Knowing how to check car battery life is essential for every vehicle owner. A well-maintained battery ensures that your car starts reliably and that all electrical systems function correctly. This article will explore the different methods to check your car battery’s life, the signs of a failing battery, and tips for maintaining its health. By the end, we will equip you with the knowledge to keep your car battery in shape.
Part 1. What is a car battery?
A car battery is a crucial component of your vehicle’s electrical system. It provides the power needed to start the engine and operate various electrical devices, such as lights, radio, and air conditioning. The most common type of car battery is the lead-acid battery, which uses lead dioxide and sponge lead plates submerged in sulfuric acid to generate electricity.
However, lithium-ion batteries are also becoming increasingly popular in electric and hybrid cars. These batteries are lighter and have a higher energy density than traditional lead-acid batteries. They charge faster and last longer, making them an excellent choice for modern vehicles.
Both types of batteries serve similar functions but have different characteristics:
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Generally less expensive, heavier, and more reliable for starting engines in cold weather. However, they have a shorter lifespan compared to lithium-ion batteries.
- Lithium-ion batteries: These are more efficient, longer-lasting, and lighter but can be more expensive upfront. Due to their superior performance, electric vehicles often use them.
Understanding these differences can help you choose the right battery for your vehicle and know what to look for when checking its life.
Part 2. How long do car batteries last?
The lifespan of a car battery can vary widely based on several factors. On average, you can expect a lead-acid battery to last between three to five years, while lithium-ion batteries may last up to eight years or more under optimal conditions. Here are some factors that influence battery life:
- Driving Habits: If you frequently take short trips, your battery may need more time to recharge. This can lead to sulfation, which shortens battery life.
- Climate Conditions: Extreme temperatures can affect battery performance. High heat can cause the electrolyte solution to evaporate, while cold weather can reduce the battery’s ability to hold a charge.
- Battery Maintenance: To significantly extend a battery’s lifespan, perform regular maintenance, such as cleaning terminals and checking fluid levels (for lead-acid batteries).
It’s essential to be aware of these factors and monitor your driving patterns closely to maximize your battery’s longevity.
Part 3. Signs of a dying car battery
Recognizing the signs of a failing battery is crucial for preventing unexpected breakdowns. Here are some common indicators that your car battery may be nearing the end of its life:
- Slow Engine Crank: If your engine takes longer than usual to start or cranks slowly, this could indicate a weak battery.
- Dimming Lights: If your headlights or dashboard lights dim when you start the engine or turn on accessories, it might be time to check your battery.
- Check Engine Light: A lit check engine light could signal an issue with your battery or charging system.
- Swollen Battery Case: A bloated or swollen case often indicates overcharging or excessive heat exposure, which can damage the internal components.
- Age of the Battery: If your battery is over three years old and showing any of these signs, it’s wise to have it tested regularly.
Awareness of these symptoms can help you take action before you find yourself stranded with a dead battery.
Part 4. How to check car battery life?
You can use several methods to assess your car battery’s health. Here’s how to check car battery life using different techniques:
Using a Multimeter
- Gather Your Tools: This test requires a digital multimeter (DMM).
- Prepare Your Vehicle: Ensure your vehicle has been turned off for at least an hour before testing for an accurate reading.
Connect the Multimeter:
- Set your multimeter to measure DC voltage.
- Connect the red probe to the positive terminal and the black probe to the battery’s negative terminal.
Read the Voltage:
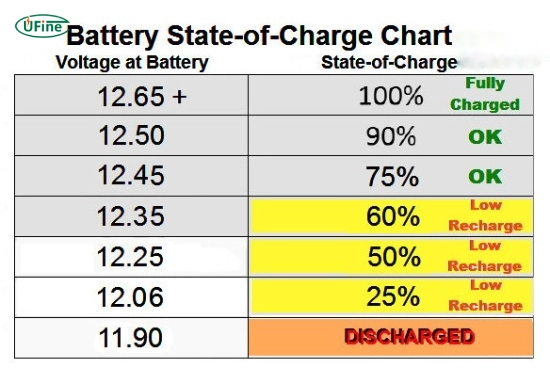
- A healthy, fully charged car battery should read between 12.4V and 12.6V.
