When working with lithium batteries or energy systems, how do you calculate watts, volts, and amps?
Understanding how to calculate watts, volts, and amps when designing or using lithium battery systems, whether for portable devices, electric vehicles, or solar energy storage. These three values form the foundation for measuring and managing power in any electrical or battery-powered system.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the core principles, provide easy-to-use formulas, and explore real-life examples — all tailored to the lithium battery use case. Whether you’re a beginner or a professional in the energy storage industry, this article will help you calculate watts from volts and amps, convert amps to watts, and answer, how do you calculate amps from watts and volts?
Part 1. What are watts, volts, and amps in battery systems?
In lithium batteries, these three terms are not just theory — they define how your battery behaves, how much power it can deliver, and what devices it can support.
Watts (W) – The Measure of Power
A watt is a unit of power. It tells you how much energy is being used per second. For a lithium battery, watts tell you how much work the battery can do — like powering a light, a motor, or a phone.
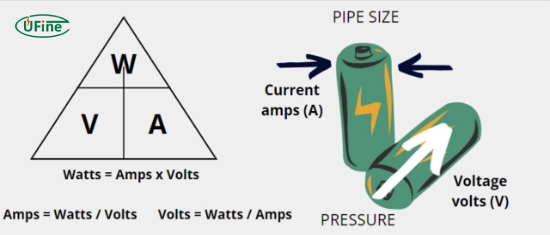
- 1 watt = 1 volt × 1 amp
Volts (V) – The Electrical Pressure
Voltage is the force that pushes electrons through a circuit. A typical lithium battery cell has a nominal voltage of 3.6V or 3.7V. Battery packs are made by combining cells in series to increase voltage.
- For example, a 12V lithium battery often contains 3 or 4 cells in series.
Amps (A) – The Flow of Current
Amperage, or current, is the amount of electricity flowing through a wire. In battery systems, amps represent how fast energy is being drawn from or delivered to the battery.
- High amp drawers can heat a battery or reduce lifespan, so correct calculation is critical.
Part 2. Why these calculations matter for lithium battery users
Whether you’re building an energy storage system, sizing a battery for an RV, or designing a solar backup, knowing how to calculate watts, volts, and amps is crucial.
Here’s why:
- Safety: Overloading a battery can cause overheating or damage.
- Efficiency: Proper sizing ensures longer battery life and better performance.
- Compatibility: Devices must match a battery’s voltage and current rating.
- Cost-effectiveness: Prevents overspending on oversized systems.
Part 3. The basic formula: Volts, Amps, Watts
The most crucial formula in electrical calculations is:
Watts = Volts × Amps
This applies to DC systems like lithium battery setups and AC systems with a slight adjustment (we’ll cover that later).
From this, we can derive:
- Amps = Watts ÷ Volts
- Volts = Watts ÷ Amps
Let’s look at how to apply these to real-world battery setups.
Part 4. How to calculate watts from volts and amps (with examples)
How do you calculate watts from volts and amps?
Use this simple equation:
Watts = Volts × Amps
Example 1: Portable lithium battery pack
- Voltage: 12V
- Current draw: 5A
- Power output = 12V × 5A = 60 watts
This means the battery is delivering 60 watts of power to the device.
Example 2: Electric scooter battery
- Voltage: 48V
- Current draw: 10A
- Power = 48 × 10 = 480 watts
This scooter draws 480 watts from the lithium battery when running.
Part 5. How to calculate amps from watts and volts (with examples)
How do you calculate amps from watts and volts?
Amps = Watts ÷ Volts
This is useful for knowing how much current a device will pull from your battery.
Example: Lithium battery powering a light
- Light power: 24 watts
- Battery voltage: 12V
- Amps = 24W ÷ 12V = 2A
So, the light will draw 2 amps from the battery.
Part 6. How to calculate volts from watts and amps?
If you’re testing a battery or designing a circuit, you may know the wattage and current but not the voltage.
Volts = Watts ÷ Amps
Example:
- Power needed: 600W
- Current available: 20A
- Voltage needed = 600 ÷ 20 = 30V
You’ll need a 30V battery pack to deliver this power at that current.
