Motorcycles are exciting machines that rely heavily on their electrical systems to start and operate efficiently. At the heart of this system is the motorcycle battery, which plays a crucial role in powering the engine, lights, and other electronic components. Understanding the voltage of a motorcycle battery is essential for any rider or mechanic. In this article, we will explore the standard voltage of motorcycle batteries, how to test them properly, common issues related to battery voltage, and maintenance tips.
Part 1. What is the standard voltage of a motorcycle battery?
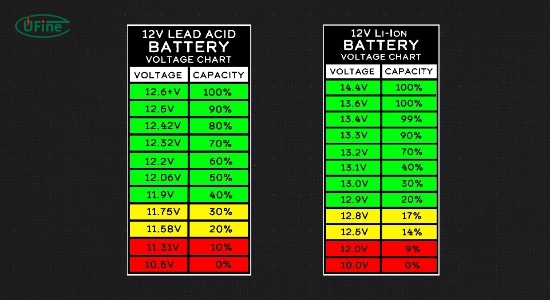
The standard voltage for most motorcycle batteries is 12 volts. This voltage is typical for modern motorcycles, ensuring they can provide a stable power supply for starting the engine and operating electrical systems.
A 12-volt battery typically displays about 12.6 to 14.4 volts when fully charged. The voltage can fluctuate based on the state of charge:
- Fully Charged: Approximately 12.6 – 14.4 volts
- Partially Charged: Around 12.4 – 12.6 volts
- Discharged: Below 12 volts, often around 10.5 volts
If your motorcycle battery reads below 10 volts, it may struggle to start the bike, indicating that it needs charging or replacement.
Part 2. Why does voltage matter in a motorcycle battery?
Voltage is critical because it directly affects the performance of your motorcycle’s electrical system. Here’s why maintaining proper voltage levels is essential:
- Starting Power: A fully charged battery ensures that your motorcycle starts quickly. Insufficient voltage can lead to slow cranking or failure to start.
- Electrical Functionality: Components such as lights, signals, and electronic displays depend on adequate voltage to function correctly. If the voltage is low, these components may not work as intended.
- Battery Lifespan: Consistently operating at low voltage can damage the battery over time, reducing its lifespan and effectiveness. A healthy battery typically lasts three to five years, but low voltage can shorten this period.
Part 3. How to test the voltage of a motorcycle battery?
Testing your motorcycle’s battery voltage is straightforward and can be done using a multimeter. Here’s how:
Gather Your Tools:
- You will need a digital multimeter, an inexpensive tool available at most hardware stores.
Set Up the Multimeter:
- Turn on the multimeter and set it to measure DC voltage (usually indicated by a “V” with a straight line).
Connect the Multimeter:
- Connect the red lead to the positive terminal of the battery.
- Connect the black lead to the negative terminal.
Read the Voltage:
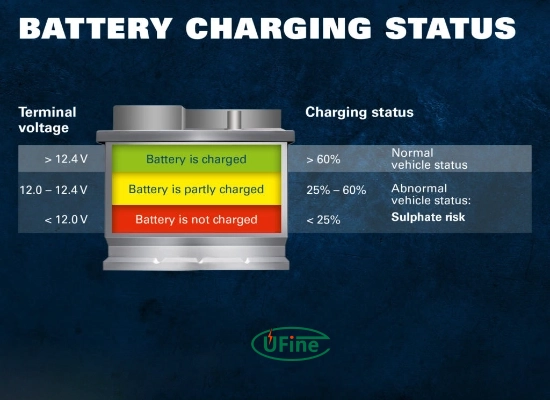
- A healthy, fully charged 12V battery should read between 12.6V and 14.4V.
- If it reads below 12V, consider charging or replacing the battery.
Check While Running:
- For a more accurate reading, check the voltage while the motorcycle is running; it should be higher because the alternator is charging.
Part 4. What causes low voltage in a motorcycle battery?
Several factors can contribute to low voltage in a motorcycle battery:
- Age and Wear: Batteries have a limited lifespan (typically 3-5 years). Over time, they lose their ability to hold charge due to internal chemical reactions.