- If it reads below 12.4V, consider recharging or replacing it.
Load Testing
Load testing helps determine how well your battery performs under stress:
- Use a load tester (available at auto parts stores).
- Connect the tester according to its instructions while ensuring all electrical systems are off.
- Apply a load (usually half of the cold cranking amps rating) for about 10 seconds while monitoring voltage; it should not drop below 9.6V.
Part 5. Testing methods explained for car batteries
There are several effective methods for checking car battery health beyond simple voltage readings:
- Hydrometer Test: This test measures the specific gravity of the electrolyte in each battery cell using a hydrometer tool. A reading below 1.265 indicates a weak or discharged cell.
- Conductance Testing: This method uses specialized equipment to measure how well the battery conducts electricity without needing significant discharge.
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect your battery for corrosion around terminals, cracks in the casing, or any signs of leakage that could indicate problems.
Part 6. Tools required for testing a car battery
To effectively test your car’s battery health, you’ll need some essential tools:
- Digital Multimeter: This is used to measure voltage and perform load tests.
- Battery Load Tester: To simulate starting conditions and assess performance under load.
- Hydrometer: This is used to check electrolyte density in lead-acid batteries.
- Safety Gear: Gloves and safety glasses are recommended when handling batteries due to potential acid exposure.
These tools will enable you to check your car’s battery health regularly.
Part 7. How to maintain your car battery?
Proper maintenance can significantly extend your car battery’s lifespan:
- Regular Cleaning: Keep terminals clean from corrosion using baking soda mixed with water; ensure connections are tight after cleaning.
- Avoid Short Trips: Take longer drives occasionally so the alternator has enough time to recharge the battery fully.
- Check Fluid Levels: For non-sealed batteries, ensure that electrolyte levels are adequate; add distilled water if necessary, but avoid overfilling.
- Temperature Control: Park in shaded areas during hot weather and indoors during extreme cold whenever possible; this helps protect against temperature-related damage.
By consistently implementing these practices, you can help ensure your car’s battery remains healthy for as long as possible.
Part 8. FAQs
-
What is the ideal voltage level for a functioning car battery?
When not under load, a fully charged car battery should ideally read between 12.6V and 12.8V. -
How often should I check my car battery?
It’s advisable to check your car’s battery at least twice a year or more frequently if it’s older than three years or if you notice any warning signs like slow cranking or dimming lights. -
Can I jump-start my car if my battery is dead?
Yes, jump-starting is an effective way to temporarily revive a dead car battery; however, it’s essential to diagnose why it died in the first place afterward so you can prevent future issues. -
What should I do if my multimeter shows low voltage?
If your multimeter indicates low voltage (below 12.4V), try recharging it first; if it doesn’t hold charge after recharging, consider replacing it with a new one as soon as possible. -
Is it safe to replace my car battery?
Yes! Replacing your car battery is safe if you follow safety precautions and proper procedures outlined in your vehicle’s manual; however, consult a professional mechanic for assistance if you need clarification on any step in the process.
Related Tags:
More Articles
10000mAh Battery Explained: How Long It Lasts, How It Works
A full guide on 10000mAh li-ion batteries, voltage, usage time, and tips. Discover how a 10000mAh battery works, how long it lasts, and how to choose.
10440 Battery Guide: Size, Voltage, Capacity, Uses & More
Understand 10440 batteries better—size, voltage, safety, and how they compare to AAA. Find the best fit for your high-performance devices.
White Stuff on Battery Terminals: A Step-by-Step Cleaning and Maintenance Guide
White stuff on battery terminals is corrosion. Learn how to clean it safely, prevent damage, and keep your battery running strong with simple steps.
Understanding How Glass Mat Batteries Work: Technology, Benefits, and Limitations
Glass mat batteries power cars, RVs, and solar systems. Learn how they work, their benefits, and what to consider before choosing one.
A Buyer’s Guide for AA Size Lithium Battery
Discover the power of AA size lithium batteries—types, voltage, capacity, and more! Learn how to choose the best one for your needs. Read now!