Custom LiPo (Lithium Polymer) batteries represent a significant stride in power storage technology, offering tailored solutions for specific needs and applications.
These batteries diverge from standard off-the-shelf models by their ability to be customized, engineered, and designed to meet distinct requirements.
This article delves into the intricate details of custom LiPo batteries, elucidating their composition, design, and applications.
Part 1. Steps to custom LiPo battery
Customizing a LiPo battery involves several crucial steps that require specific data and considerations from the customer. To ensure the creation of an optimal battery, the following details are essential:
Dimensions: Providing precise measurements, including length, width, and thickness, is crucial for fitting the battery into the desired device or space.
Capacity: Understanding the required energy storage capacity in milliampere-hours (mAh) or watt-hours (Wh) helps determine the runtime and power output of the battery.
C-rate: This denotes the rate at which the battery can be charged or discharged relative to its capacity. Knowledge of the C-rate helps select a battery that can meet the required power demands.
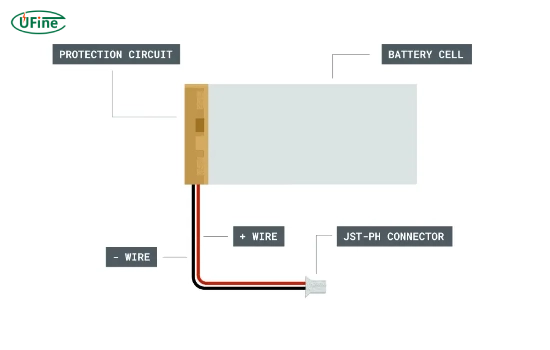
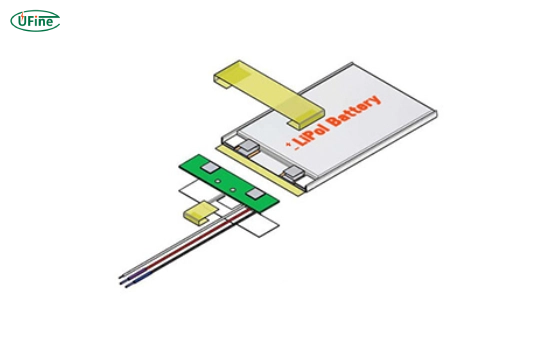
Protection Circuit Module (PCM): Specifying the need for a PCM is essential for safety. The PCM safeguards against overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits.
Enclosure: Information about the desired casing or enclosure material, design, and IP (Ingress Protection) rating requirements for durability or specific environmental conditions.
Connectors: Identifying the type of connectors required for seamless integration into the device or system.
Part 2. Choose custom LiPo battery cells
Selecting a suitable battery cell is crucial for crafting custom LiPo batteries tailored to specific needs. Here’s a detailed exploration of various cell types and considerations:
Lithium-ion Battery (Li-ion)
- Selection Criteria: Opt for lithium-ion chemistry for higher energy density.
- Attributes: Available in diverse shapes and sizes, offering versatility for various applications.
- Applications: Widely used in smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles due to their energy-to-weight ratio.
18650 Battery
- Selection Criteria: Consider these cylindrical lithium-ion cells standardized in size.
- Attributes: Known for their cylindrical shape and high capacity relative to size.
- Applications: Found in laptops, power banks, flashlights, and electric vehicles.
Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery (LiFePO4)
- Selection Criteria: Choose cells employing iron phosphate chemistry for stability.
- Attributes: Known for robust construction and superior thermal stability.
- Applications: Popular in solar energy storage, electric vehicles, and backup power systems for safety and longevity.
High/Low-Temperature Battery
- Selection Criteria: Choose cells engineered with chemistries optimized for extreme temperature ranges.
- Attributes: These cells are designed to maintain performance in frigid or scorching conditions.
- Applications: Ideal for aerospace, automotive, or medical devices operating in extreme climates.
Ultra-Thin Battery
- Selection Criteria: Opt for cells with slim and compact designs without compromising performance.
