Lithium-ion batteries have become the backbone of modern energy storage, powering everything from smartphones to electric vehicles (EVs). As the world pivots toward renewable energy and sustainable technologies, understanding the materials used in these batteries becomes crucial. One of the key materials is copper, which plays an essential role in the battery’s functionality. But how much copper goes into a lithium-ion battery? Let’s dive deeper into the details, breaking down the question step by step.
Part 1. What is a lithium-ion battery?
A lithium-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses lithium ions as the main component of its electrochemistry. Consumers widely use these batteries for their high energy density, long lifespan, and lightweight design. Unlike traditional batteries, lithium-ion batteries rely on the movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode to store and release energy.
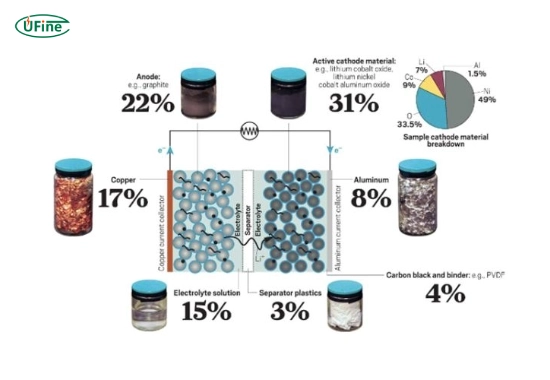
The battery consists of four major components:
- Cathode: Manufacturers often make the positive electrode from materials like lithium cobalt oxide or lithium iron phosphate.
- Anode: Manufacturers typically make the negative electrode from graphite.
- Electrolyte: The medium that allows lithium ions to flow between the cathode and anode.
- Separator: A material that prevents the electrodes from touching while allowing ion flow.
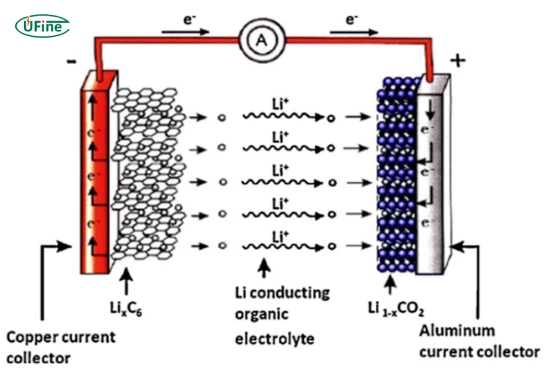
Copper is primarily used in the anode’s current collector, making it a critical material in the design and operation of lithium-ion batteries.
Part 2. Why is copper used in lithium-ion batteries?
Manufacturers use copper in lithium-ion batteries because of its high electrical conductivity, durability, and corrosion resistance. Copper serves as the current collector for the anode, enabling the efficient flow of electrons during charge and discharge cycles.
The key reasons for copper’s importance include:
- High conductivity: Copper allows for minimal energy loss during the flow of electricity.
- Thermal stability: It can withstand the heat generated during battery operation.
- Durability: Copper’s resilience ensures the battery’s performance over many cycles.
The absence of copper would significantly compromise the performance and efficiency of a lithium-ion battery.
Part 3. How much copper do manufacturers typically use in a lithium-ion battery?
The amount of copper in a lithium-ion battery depends on its application and design. For example, a tiny battery for a smartphone will use far less copper than a large battery for an electric vehicle.
General Estimates:
- Smartphone batteries: Contain approximately 1-2 grams of copper.
- Laptop batteries: Use around 20-50 grams of copper.
- Electric vehicle (EV) batteries: Can contain up to 90 pounds (40 kg) of copper, depending on the battery size.
Copper’s use is particularly significant in EVs because these batteries are much larger and require more robust current collectors.
Part 4. Where is copper located in a lithium-ion battery?
Manufacturers place copper in a lithium-ion battery’s anode current collector, a thin layer of copper foil that supports the anode material (typically graphite).
Here’s a breakdown of its role:
- The copper foil acts as a conductor, collecting the electrons generated during the battery’s discharge phase and transmitting them to the external circuit.
- It also provides structural support to the anode material, ensuring uniform distribution of lithium ions during charging and discharging.
- The thickness and surface area of the copper foil vary depending on the battery’s design and intended application.
Part 5. How does copper usage vary in different types of lithium-ion batteries?
There are several types of lithium-ion batteries, each with a unique chemistry and design. While the amount of copper used remains relatively consistent, the specific battery type can influence other material requirements.
Common Types of Lithium-Ion Batteries:
- Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LCO): Used in smartphones and laptops; contains small amounts of copper due to the lower energy capacity.
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP): Popular in EVs and energy storage systems, these batteries use more copper due to their larger size.
- Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC): Widely used in EVs, with significant copper usage depending on the battery’s size.
Generally, batteries designed for larger-scale applications like EVs or grid storage systems require more copper than those for consumer electronics.
