18650 Battery Charging Guide: What Is an 18650 Battery and How Should You Charge It? An 18650 battery is a cylindrical rechargeable lithium-ion cell (18 mm × 65 mm) widely used in flashlights, laptops, power tools, medical devices, EV battery packs, and industrial equipment. Because lithium-ion chemistry is sensitive to voltage, current, and temperature, charging 18650 batteries correctly is critical for safety, performance, and cycle life.
This guide explains how to charge an 18650 battery safely, the charging principle behind lithium-ion cells, how to choose the right 18650 battery charger, and practical engineering tips to maximize lifespan in real applications.
Part 1. Common applications of 18650 batteries
18650 cells are favored for their standardized size, high energy density, and mature supply chain. Typical applications include:
- LED flashlights and headlamps
- Laptops and consumer electronics
- Power tools and industrial equipment
- Electric bikes, scooters, and EV battery modules
- Medical and portable diagnostic devices
In most of these use cases, improper charging is the main cause of premature failure and safety incidents—making charger selection and charging control essential.
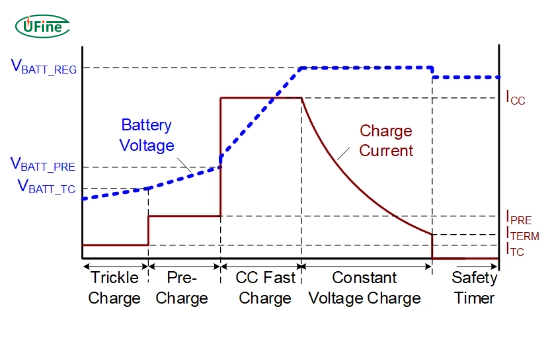
Part 2. 18650 battery charging principle (CC/CV explained)
Charging an 18650 lithium-ion battery follows a strict CC/CV (Constant Current / Constant Voltage) profile defined by cell manufacturers and standards such as IEC 61960.
- Constant Current (CC): The charger supplies a fixed current (typically 0.5C–1C) until the battery voltage reaches 4.20 V ± 0.05 V.
- Constant Voltage (CV): The charger holds the voltage at 4.2 V while the current gradually tapers down to ~0.05C, indicating a full charge.
This method prevents overvoltage, lithium plating, overheating, and accelerated aging. Any charger used for 18650 battery charging must support CC/CV control designed specifically for lithium-ion cells.
For a detailed charger selection guide, see: How to Choose an 18650 Battery Charger
Common charging mistakes to avoid
- Using non-lithium chargers or DIY power supplies
- Charging above 4.2 V per cell
- Charging at high current without temperature monitoring
- Charging in freezing or high-temperature environments
These mistakes can permanently reduce capacity or create serious safety risks.
Part 3. How to charge an 18650 battery step by step
Check the Battery
Ensure the cell is not swollen, leaking, or mechanically damaged.
Insert into a Compatible Charger
Use a charger designed for 18650 lithium-ion batteries.
Constant Current Phase
Charger applies 0.5C–1C current until the voltage rises to 4.2 V.
Constant Voltage Phase
Voltage is held at 4.2 V while current tapers.
Charge Termination
Charging stops automatically when current drops to ~0.05C.
Typical charging time: 2–3 hours at 1C. Lower currents increase charge time but reduce thermal stress.
1 How environment affects 18650 charging
Charging temperature has a direct impact on safety and battery health.
Recommended charging range: 0 °C to 45 °C (32 °F to 113 °F)
- Charging below 0 °C risks lithium plating
- Charging above 45 °C accelerates degradation and increases safety risk
For deeper technical background, manufacturers often reference IEC and UL lithium-ion guidelines (e.g., IEC 62133).
2 Fast charging vs. slow charging
Fast charging uses currents above 1C to reduce downtime, which is common in power tools and EV modules. However, higher current increases internal temperature and shortens cycle life. Slow charging (≤0.5C) generates less heat and is preferred for applications prioritizing longevity over speed.
Related article: Fast charging vs. slow charging
3 Understanding charging rates: what does “1C” mean?
“1C” means charging at a current equal to the battery’s rated capacity. For example, a 2600 mAh 18650 charged at 1C uses 2.6 A. While many cells tolerate 1C charging, frequent charging above this level accelerates aging.
Part 4. How to choose the right 18650 battery charger
Selecting the correct charger is as important as choosing the cell itself. Key selection factors include:
- Voltage Accuracy: Precise 4.2 V termination
- Charging Current: Adjustable current (0.5A–3A per slot)
- Independent Channels: Required for charging multiple cells safely
- Safety Protections: Overcharge, reverse polarity, short-circuit, and thermal protection
- Compliance: CE, UL, or IEC-aligned designs
| Charger | Max Current | Key Safety Features | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| XTAR VC4S | 3A | Temperature sensing, CV cut-off | Engineering & lab use |
| Nitecore SC2 | 2A | Multiple protections | Portable charging |
| Efest LUC Blu6 | 2A | Reverse polarity protection | Multi-cell users |
Types of 18650 battery chargers
- Smart Chargers: Automatically adjust voltage and current based on battery condition.
- Multi-Bay Chargers: Independently charge 2–6 cells; ideal for pack assembly and maintenance.
- USB Portable Chargers: Useful for field work and travel.
- High-Speed Chargers: Designed for time-critical applications with enhanced thermal control.
Part 5. FAQs about charging 18650 batteries
How do I charge an 18650 battery safely?
Use a lithium-ion charger with CC/CV control, charge within 0–45 °C, and stop immediately if abnormal heat or swelling occurs.
Can I charge multiple 18650 batteries at once?
Yes, if the charger has independent channels. Never mix cells of different capacities or aging levels.
Is it normal for an 18650 battery to feel warm?
Slight warmth is normal. Excessive heat indicates a problem and charging should stop immediately.
Should I use a protected or unprotected 18650?
Protected cells add safety for consumer use. Unprotected cells are common in battery packs where protection is handled by the BMS.
Part 6. Conclusion
Understanding how to charge 18650 batteries correctly is essential for safety, reliability, and long-term performance. By using a proper 18650 battery charger, following CC/CV charging principles, and controlling temperature and current, users can significantly extend battery life and reduce risk.
For industrial-grade 18650 lithium-ion batteries, custom battery packs, or charging solutions, you can also contact our technical team for application-specific support.
Part 7. Key takeaways
- 18650 batteries must be charged using a CC/CV profile with a strict 4.2 V limit.
- Charging current (C-rate) directly affects heat generation and cycle life.
- Temperature control during charging is as important as voltage accuracy.
- Smart chargers with independent channels offer the highest safety margin.
- Avoid fast charging unless the application truly requires it.
- Proper charging practices can double the usable lifespan of an 18650 cell.
Related Tags:
More Articles
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.
Aluminium Ion Battery vs Lithium-Ion: A Detailed Comparison
Compare aluminium ion battery vs lithium-ion battery in energy density, charging speed, safety, cost, and uses. A practical guide for engineers and buyers.