- Part 1. What is battery capacity?
- Part 2. Why is battery capacity necessary for campervans?
- Part 3. Identifying your power needs
- Part 4. Converting watt-hours to amp-hours
- Part 5. Determining days of autonomy
- Part 6. Accounting for depth of discharge
- Part 7. What is the best way to select the right battery for my campervan?
- Part 8. How can I effectively charge my campervan battery?
- Part 9. FAQs
When planning your next campervan adventure, understanding how to calculate the battery capacity for your van is crucial. A well-calculated battery capacity ensures you have enough power to run your appliances and enjoy your travels without interruptions. This guide will provide a comprehensive, step-by-step approach to calculating the battery capacity you need for your campervan, making it easy for beginners and seasoned travelers.
Part 1. What is battery capacity?
Battery capacity refers to the energy a battery can store and deliver over a specific period. Manufacturers typically measure it in Amp Hours (Ah), which shows how many amps a battery can provide for one hour. For instance, a 100Ah battery can deliver 100 amps for one hour or 50 amps for two hours.
Understanding battery capacity is essential for campervan owners because it directly impacts how long appliances can be run without recharging.
Part 2. Why is battery capacity necessary for campervans?
Knowing your battery capacity helps you:
- Plan your energy usage: By understanding how much power you have, you can manage your appliances better.
- Avoid running out of power: A well-calculated battery capacity ensures you have enough energy for your needs, especially during extended off-grid trips.
- Select the right battery: With the right calculations, you can choose a battery that fits your lifestyle and energy consumption.
Part 3. Identifying your power needs
Identify the electrical devices you will use in your campervan to calculate your battery capacity. Common devices include:
- Lighting: LED lights typically consume less power than traditional bulbs.
- Refrigerator: A significant power consumer, especially if it runs continuously.
- Heating/Cooling: Fans, heaters, or air conditioning units can draw substantial power.
- Electronics: Laptops, phones, and other gadgets also contribute to your daily power consumption.
Step 1: List Your Devices
Create a comprehensive list of all the devices you plan to use. For each device, note the wattage (W) and the average hours you expect to use it daily. This will help you understand your overall power consumption.
Step 2: Calculate Daily Power Consumption
Once you have your list, calculate your daily power consumption using the following formula:
Daily Power Consumption (Wh) = Wattage (W) × Hours Used (h)
Example Calculation
If you have:
LED lights: 10W for 5 hours = 50Wh
Refrigerator: 60W for 24 hours = 1440Wh
Laptop: 50W for 2 hours = 100Wh
Total daily consumption would be:
50Wh + 1440Wh + 100Wh = 1590Wh
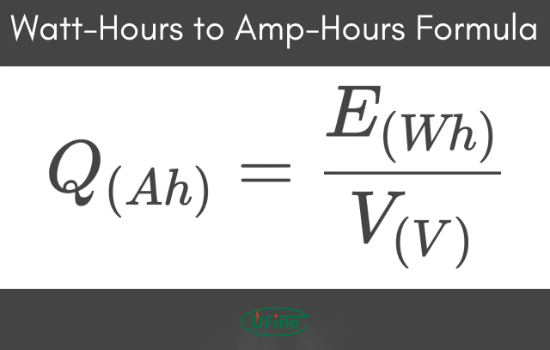
Part 4. Converting watt-hours to amp-hours
Most batteries have amp-hours (Ah) ratings, so you must convert your daily power consumption from watt-hours to amp-hours. You can do this using the following formula:
Amp Hours (Ah) = Watt Hours (Wh) / Voltage (V)
For a typical campervan battery system operating at 12V, the calculation would be:
Amp Hours = 1590Wh / 12V = 132.5Ah
Part 5. Determining days of autonomy
Next, decide how many days your battery will last without recharging. This is known as the days of autonomy. A standard recommendation is to aim for two to three days of power reserve, especially if you plan to camp off-grid.
Example Calculation for Days of Autonomy
If you want your battery to last for three days, you would multiply your daily consumption by the number of days:
Total Capacity Needed (Ah) = Daily Consumption (Ah) × Days of Autonomy
Using our previous example:
Total Capacity Needed = 132.5Ah × 3 = 397.5Ah
Part 6. Accounting for depth of discharge
Not all batteries can handle a full discharge without damage. It’s essential to consider the depth of discharge (DoD), which varies by battery type:
- Lead-acid batteries: Recommended DoD is 50%.
- Lithium batteries: Can typically handle a DoD of 80-90%.
Adjusting for DoD
To ensure longevity, adjust your total capacity needed based on the DoD:
Adjusted capacity = Total Capacity Needed / DoD
For a lithium battery with a 90% DoD:
Adjusted Capacity = 397.5Ah / 0.9 = 441.67Ah
Part 7. What is the best way to select the right battery for my campervan?
Once you have calculated your adjusted battery capacity, the next step is to choose a battery that meets or exceeds your requirements. Selecting the right battery is crucial for ensuring your campervan can reliably power your devices throughout your adventures. Here are the most common types of batteries used in campervans, along with their advantages and disadvantages:
1. AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) Batteries
AGM batteries are popular for campervans due to their durability and reliability. Here’s what you need to know:
- Deep Cycle Capability: AGM batteries are designed for deep cycling and can be discharged and recharged repeatedly without significant damage. This makes them suitable for applications where power needs to be drawn over extended periods.