Part 6. How is copper extracted and processed for battery production?
Copper used in lithium-ion batteries begins its journey as ore mined from the earth. The process includes the following steps:
- Mining: Extracting copper ore from open-pit or underground mines.
- Processing: Workers crush and refine the ore to produce pure copper.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturers turn the copper into thin foils for current collectors in lithium-ion batteries.
As demand for lithium-ion batteries grows, pressure on copper mining and production increases, highlighting the need for sustainable practices and recycling efforts.
Part 7. How does copper impact battery performance?
Copper is directly involved in the efficiency and longevity of lithium-ion batteries. Its high conductivity minimizes energy loss, while its structural properties ensure the stability of the anode material.
If someone used lower-quality materials in place of copper, the following issues could arise:
- Reduced efficiency: Poor conductivity would result in energy loss.
- Shortened lifespan: The battery would degrade faster due to thermal instability and structural inconsistencies.
In short, copper is indispensable for maintaining the performance standards we expect from lithium-ion batteries.
Part 8. Is the demand for copper in lithium-ion batteries increasing?
Yes, the demand for copper in lithium-ion batteries is growing rapidly. Several factors drive this:
- The rise of electric vehicles: EVs require large battery packs, each containing significant amounts of copper.
- Energy storage systems: Grid-scale solutions are becoming more popular, increasing copper demand.
- Consumer electronics: The proliferation of smartphones, laptops, and other devices continues to drive the need for lithium-ion batteries.
According to industry analysts, the demand for lithium-ion batteries in copper could increase by over 50% in the next decade.
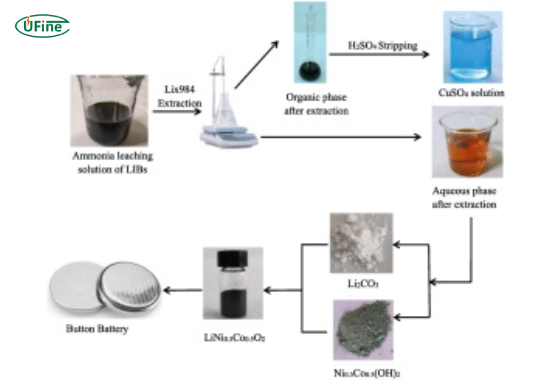
Part 9. Can copper in lithium-ion batteries be recycled?
Yes, copper can be recycled from used lithium-ion batteries. Battery recycling processes recover valuable materials like lithium, cobalt, nickel, and copper to reduce waste and environmental impact.
Recycling Process:
- Batteries are collected and dismantled.
- Materials like copper foil are separated from the other components.
- The copper is refined and reused in new batteries or other applications.
Recycling copper conserves resources and reduces the need for mining, making it an essential part of a sustainable battery supply chain.
Part 10. What are the environmental implications of copper used in batteries?
While copper is a critical material for lithium-ion batteries, its extraction and processing have significant environmental impacts:
- Mining: Copper mining can destroy habitats, soil, and water pollution.
- Energy consumption: Extracting and refining copper requires substantial energy, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
To mitigate these effects, companies are investing in recycling technologies and sustainable mining practices. Governments are also introducing policies to promote the circular economy in the battery industry.
Part 11. FAQs
-
Why is copper important in lithium-ion batteries?
Copper is essential in lithium-ion batteries because it is the anode’s current collector, enabling efficient electron flow and structural stability. -
How much copper is used in an EV battery?
An electric vehicle battery can contain up to 90 pounds (40 kg) of copper, depending on its size and design. -
Can copper from lithium-ion batteries be recycled?
Yes, copper can be recycled from used lithium-ion batteries, reducing environmental impact and conserving resources. -
What happens if copper is replaced with another material?
Replacing copper with a less conductive material would reduce battery efficiency, shorten lifespan, and compromise performance. -
Is the demand for copper batteries expected to grow?
Yes, copper demand for lithium-ion batteries is projected to grow significantly due to the increasing adoption of EVs and renewable energy systems.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Jigsaw Tool Battery for Long-Lasting Power
Discover the top jigsaw tool batteries for power & runtime. Compare Li-ion vs. NiCd, top brands, and tips to extend battery life. Read now
The Logistics of Bulk Battery Orders: Shipping, Storage, and Hazmat Compliance
Learn how to safely manage bulk battery orders with tips on shipping, storage, and hazmat compliance for smarter, safer logistics.
Microcurrent Facial Device Battery Guide & Tips
Learn all about microcurrent facial device batteries, from types to lifespan, and how to choose a reliable supplier for long-lasting, safe skincare performance.
Power Pack Battery vs. Power Bank: What’s the Difference?
Power pack vs power bank: Learn the key differences, pros, and best uses to choose the right portable power source for your lifestyle.
What Is a Power Pack Battery and How Does It Work?
A power pack battery stores energy for off-grid use, emergencies, or travel. Learn how it works and how to choose the right one for your needs.