- Part 1. Can you safely connect lithium batteries with different amp hours?
- Part 2. What is a lithium battery amp hour (Ah)?
- Part 3. What are the risks of connecting lithium batteries with different amp hours?
- Part 4. Why would you want to connect lithium batteries?
- Part 5. Pros and cons of connecting batteries with different amp hours
- Part 6. Series vs parallel connections for different Ah batteries
- Part 7. Is a higher Ah battery better?
- Part 8. Step-by-step: How to connect lithium batteries with different amp hours
- Part 9. Precautions when connecting lithium batteries
- Part 10. 4 Common Mistakes When Connecting Mismatched Lithium Batteries
- Part 11. Tools you'll need for connecting lithium batteries
- Part 12. FAQs: Connecting lithium batteries with different amp hours
Learning how to connect lithium batteries with different amp hours correctly is critical for solar, RV, and off-grid systems. This guide reveals professional methods to avoid battery damage while maximizing capacity.
Part 1. Can you safely connect lithium batteries with different amp hours?
Yes, but only in parallel with a Battery Management System (BMS). Connecting lithium batteries with different Ah ratings in series risks overcharging and cell damage. In parallel, the BMS ensures balanced current flow, protecting smaller-capacity batteries. Key requirements:
- Same voltage (e.g., all 12V)
- Identical chemistry (e.g., LiFePO4)
- BMS with individual cell monitoring
Part 2. What is a lithium battery amp hour (Ah)?
An amp hour (Ah) measures a battery’s capacity. It tells you how much electrical current a battery can deliver over time. For instance:
- A 100Ah battery can provide 100 amps of current for one hour.
- Alternatively, it could provide 10 amps of current for 10 hours.
This measurement is critical when designing battery systems. The higher the Ah, the longer a battery can run before recharging. However, connecting batteries with different amp-hour ratings requires special attention to avoid performance issues.
Part 3. What are the risks of connecting lithium batteries with different amp hours?
While connecting mismatched Ah lithium batteries is technically possible, critical risks require mitigation. The core challenge is unbalanced charge/discharge cycles between batteries of different capacities. For example:
- Over-discharging small batteries: A 100Ah battery paired with 200Ah in parallel will discharge twice as fast under the same load.
- BMS failure scenarios: If the BMS cannot balance current, the smaller battery may drop below 10V while the larger remains at 12.8V.
- Thermal runaway risk: Extreme voltage differences (>0.5V) between parallel batteries can cause overheating and fires.
Part 4. Why would you want to connect lithium batteries?
Connecting lithium batteries is necessary for many applications requiring more power or capacity. Here are the main reasons:
- Increasing voltage: Connecting batteries in series increases the voltage, which is essential for systems that require higher voltage levels.
- Increasing capacity: Parallel connections increase the amp-hour capacity, providing more energy storage to power your devices for longer.
- Customizing systems: Combining batteries with different Ah ratings can better use existing resources, especially if you already have mismatched batteries.
Understanding your power requirements is key to deciding how to connect your batteries.
Part 5. Pros and cons of connecting batteries with different amp hours
Before proceeding, weighing the advantages and disadvantages of connecting batteries with different amp-hour ratings is essential.
Pros:
- Flexibility: You can combine batteries you already own, even with different capacities.
- Increased capacity or voltage: You can extend runtime or meet higher voltage requirements depending on how you connect them.
- Cost-effective: Instead of buying new batteries, you can use mismatched batteries in your setup.
Cons:
- Uneven wear and tear: Batteries with smaller capacities may wear out faster than larger ones.
- Complexity: Connecting mismatched batteries requires careful planning and monitoring.
- Potential inefficiency: If not balanced properly, the system may not perform at its best.
By understanding these pros and cons, you can decide whether connecting batteries with different Ah ratings is the right choice for your project.
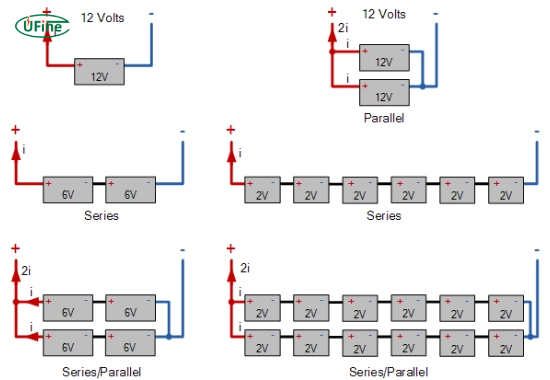
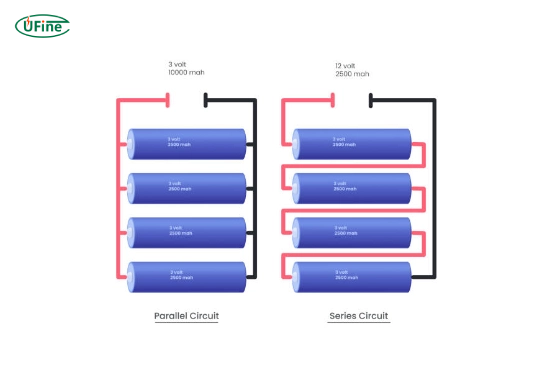
Part 6. Series vs parallel connections for different Ah batteries
| Connection Type | Total Voltage | Total Capacity | Safe with Different Ah? | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parallel | Same as single battery | Ah1 + Ah2 | ✅ Yes (with BMS) | 12V 100Ah + 12V 200Ah = 12V 300Ah |
| Series | V1 + V2 | Same as lowest Ah battery | ❌ No | 12V 100Ah + 12V 200Ah = 24V 100Ah (Unsafe!) |
Key Notes:
- Parallel connections are the only safe method for mismatched Ah batteries.
