- Part 1. What is a car battery?
- Part 2. What does ampere rating mean?
- Part 3. How many amps does a typical car battery have?
- Part 4. How do you measure car battery amps?
- Part 5. How do cranking amps differ from pulse hot cranking amps?
- Part 6. What factors affect car battery amperage?
- Part 7. How many amps does a car battery draw when starting?
- Part 8. What is a parasitic drain?
- Part 9. How does driving style affect car battery performance?
- Part 10. FAQs
When considering how many amps are in a car battery, it’s essential to understand what this measurement means for your vehicle. A car battery is more than just a power source; it plays a vital role in starting your engine and powering electrical components. In this article, we will delve into the details of car batteries, their amperage ratings, and the factors that influence their performance.
Part 1. What is a car battery?
A car battery is a rechargeable device that stores electrical energy for your vehicle. The lead-acid battery is the most common type, and it consists of six cells, each producing about 2.1 volts. Together, these cells provide 12 volts, which is standard for most vehicles.
However, another type of battery is gaining popularity: the lithium battery. Lithium batteries are lighter and can deliver more power than traditional lead-acid batteries. They also have a longer lifespan and can handle deeper discharges without damage. While lead-acid batteries are still widely used, lithium batteries are becoming more common in electric vehicles and high-performance applications.
The primary function of any car battery, whether lead-acid or lithium, is to provide the necessary electrical energy to start the engine and power various electrical systems when the engine is off. Understanding how many amps are in a car battery helps you gauge its effectiveness in performing these tasks.
Part 2. What does ampere rating mean?
The ampere rating of a car battery indicates its capacity to deliver current over time. This rating is crucial for understanding how much electrical power the battery can provide at any given moment.
- Cranking Amps (CA): This measures how much current a fully charged battery can deliver for 30 seconds at 32°F (0°C) without dropping below 7.2 volts. It’s beneficial for understanding how well the battery will perform in moderate temperatures.
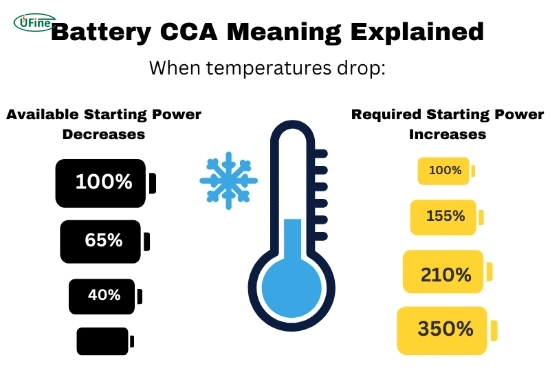
- Cold Cranking Amps (CCA): This rating is similar to cranking amps but measures performance at 0°F (-18°C). CCA provides insight into how well the battery will start an engine in cold weather conditions, making it an essential factor for those in colder climates.
- Amp-Hour (Ah) Rating: This indicates how long a battery can deliver a specific amount of current. For example, a battery with an amp-hour rating of 100 Ah can provide 5 amps for 20 hours before being depleted.
Part 3. How many amps does a typical car battery have?
Typically, car batteries have an ampere rating ranging from 550 to 1000 amps, depending on their size and design. Smaller vehicles may require batteries with lower ratings, while larger vehicles or those with more electronic features may need batteries with higher ratings.
For instance, compact cars might use batteries rated around 400-600 CCA, while trucks or SUVs may require ratings upwards of 700-800 CCA to ensure reliable starting power under various conditions.
Part 4. How do you measure car battery amps?
You can use a multimeter to measure a car battery’s amperage accurately. Here’s how:
- Set your multimeter to measure DC voltage.
- Connect the red lead to the positive terminal and the black to the negative one.
- Read the voltage displayed on the multimeter.
You must know the resistance (in ohms) to calculate amps using Ohm’s Law. The formula is:
- Amps = Volts / Resistance (Ohms)
For practical purposes, if you only want to check if your battery is charged, you can refer to standard voltage readings:
- 12.6 volts: Fully charged
- 12.4 volts: Approximately 75% charged
- 12.2 volts: About 50% charged
- 12.0 volts: Roughly 25% charged
- 11.9 volts or below: Considered dead
How Many Volts Is a Car Battery? How to Check Car Battery Life?