- Attributes: These cells maintain capacity while fragile to fit tight spaces.
- Applications: Suited for integration into smart cards, wearables, and IoT devices due to their space-saving design.
High C-Rate Battery
- Selection Criteria: Look for cells capable of high discharge rates without voltage drop.
- Attributes: Engineered with advanced materials to support rapid energy transfer.
- Applications: Commonly used in drones, RC vehicles, or power tools requiring bursts of power.
The choice of battery cells hinges on specific performance, environmental, and application requirements. By understanding the attributes of each cell type, you can effectively craft custom LiPo batteries tailored to unique needs, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Part 3. Choose LiPo battery management system
A Protection Circuit Module (PCM) is crucial in safeguarding batteries. Here’s an in-depth look at its methods of battery protection:
Battery Protection Board Functionality
- Overcharge Protection: The PCM monitors voltage levels during charging, halting the charging process when the battery reaches its maximum safe voltage. Suppose a LiPo battery’s maximum voltage is 4.2 volts per cell. In that case, the PCM stops charging when this limit is reached to prevent overcharging.
- Over-Discharge Protection: Prevents the battery from being discharged beyond safe levels by disconnecting the load when the voltage drops too low. If the minimum safe voltage for a battery is 3 volts per cell, the PCM disconnects the load when this threshold is reached to prevent damage.
- Short-Circuit Protection: Detects and isolates a short circuit to prevent excessive current flow that can damage the battery. In the event of a short circuit, the PCM interrupts the circuit to control high current flow, protecting the battery and surrounding components.
Battery BMS and PCM
When selecting BMS and PCM units for LiPo batteries, several key specifications and functionalities should be considered
Size and Form Factor:
BMS and PCM units come in various sizes and shapes to accommodate different battery configurations. Options include compact board designs for smaller devices or larger modules for higher-capacity batteries.
Voltage Range:
BMS and PCM units cater to specific voltage requirements, ensuring compatibility with various battery setups. Variants are available for different voltage ranges, such as 3.7V, 7.4V, or 11.1V for LiPo batteries.
Current Handling Capacity:
These units’ maximum current handling capabilities vary, tailored to match the battery’s discharge rates. Capacities can range from lower amperage for small devices to higher for power-intensive applications.
Communication Protocols:
Some BMS units support communication protocols for data exchange and monitoring, enhancing battery management. Protocols like SMBus, I2C, CAN bus, or UART facilitate communication with external systems or devices.
Battery Status Monitoring:
BMS and PCM modules monitor various battery parameters, including voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge. They enable real-time monitoring and provide data on the battery’s health and performance.
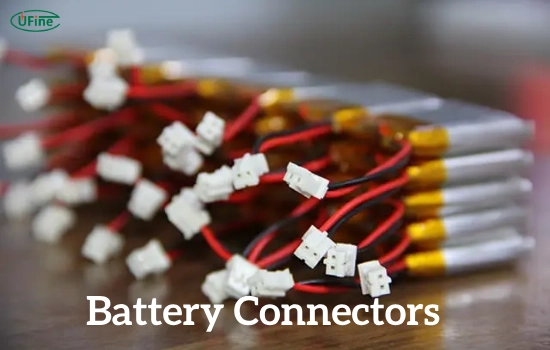
Part 4. Choose LiPo battery connectors
Battery connectors are crucial in establishing electrical connections between batteries and devices. They ensure efficient power transfer and secure connections.