- Limited Depth of Discharge (DoD): While AGM batteries can handle deep cycling, they typically have a recommended DoD of around 50%. This means you should only use half of the battery’s capacity to prolong its lifespan.
- Maintenance-Free: AGM batteries are sealed and do not require regular maintenance, such as adding water, making them convenient for campervan owners.
- Weight: They tend to be heavier than other batteries, essential if you’re trying to minimize weight in your campervan.
- Cost: AGM batteries are generally more affordable than lithium-ion batteries but can be more expensive than traditional lead-acid batteries.
2. Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are becoming increasingly popular among campervan enthusiasts for several reasons:
- Higher Depth of Discharge (DoD): Unlike AGM batteries, lithium-ion batteries can typically be discharged up to 80-90% without harming their lifespan. This allows you to use a larger portion of the battery’s capacity, making them more efficient.
- Longer Lifespan: Lithium-ion batteries have a significantly longer lifespan than AGM batteries. They can last for 10 years or more with proper care, saving you money in the long run.
- Lightweight: These batteries are much lighter than AGM batteries, which can help improve your vehicle’s overall weight distribution and fuel efficiency.
- Faster Charging: Lithium-ion batteries charge more quickly than AGM batteries, allowing you to replenish your power supply in less time.
- Cost: While lithium-ion batteries are more expensive upfront, their longevity and efficiency can make them a worthwhile investment.
Choosing the Right Battery for Your Needs
When selecting a battery, consider the following factors:
- Capacity: Ensure the battery meets or exceeds your calculated capacity needs.
- Weight: Consider the weight of the battery and how it affects your campervan’s overall load.
- Budget: Evaluate your budget and consider the long-term savings of investing in a more expensive battery type.
- Usage: Think about how you plan to use your campervan. Investing in a lithium-ion battery may be beneficial if you often camp off-grid and rely heavily on battery power.
Part 8. How can I effectively charge my campervan battery?
Once you’ve selected the right battery for your campervan, the next step is to consider how you will recharge it. A reliable charging system is essential for ensuring your battery remains topped up and ready for use. Here are some standard methods for charging your campervan battery:
1. Solar Panels
Solar power is one of the most popular and eco-friendly options for charging campervan batteries, especially for those who enjoy off-grid camping. Here’s why:
- Renewable Energy Source: Solar panels harness the sun’s energy, providing a sustainable and renewable power source.
- Low Operating Costs: Once installed, solar panels have minimal operating costs. They require little maintenance and can last for decades.
- Flexible Installation: Solar panels can be mounted on the roof of your campervan, allowing you to take advantage of sunlight wherever you park.
- Battery Management Systems: Many solar charging systems include management systems that help optimize charging and protect batteries from overcharging.
2. Alternator Charging
Using your vehicle’s alternator to charge the battery while driving is another effective method:
- Convenient: This method allows you to charge your battery while on the road, ensuring you top up the battery by the time you reach your next destination.
- Automatic Charging: As long as your engine runs, the alternator will charge your battery, making it a convenient option for those who frequently travel.
- Considerations: It’s essential to ensure your alternator is powerful enough to charge your battery effectively, especially if you have a high-capacity battery. You may also need a battery isolator to prevent draining your starting battery.
3. Shore Power
When you have access to an external power source, shore power charging is a straightforward and efficient option:
- Fast Charging: Connecting to an electrical outlet allows rapid battery charging, ensuring ample power for your needs.
- Convenience: This method is beneficial when parked at campgrounds or RV parks that offer electrical hookups.
- Battery Charger: Use a quality battery charger designed for your battery type to ensure safe and effective charging.
Choosing the Right Charging Method
When deciding on a charging method, consider your travel habits, budget, and the availability of resources. Many campervan owners opt for a combination of these charging methods to ensure a reliable and flexible power supply while on the road. Understanding your options lets you keep your campervan battery charged and ready for your next adventure.
Part 9. FAQs
-
What is a leisure battery?
A leisure battery is designed to provide a steady current over an extended period, making it ideal for powering appliances in campervans and boats. -
How do I calculate the power usage of my devices?
To calculate power usage, multiply the wattage of each device by the number of hours you expect to use it daily. -
What is the difference between Amp Hours and Watt Hours?
Amp Hours measure the total charge a battery can deliver over time, while Watt Hours measure the total energy a battery can store. -
How often should I recharge my campervan battery?
Recharge your battery whenever possible, especially after heavy usage, to maintain battery health and longevity. -
Can I use regular car batteries in my campervan?
Regular car batteries are unsuitable for deep cycling and can be damaged if used for prolonged periods. It’s best to use leisure batteries designed for this purpose.
Related Tags:
More Articles

고방전 배터리는 높은 전류와 발열로 배터리수명이 줄어듭니다. 구조적 한계, 사용 패턴, 충전 습관 등 실제 수명 단축 요인을 체계적으로 분석했습니다.
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.