- Corrosion: Corroded terminals can impede electrical flow, leading to lower voltage readings and poor performance.
- Faulty Charging System: If your motorcycle’s charging system (stator or regulator/rectifier) is malfunctioning, it may not adequately charge the battery while riding.
- Frequent Short Rides: Short trips can prevent your battery from fully charging since it may need more time at higher RPMs for optimal charging.
Part 5. What are the common symptoms of low battery voltage?
Recognizing symptoms of low battery voltage can help prevent more significant issues down the line:
- Difficulty Starting: If you notice sluggish cranking when starting your bike, it may indicate low battery voltage.
- Dim Lights: Dimming headlights or dashboard lights often suggest inadequate power supply from the battery.
- Electrical Failures: Non-functioning electrical components (like turn signals or horns) can also signal low voltage issues.
- Warning Lights: Some motorcycles have built-in warning lights that indicate electrical system or battery performance issues.
Part 6. How can you maintain proper battery voltage?
To keep your motorcycle battery in optimal condition:
- Regular Charging: Use a smart charger during long periods of inactivity to maintain charge levels without overcharging.
- Clean Terminals: Regularly check and clean battery terminals to prevent corrosion using a mixture of baking soda and water if necessary.
- Check voltage Regularly: Make it a habit to test your battery’s voltage at least once every few months, especially before long rides.
- Avoid Deep Discharges: Do not regularly discharge your battery below 12 volts, which can significantly reduce lifespan.
Part 7. What should you do if your motorcycle battery is low?
If you find that your motorcycle’s battery is low on voltage, consider these steps:
Recharge the Battery:
Use an appropriate charger designed for your type of battery (lead-acid or lithium).
Inspect Connections:
Check all wiring and connections for corrosion or damage; clean any corroded terminals carefully.
Replace if Necessary:
If the battery consistently shows low voltage after charging, it may be time for a replacement.
Consult a Professional:
If you need help diagnosing or fixing issues with your motorcycle’s electrical system, consult a professional mechanic.
Part 8. How does temperature affect motorcycle battery performance?
Temperature plays a significant role in how well your motorcycle battery performs:
- Cold Weather Effects: Batteries lose about 20% of their capacity at freezing temperatures (32°F / 0°C), making starting difficult due to increased internal resistance.
- Hot Weather Effects: Extreme heat can accelerate chemical reactions within batteries, potentially leading to faster degradation and reduced lifespan due to the evaporation of electrolyte fluid in lead-acid batteries.
Part 9. What types of batteries are available for motorcycles?
Motorcycle batteries come in various types, each with unique characteristics:
Lead-Acid Batteries:
The most common type they are reliable but requires regular maintenance, like checking water levels in non-sealed types.
AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) Batteries:
A subtype of lead-acid batteries that are sealed and maintenance-free offers better vibration resistance and faster recharging times.
Lithium-Ion Batteries:
Lightweight with high power density, they offer longer life but require specific chargers and may be more expensive upfront than traditional batteries.
What is the Best Lithium Motorcycle Battery?
Part 10. FAQs
-
What happens if I disconnect my motorcycle battery?
If done incorrectly, connecting your motorcycle battery can damage the battery and electrical components, potentially leading to costly repairs or replacements. -
How long do motorcycle batteries last?
Typically, a well-maintained motorcycle battery lasts three to five years, depending on usage patterns and environmental conditions such as temperature extremes. -
Can I jump-start my motorcycle with a car?
Yes, but ensure that you follow proper procedures. Car batteries have higher voltages, which could damage your bike’s electrical system if done improperly; always connect positive first, then negative last, when jump-starting. -
How do I know when it’s time to replace my motorcycle battery?
If your bike struggles to start consistently or notices significant voltage drops during tests even after charging it fully, it’s likely time for a replacement. Also, look for physical signs like swelling or leakage from the battery casing. -
Is it safe to leave my motorcycle plugged into a charger?
Yes, as long as you use an appropriate smart charger for motorcycles. This helps maintain an optimal charge without overcharging, which could lead to damage over time.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.