage: More expensive due to the advanced technology and materials required.
- Low Voltage: More cost-effective, making them suitable for budget-conscious applications.
Charging Speed
- High Voltage: Faster charging times are beneficial for applications needing quick turnaround.
- Low Voltage: Slower charging, suitable for applications with less urgent power needs.
Application Scope
- High Voltage: Ideal for high-power applications like electric vehicles, industrial machinery, and large-scale energy storage systems.
- Low Voltage: Best for low-power applications like consumer electronics, medical devices, and portable tools.
Maintenance
- High Voltage: Often requires more complex maintenance routines due to the advanced technology.
- Low Voltage: Easier to maintain and manage, with more straightforward maintenance requirements.
Part 7. FAQs
-
What are the main differences between high-voltage and low-voltage batteries?
High-voltage batteries have higher energy density, efficiency, and faster charging times, while low-voltage batteries are safer, more cost-effective, and simpler to manage. -
Which type of battery is better for electric vehicles?
High-voltage batteries are better for electric vehicles due to their higher energy density, efficiency, and faster charging capabilities. -
Are high-voltage batteries more expensive than low-voltage batteries?
Yes, high-voltage batteries are generally more expensive due to the advanced technology and materials required. -
Can low-voltage batteries be used in industrial applications?
While some industries use low-voltage batteries, they generally prove less efficient and unsuitable for high-power requirements. -
What safety measures are required for high-voltage batteries?
High-voltage batteries require more safety measures, including proper insulation and protective coatings, to prevent electric shock and other hazards.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.