Part 5. How do cranking amps differ from pulse hot cranking amps?
Understanding the difference between cranking amps and pulse hot cranking amps is essential for evaluating your car’s starting power:
- Cranking Amps (CA) refers to the current that a fully charged battery can deliver at room temperature (32°F) for about 30 seconds without dropping below a specific voltage.
- Pulse Hot Cranking Amps (PHCA) measure how much current can be delivered during short bursts when starting an engine under warm conditions (typically around 80°F). This measurement can be significantly higher than CA and CCA because batteries can deliver more power when warm.
Knowing these differences helps you choose the right battery based on climate and vehicle requirements.
Part 6. What factors affect car battery amperage?
Several factors can influence the amperage output of a car battery:
- Temperature: Cold weather significantly reduces a battery’s ability to deliver current due to increased internal resistance.
- Battery Age: Older batteries lose capacity over time and may not deliver their rated amperage effectively as they degrade.
- State of Charge: A fully charged battery will perform better than one partially or fully discharged.
- Electrical Load: The more accessories and systems your vehicle has running, such as lights, air conditioning, or audio systems, the more amps your battery needs to supply.
Part 7. How many amps does a car battery draw when starting?
A typical car battery can draw between 400 and over 1000 amps when starting an engine, depending on engine size and temperature conditions. Larger engines require more power to crank over than smaller engines due to their increased mechanical resistance.
Part 8. What is a parasitic drain?
Parasitic drain refers to the small amount of current drawn from the battery when the vehicle is turned off. Most vehicles have a parasitic draw ranging from 20 mA to 50 mA, but this can increase with aftermarket accessories or faulty wiring, leading to quicker depletion of your car’s battery.
If not appropriately managed, parasitic drain can result in a dead battery after several days or weeks of inactivity.
Part 9. How does driving style affect car battery performance?
Your driving habits significantly impact how well your car’s electrical system charges and maintains its battery:
- Frequent Short Trips: If you often take short drives where your engine doesn’t run long enough to recharge the battery fully, it may lead to premature wear and reduced capacity over time.
- High Electrical Load Usage: Using multiple electronic devices while driving—like GPS systems, heated seats, or high-powered audio systems—can increase demand on the alternator and strain the overall health of your battery.
Part 10. FAQs
-
What happens if I use a battery with an amp rating too low?
Using a battery with an amp rating that is too low may result in insufficient power to start your vehicle or run electrical systems effectively. It might lead to problems like slow cranking or failure to start altogether. -
Can I replace my car battery with one that has higher amps?
Yes, you can replace your car battery with higher amp ratings if it fits in your vehicle and meets other specifications like size and terminal configuration. However, ensure it complies with manufacturer recommendations for optimal performance. -
How often should I check my car battery’s amperage?
It’s advisable to check your car battery’s amperage at least once every six months or before long trips, especially if you notice any starting issues or unusual electrical behavior in your vehicle. -
What should I do if my car won’t start?
If your car doesn’t start, first check the voltage of your battery using a multimeter. If it’s below 12 volts, consider charging or replacing it, as it may not be able to provide sufficient power for starting. -
How long do car batteries last?
On average, most conventional lead-acid car batteries last between three to five years under normal usage conditions; however, their lifespan can vary based on usage patterns and environmental conditions like temperature extremes.
Related Tags:
More Articles

What are Watts and Watt Hours in Battery?
Understand watt vs watt-hour in batteries, how to calculate battery watt hours, and what Wh means for car batteries, devices, and energy storage.
A Complete Guide to the Best Batteries for Flashlights
Compare the best batteries for flashlights, including AA, AAA, 18650, 21700, CR123A. See which battery offers the best brightness, runtime, and reliability.
How Long Do Rechargeable AA Batteries Last?
How long do rechargeable AA batteries last? Compare NiMH and lithium AA lifespan, recharge cycles, key factors, and performance vs alkaline batteries.
How Much Current Can a 9V Battery Really Supply?
Discover how many amps a 9V battery can supply, its actual current output, discharge rate, and capacity for alkaline, lithium, and rechargeable 9V batteries.
12V STD vs 12V AGM: Meaning, Differences, and Which Is Better
Understand what STD and AGM batteries mean, their key differences, and which 12V battery fits your needs best in 2026.