When you’re choosing a battery, you may encounter the phrase, “higher amps are better.” This assertion sounds straightforward, but it opens up a world of questions. What does it mean for your devices, and how does it impact their performance? In this article, we will delve into the concept of amps, their relation to battery performance, and whether higher amps are indeed beneficial. By the end, you’ll be equipped to make informed decisions about your battery needs.
Part 1. What’s the amps?
To understand battery performance, you first need to grasp what amps, or amperes, are. Amps measure the flow of electric current in a circuit. Picture water flowing through a pipe; amps represent the volume of water passing through at any given moment. More amps indicate a stronger current and, consequently, the capacity to power devices more effectively.
Part 2. What is Amps related To?
Amps are interconnected with several critical battery parameters:
-
Voltage: Voltage (V) represents the electrical potential, while amps measure current flow. The two work together to determine wattage (W), the total power output.
-
Capacity: This is often rated in amp-hours (Ah), indicating how long a battery can deliver a specific current. For instance, a 10Ah battery can theoretically provide 1 amp for 10 hours.
-
Resistance: The resistance within the battery and connected circuits influences how many amps can flow. High resistance can limit the current, affecting performance.
Understanding these relationships is essential for assessing battery suitability for various applications.
Conversion of Watt Hour to Amp Hour (Wh to Ah)
Part 3. How do Amps affect battery performance?
Amps have several implications for battery performance:
Power Delivery
Higher amps usually translate to better power delivery. Devices that require quick bursts of energy, such as power tools or electric vehicles, benefit significantly from batteries with higher amp ratings. For example, an electric drill powered by a high-amp battery can drill through tough materials much more effectively.
Device Compatibility
Not all devices can handle high amp outputs. For instance, if a device is designed for a lower amp battery and you connect a higher amp one, the excess current could damage its internal components. Therefore, understanding your device’s amp requirements is crucial.
Heat Generation
Another aspect to consider is heat generation. Higher amps can produce more heat, which can reduce battery life and performance over time. For example, a battery used in a high-drain device may overheat if not adequately managed, leading to premature failure.
Part 4. Is higher Amps of a battery the better?
While it seems intuitive to think that higher amps are always advantageous, this isn’t necessarily true. The ideal amp rating depends on the application:
-
High-Demand Devices: For power tools and high-performance electronics, higher amps can indeed enhance performance. These devices need significant power for optimal functionality.
-
Low-Demand Devices: For everyday items like remote controls or simple flashlights, using a battery with excessively high amps can lead to inefficiency and unnecessary heat. In these cases, a battery with lower amps is often sufficient.
Part 5. What happens if I put a higher Amp battery in my device?
If you use a higher amp battery than what your device is rated for, several things can happen:
Potential Benefits
- Improved Performance: For devices capable of handling the higher output, you may experience enhanced performance and quicker operation.
Risks
-
Overheating: Excessive current can lead to overheating, particularly in devices not designed for high power. This can reduce battery life and even cause failure.
-
Damage: Sensitive electronic components may not withstand the increased current, leading to malfunction or total failure.
-
Shortened Lifespan: Regularly running devices on higher amps than intended can accelerate wear and tear.
Part 6. What happens If I put a lower amp battery in my device?
Using a lower amp battery presents its own set of challenges:
Performance Issues
-
Underperformance: The device may not operate at full capacity, leading to slow performance or failure to turn on altogether.
-
Voltage Drop: If the battery cannot supply the required amps, the voltage may drop, resulting in erratic operation.
Damage Potential
- Wear and Tear: Prolonged use of a lower amp battery can lead to strain on the device, potentially causing long-term damage.
Part 7. What Amps battery should I use?
Choosing the right amp battery requires understanding your device’s specifications:
-
Check Manufacturer Specifications: The easiest way to know what amp rating to look for is by checking the device’s manual or manufacturer’s website.
-
Evaluate Usage: If you plan to use your device in high-demand situations (like power tools), you may want to opt for a higher amp battery.
-
Consult with Experts: When in doubt, seek advice from knowledgeable individuals in hardware stores or consult online forums dedicated to your device type.
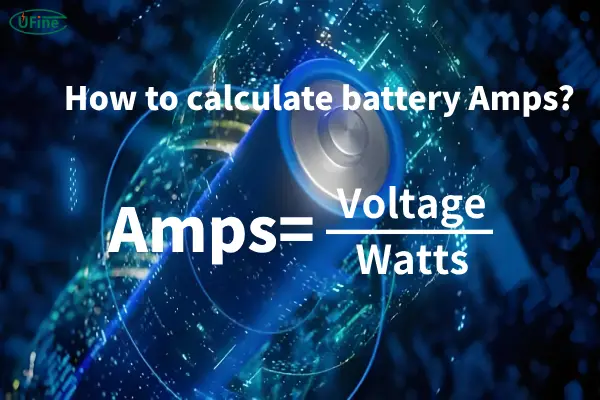
Part 8. How to calculate battery Amps?
Calculating battery amps can be straightforward. Use the formula:
Example Calculation:
If your device requires 120 watts and operates on a 12V battery:
This simple calculation allows you to determine the appropriate battery for your device based on its power needs.
Part 9. Final words
In conclusion, the question of whether higher amps are always better is nuanced. While higher amps can enhance performance in high-demand applications, they can also pose risks in devices designed for lower current levels. By understanding amps and their impact on battery performance, you can make informed choices that ensure your devices operate efficiently and effectively. Always consider the specific needs of your device and the required amp rating to make the best battery selection. Your choice can lead to improved performance and a more satisfying user experience.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.