- Series connections force the lower Ah battery to over-discharge rapidly.
Need help choosing? Read our guide on Parallel vs Series Connections for Lithium Batteries.
Part 7. Is a higher Ah battery better?
A higher Ah battery is not inherently better; it depends on your needs. Here’s when a higher Ah battery is advantageous:
- Longer runtime: A higher Ah battery can store more energy, allowing your devices to run longer without recharging.
- Heavy-duty applications: A higher Ah battery is better suited to handle the load if you power high-demand equipment.
However, higher Ah batteries are typically larger, heavier, and more expensive. A lower Ah battery could be more practical if your system doesn’t need extended runtime or high capacity.
Part 8. Step-by-step: How to connect lithium batteries with different amp hours
Follow these steps to connect mismatched Ah lithium batteries in parallel safely:
- Match Voltages
Charge all batteries to 100% SOC with a voltage difference ≤0.1V. - Install BMS
Use a BMS with per-battery monitoring (e.g., Daly 4S 12V 100A Smart BMS). - Connect in Parallel
Battery 1 Battery 2 Total Capacity 100Ah 200Ah 300Ah - Test Under Load
Use a 20A discharge test – voltage drop difference should be <3%.
Warning: Never connect >30% Ah difference batteries in series. Example: 100Ah + 150Ah is acceptable, 100Ah + 300Ah is unsafe.
Part 9. Precautions when connecting lithium batteries
Avoid mixing old and new batteries: Older batteries may have degraded capacities, leading to uneven performance.
- Monitor temperature: Improper connections can cause batteries to overheat, which is dangerous.
- Use proper cables: Thin cables may not handle the load and could result in voltage drops or overheating.
- Refrain from mixing chemistries: Always use batteries of the same chemical type (e.g., lithium iron phosphate).
Part 10. 4 Common Mistakes When Connecting Mismatched Lithium Batteries
- Mixing Old & New Batteries: Aging batteries cause imbalance. Keep cycles within 20%.
- Ignoring BMS Alerts: 68% of failures stem from bypassing BMS warnings.
- Using Undersized Cables: For 100Ah+ systems, use ≥4 AWG cables to prevent overheating.
- Series Connections with Different Ah: Causes 12V+24V systems to fail within 6 months.
Part 11. Tools you’ll need for connecting lithium batteries
Here’s a list of essential tools and accessories:
- Multimeter or voltmeter
- High-quality battery cables
- Battery management system (BMS)
- Fuse or circuit breaker
- Insulated screwdrivers and wrenches
Having the right tools helps ensure a safe and efficient setup.
Part 12. FAQs: Connecting lithium batteries with different amp hours
Can I connect a 100Ah lithium battery with a 200Ah battery?
Yes, but only in parallel with a Battery Management System (BMS). The BMS will balance current flow to prevent over-discharging the smaller battery. Ensure both are the same voltage (e.g., 12V) and chemistry (e.g., LiFePO4).
What happens if I connect different Ah batteries in series?
This is dangerous. Series connections require identical capacities. A 100Ah + 200Ah series setup will cause the 100Ah battery to discharge twice as fast, leading to over-discharge and potential thermal runaway.
How much voltage difference is allowed when connecting batteries?
Max 0.1V difference. Before connecting, charge all batteries to full and use a multimeter to verify voltages. A 12.8V battery should only pair with others between 12.7V-12.9V.
Can I mix old and new lithium batteries?
Not recommended. Aging batteries lose capacity – a 2-year-old 100Ah battery may act like 80Ah. Mixing with new batteries causes imbalance. Keep cycles within 20% (e.g., 100Ah + 120Ah max).
What size cable should I use for 200Ah parallel connections?
Use 2 AWG cables for 0-5ft runs or 4 AWG for 5-10ft. Example: Two 12V 100Ah batteries in parallel require cables rated for at least 100A continuous current.
Related Tags:
More Articles

고방전 배터리는 높은 전류와 발열로 배터리수명이 줄어듭니다. 구조적 한계, 사용 패턴, 충전 습관 등 실제 수명 단축 요인을 체계적으로 분석했습니다.
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.