|
Connector Brand |
Connector Models |
Attributes |
|
Amass |
XT60 |
High-current applications, secure and reliable connection |
|
JST (Japan Solderless Terminal) |
PH series, SH series, XH series |
Compact, suitable for smaller devices due to size and efficiency |
|
W.S. Deans Company |
Ultra Plug, T-Connectors |
Low-resistance properties, ideal for high-current applications |
|
Anderson Power Products |
PP15 to PP180 series |
Versatile connectors used across industries, high-current handling, durable |
|
E-flite (Horizon Hobby) |
EC3, EC5 |
Designed for high-power applications in RC vehicles and aircraft |
|
Molex Incorporated |
Micro-Fit 3.0, Mini Fit Jr., Mega-Fit |
Reliable, diverse range used in various electronics, compatibility |
|
Tamiya |
Tamiya Plug |
Simple, easy-to-use connection system commonly found in RC vehicles |
Part 5. LiPo battery certifications
Battery certifications ensure safety, compliance, and quality standards in the global market. Here are some prominent international certifications:
UL 1642,UL 2054, UL 2271 (Underwriters Laboratories)
- Description: A widely recognized certification ensuring battery safety and compliance with international standards.
- Application: Commonly sought batteries for consumer electronics, automotive, and industrial applications.
CE Marking (Conformité Européenne)
- Description: Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- Application: Essential for batteries entering European markets to meet safety requirements.
FCC (Federal Communications Commission)
- Description: Ensures electromagnetic interference compliance for electronic devices, including batteries, in the United States.
- Application: Crucial for batteries used in devices that emit radio frequency energy.
IEC 62133 (International Electrotechnical Commission)
- Description: Specifies safety requirements for portable primary (non-rechargeable) and secondary (rechargeable) lithium batteries.
- Application: Essential for global battery manufacturers to ensure safety and compliance.
UN38.3 (United Nations Transportation Testing)
- Description: Sets standards for safely transporting lithium-ion batteries, including packaging and handling requirements.
- Application: Mandatory for batteries shipped internationally to ensure safety during transportation.
ISO 9001 (International Organization for Standardization)
- Description: Focuses on quality management systems, ensuring consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
- Application: Useful for battery manufacturers to demonstrate commitment to quality processes.
RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive)
- Description: Ensures compliance with restricted substances in electronics, reducing environmental impact.
- Application: Batteries must be free from hazardous materials when sold in the European Union and other regions.
Part 6. FAQs
-
Is it legal to ship LiPo batteries?
Shipping LiPo batteries involves strict regulations due to their fire risk. Many carriers have specific guidelines requiring proper packaging, labeling, and limitations on quantity per shipment to comply with transportation safety standards. -
What is the life expectancy of a LiPo battery?
Factors like usage patterns, charging practices, and storage conditions influence a LiPo battery’s lifespan. Generally, they last around 300-500 charge cycles or 2-3 years before significant degradation in capacity. -
Are puffed LiPo batteries safe?
Puffed LiPo batteries indicate internal damage, potentially due to overcharging, high temperatures, or physical stress. They are unsafe and should be immediately removed from use and adequately disposed of to avoid safety hazards like fire or explosion. -
How do I check the health of my LiPo battery?
To assess a LiPo battery’s health, inspect for physical damage, swelling, or puffiness. Measure its voltage levels using a multimeter to ensure they align with the expected voltage range for the battery’s state of charge. Additionally, perform a capacity test to check its ability to hold a charge compared to its original capacity. Regular maintenance and proper storage practices can also help maintain battery health.
Related Tags:
More Articles

White Stuff on Battery Terminals: A Step-by-Step Cleaning and Maintenance Guide
White stuff on battery terminals is corrosion. Learn how to clean it safely, prevent damage, and keep your battery running strong with simple steps.
Understanding How Glass Mat Batteries Work: Technology, Benefits, and Limitations
Glass mat batteries power cars, RVs, and solar systems. Learn how they work, their benefits, and what to consider before choosing one.
A Buyer’s Guide for AA Size Lithium Battery
Discover the power of AA size lithium batteries—types, voltage, capacity, and more! Learn how to choose the best one for your needs. Read now!
Li-Ion Battery Prices – Where to Buy Cheap & Safe
Discover li-ion cell prices, key market factors, and how to find affordable custom batteries from top suppliers like Ufine Battery.
How Long Does a 2200mAh Battery Last?
Discover everything about 2200mAh batteries—types, charging time, lifespan, and whether it’s enough for your device.