Batteries are the backbone of countless electronic devices, from the smartphones in our pockets to the electric vehicles transforming the transportation industry. Understanding the differences between the various components that make up a battery – the individual cells, the modules that contain those cells, and the larger battery packs – is crucial for effectively maintaining, repairing, and optimizing these power sources.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the distinctions between battery cells, modules, and packs, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently identify and work with these key battery elements. Whether you’re an electronics hobbyist, a technician servicing EVs, or simply curious about the inner workings of the batteries powering your daily life, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of these fundamental battery building blocks.
Part 1. What is a battery cell?
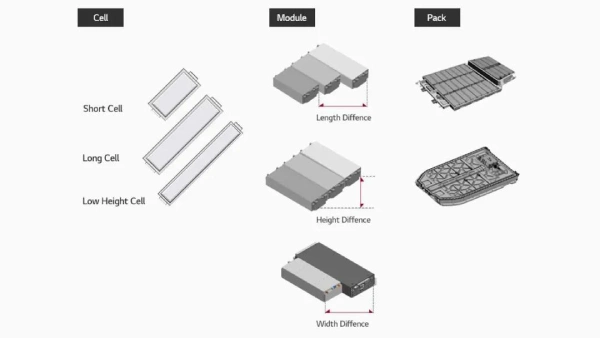
The general structure of lithium batteries is a cell, battery module and battery pack. Battery cell technology is the cornerstone of battery systems. The process of assembling lithium battery cells into groups is called PACK, which can be a single battery or a battery module connected in series and parallel.
The battery cell refers to the most basic component of the battery. Usually, an electrochemical device is enclosed in a metal casing. It is a unit that stores and releases electrical energy, converting chemical energy into electrical energy through chemical reactions. The battery core usually consists of a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a separator, and an electrolyte.
- Anode and Cathode: The positive and negative electrodes are the two polar ends of the battery cells. A diaphragm separates them. The positive and negative electrodes contain active materials and are usually the site of chemical reactions. Suppose batteries are classified according to the positive electrode material. In that case, they can be divided into many types, such as common ternary lithium batteries, lithium iron phosphate batteries, etc.
- Separator: The separator is a charged ion-permeable membrane that prevents direct contact between the positive and negative electrodes. But allows ions to pass between the two poles.
- Electrolyte: An electrolyte is a liquid or solid that acts as an ion transport medium, helping to maintain the flow of ions in the cell.
Cell type and construction vary by battery type and application. Common battery cells types include lithium-ion batteries, nickel-metal hydride batteries, lead-acid batteries, etc. Battery cells are widely used in various electronic devices and applications, such as mobile phones, laptops, electric vehicles, etc. The performance and characteristics of the battery core have an important impact on the battery’s capacity, voltage, cycle life, and safety.
Part 2. What is a battery module?
A battery module is a unit assembled from multiple battery cells. Used to provide higher voltage and capacity. It is a component in the battery system, usually consisting of several cells, connectors, a battery management system (BMS), and casing.
1. How do battery cells form a battery module?
A battery module is a system composed of a certain number of cells in a designed series and parallel structure as needed. By connecting the cells in series, the voltages of multiple cells are accumulated, thereby achieving an output voltage based on a corresponding multiple of the cell voltage.
By connecting cells in parallel, the capacities of multiple cells are accumulated to provide an electrical energy capacity based on a corresponding multiple of the cell capacity. The design and structure of the battery pack can be customized according to different spatial structures and application scenarios.
2. What is battery module BMS?
In addition, the battery module usually contains a battery management system (BMS). It monitors and manages the battery’s charge and discharge process to ensure battery safety and stable performance. BMS can monitor parameters such as battery cell voltage, temperature, and current and perform battery status estimation and balance control to avoid overcharging, over-discharging, over-temperaturing, etc. And provide communication interfaces for data interaction with external systems.
Battery modules usually also have a casing or protective structure. They protect the cells and BMS and provide physical support and isolation. The enclosure provides protection, dissipates heat, and protects the battery system from damage from the external environment.
The design and structure of the battery module can be customized according to needs, such as size, shape, capacity, and function. The function of the battery module is to improve the combination density and reliability of battery cells while facilitating the assembly, connection, and management of battery packs.
In the traditional battery pack manufacturing process, lithium batteries are first assembled into battery modules with a designed structure, and then the battery modules are installed into the battery pack with a designed structure. This forms a three-level assembly model: Lithium Cell →Battery module→Battery pack.