Part 7. How to convert amps to watts in lithium battery systems
How do you convert amps to watts?
You need to know the voltage. Then use:
Watts = Volts × Amps
Example:
- A 24V battery delivering 8A
- Watts = 24 × 8 = 192W
So, the system is providing 192 watts of power.
Artikel Terkait: Watts to Amps: Complete Guide with Formulas, Calculations, and Common Mistakes
Artikel Terkait: Watts to Amps: What’s the Difference Between Volts and Amps? A Beginner’s Guide
Part 8. Advanced battery scenarios: Series and parallel wiring
When connecting lithium battery cells, you can wire them in series or parallel, affecting your calculations.
Series: Increases voltage
- 4 cells at 3.7V = 14.8V system
- Amps stay the same
Parallel: Increases capacity (amp-hours)
- 4 cells at 3.7V, 2.5Ah = 3.7V, 10Ah pack
- Voltage stays the same
Example:
A 48V battery system made from 13 cells in series (13S) with 4 in parallel (4P):
- Voltage: 13 × 3.7V = 48.1V
- Capacity: 4 × 2.5Ah = 10Ah
- Total energy: 48.1V × 10Ah = 481Wh
Part 9. AC vs DC: Does the formula change?
In AC systems, especially for inverters or grid-tied systems, you must factor in the power factor (PF).
Watts = Volts × Amps × Power Factor
For most residential loads, PF is around 0.9 to 1.0. In DC systems like lithium batteries, PF = 1, so the basic formula holds.
Be aware of this difference when sizing inverters or hybrid systems.
Part 10. Calculating runtime and energy usage
Beyond just amps and watts, you’ll often want to know how long a battery will last.
Runtime (hours) = Battery capacity (Wh) ÷ Load power (W)
Example:
- Battery: 12V, 100Ah = 1200Wh
- Device: 60W
- Runtime = 1200Wh ÷ 60W = 20 hours
This battery can power the device for 20 hours.
Part 11. Common lithium battery use cases
Let’s look at how these calculations apply in real-world lithium battery applications:
- Solar energy storage
Know how many watts your panels produce and how much your battery can store.
Use amps to size your charge controller. - Electric bikes and scooters
Motor controllers are rated in amps.
Battery packs need to match the voltage and deliver enough watts. - Backup power systems
Calculate runtime for essential devices (fridge, lights, router).
Ensure batteries can handle peak amp draw. - Portable power stations
Often rated in watt-hours (Wh).
Know your device wattage to estimate usage time.
Part 12. FAQs about calculating watts, volts, and amps
How do you calculate amps from watts and volts?
Use the formula:
Amps = Watts ÷ Volts
This tells you how much current a device will draw from your battery.
How do you calculate watts from volts and amps?
Use the formula:
Watts = Volts × Amps
This gives you the power used or delivered by a system.
How do you convert amps to watts in a battery system?
Multiply the amps by the system’s voltage:
Watts = Volts × Amps
How do I know what size lithium battery I need?
Calculate your daily energy needs in watt-hours, then select a battery with that capacity plus some buffer.
Can I use a 24V battery with a 12V device?
No. Voltage mismatch can damage your device. Always match voltage ratings properly.
Related Tags:
More Articles

What You Need to Know About AA 3.6V Lithium Battery
Learn all about AA 3.6V lithium batteries—voltage, size, capacity, uses, and the best replacements. Discover why they’re powerful, and highly reliable.
What Are Lithium Salts and Why They Matter in Battery Electrolytes
Lithium salts in electrolytes are key to battery performance, powering everything from phones to EVs and shaping the future of clean energy.
Lithium AAA Battery Guide: Power, Performance & Chargers
Explore lithium AAA batteries—voltage, capacity, weight, top brands, and more. Learn how to choose the best battery for your device and why it really matters.
Comprehensive Analysis of U.S. Tariffs on Chinese Lithium Batteries
U.S. tariffs on Chinese lithium batteries in 2025 impact costs, supply chains, and EV, energy storage, and electronics industries globally.
What Are Lithium Button Batteries?
Learn about lithium button batteries (CR2032, CR2025), their uses, safety tips, and how to replace them properly.