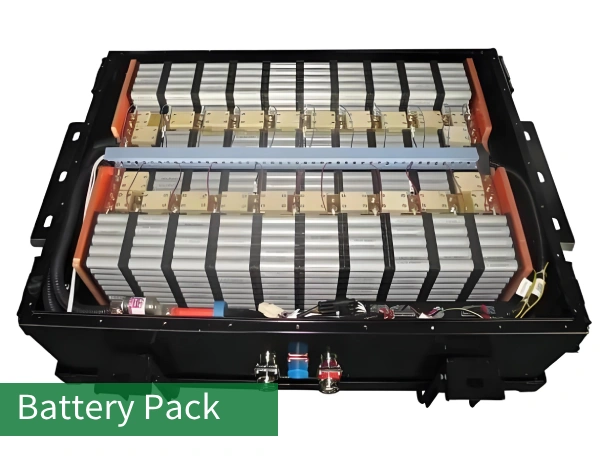
Part 3. What is a battery pack?
A battery pack is an integral unit assembled from multiple battery modules. It is used to store and provide electrical energy. It is a higher-level component in the battery system.
1. Battery pack structure
It usually consists of several battery modules, connectors, battery BMS, cooling system, electrical interface, and casing.
2. How do battery modules form a battery pack?
The main function of the battery pack is to integrate multiple battery modules to form an overall unit. Battery modules are connected in parallel or series to increase the battery system’s voltage, capacity, or power. The battery pack is also responsible for providing other functions and features required by the battery system, such as electrical interfaces to connect to external systems, cooling systems to control temperature, enclosures to protect the batteries, and other ancillary equipment and components.
3. Battery pack BMS
Like battery modules, battery packs are also equipped with a BMS to monitor and manage the entire battery system. BMS monitors the status of the battery module, controls the charging and discharging process, and implements battery protection and balance control to ensure battery safety and stable performance.
Battery packs usually also have a cooling system. This cooling system is used to control battery temperature. The heat dissipation system can effectively cool the battery module to prevent overheating and maintain the battery within a suitable operating temperature range.
The battery pack also includes a shell or protective structure to protect the battery module and BMS and provide physical support and isolation. At the same time, the safety and reliability of the battery system are ensured.
4. Battery pack application
Battery packs are widely used in electric vehicles, hybrid vehicles, energy storage systems, and other applications requiring large capacity and high voltage. It is a key component of electric energy systems, providing a higher level of electrical energy storage and management to meet the needs of different applications.
Part 4. How to distinguish battery cells, battery modules and battery packs?
The fact is, the battery is a general term. Battery cells, modules, and packs are different stages in battery applications.
In the battery pack, to safely and effectively manage hundreds of single battery cells, the cells are not randomly placed in the power battery shell but orderly according to modules and packages. The smallest unit is the battery cell. A group of cells can form a module. Several modules can be combined into a package.
The difference between battery cells, battery modules, and battery packs
1. Battery cells
The battery cell is the smallest power battery unit and the electrical energy storage unit. It must have a high energy density to store as much electrical energy as possible. In addition, the life span of the battery core is also the most critical factor. Damage to any battery core will damage the entire battery pack.
2. Battery module
When multiple battery cells are packaged together in the same housing frame and connected to the outside through a unified boundary, they form a battery module.
3. Battery pack
When the BMS and thermal management system jointly controls or manages several modules, this unified whole is called a battery pack.
A battery pack is a power supply device that contains multiple battery modules. It can be thought of as a larger battery system. It facilitates the installation, connection, and management of battery modules and provides necessary protection and monitoring functions. By being equipped with a BMS, the battery pack can not only improve the safety of the battery but also proactively perform thermal management to respond to battery and environmental temperature changes, improving the efficient operating range of lithium batteries.
Part 5. Summary
The general structure of lithium batteries is a battery cell-battery module-battery pack. Battery cell technology is the cornerstone of battery systems. The process of assembling lithium battery cells into groups is called PACK, which can be a single battery or a battery module connected in series and parallel.
The production process from a simple battery cell to a battery pack is also quite complex and requires multiple processes. As a professional lithium battery manufacturer, Ufine has many years of experience in battery research and development, production, and packaging. Ufine provides customized solutions for lithium batteries for various applications. If you have any questions or needs, please contact us at sales@ufinebattery.com
Related Tags:
More Articles

Paper Battery vs. Flexible Battery: What’s the Difference and Which Is Better?
Paper vs. flexible batteries: learn the key differences, benefits, and which power source fits best for wearables, sensors, and smart tech.
What to Know Before Buying a Tiny LiPo Battery for Your Project
Tiny LiPo batteries are powerful and compact. Learn how to choose the right one for your project with specs, safety, and charging tips.
Bloated LiPo Battery: Will It Explode?
Will a bloated LiPo battery explode? Discover the causes, risks, safety steps, and expert tips to avoid disaster and protect your gear. Must-read safety guide!
12V 100Ah Lithium Ion Battery Price: Full Guide
Learn about 12V 100Ah lithium-ion battery price, from cost ranges to best brands, hidden fees, and how to get the best deal. A must-read for smart buyers!
Resistance and Conductivity: What It Means for Your Lithium Batteries
Resistance and conductivity impact lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety—learn how they work and why they matter.