Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries have become increasingly popular due to their stability, safety, and longevity. However, not all LiFePO4 cells are created equal. Typically, people classify them into three grades: Grade A, Grade B, and Grade C. Understanding the differences between these grades is crucial when selecting the suitable cells for your application. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the nuances of each grade, helping you make an informed decision.
Part 1. What are LiFePO4 cells?
LiFePO4 cells, also known as lithium iron phosphate batteries, are becoming increasingly popular in various applications due to their high safety standards, long life, and stable performance. These cells are typically classified into three grades—Grade A, B, and C—each with its unique characteristics. Understanding the differences between these LiFePO4 cells is crucial to choosing the right one for your needs.
Why is Grading Important?
The grading of LiFePO4 cells is essential because it directly impacts the battery’s performance, safety, and lifespan. Using the wrong grade can lead to suboptimal performance, reduced efficiency, and even safety hazards. Therefore, understanding the grades and their differences is vital for investing in LiFePO4 batteries.
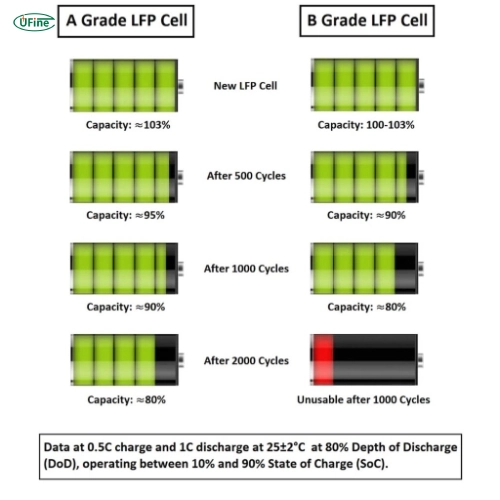
Part 2. Grade A LiFePO4 cells: Top features and benefits
Grade A LiFePO4 cells are the highest quality available. Here are some key characteristics:
1. Superior Performance
Grade A cells offer the best energy density, discharge rates, and efficiency. They are manufactured with the highest quality control standards, ensuring minimal internal resistance and maximum capacity.
2. Longevity
These cells can endure thousands of charge and discharge cycles without significant degradation. This makes them ideal for applications where longevity is crucial, such as in electric vehicles and stationary energy storage systems.
3. Consistency
Grade A cells provide consistent performance across the board. Each cell in a batch will have nearly identical specifications, which is crucial for applications requiring uniformity.
4. Safety
Grade A cells are manufactured to the highest standards and undergo rigorous testing to meet safety regulations. This makes them less prone to overheating, swelling, or leaking.
Part 3. Grade B LiFePO4 cells: Top features and benefits
Grade B cells are a step down from Grade A but perform well. Here are their main characteristics:
1. Good Performance
While not stellar as Grade A cells, Grade B cells still perform well. They have higher internal resistance and slightly lower capacity but are still reliable for many applications.
2. Moderate Longevity
Grade B cells have a shorter lifespan compared to Grade A cells. They can endure many cycles, but their performance will degrade faster.
3. Slight Variability
There is more variability in the performance of Grade B cells. This means that only some cells in a batch will have the exact specifications, which could concern some applications.
4. Adequate Safety
These cells meet safety standards, but manufacturers do not subject them to the same rigorous testing as Grade A cells. They are still safe to use but may be more prone to minor issues.
Part 4. Grade C LiFePO4 cells: Top features and benefits
Users typically use Grade C cells in less critical applications because they are the lowest quality. Here are their characteristics:
1. Lower Performance
Grade C cells have the highest internal resistance and the lowest capacity. They are not suitable for high-performance applications and may not deliver consistent results.
2. Shorter Longevity
These cells have the shortest lifespan, with significant degradation occurring after fewer charge and discharge cycles than Grade A and B cells.
3. High Variability
There is considerable variability in the performance of Grade C cells. This inconsistency can be problematic for applications requiring uniformity and reliability.
4. Basic Safety
Manufacturers subject Grade C cells to basic safety standards but do not conduct extensive testing. They are more likely to encounter issues such as overheating or swelling.
Part 5. How do we identify the grade of LiFePO4 cells?
Identifying the grade of a LiFePO4 cell can be challenging, especially for those new to the technology. Here are some tips to help you distinguish between the grades:
1. Manufacturer Reputation
Reputable manufacturers are more likely to produce high-quality grade A cells. Research the manufacturer’s background and reviews to gauge their reliability.
2. Specifications and Testing
Examine the cell’s specifications and see if they match those typically associated with Grade A, B, or C cells. Request test results if available.
3. Visual Inspection
While not always reliable, a visual inspection can sometimes reveal the quality of the cell. Look for any signs of defects or inconsistencies.
4. Price Point
Grade A cells are usually more expensive due to their superior quality. If the price seems too good to be true, the cells might be of a lower grade.
5. Supplier Transparency
A trustworthy supplier will be transparent about the grade of their cells. Ask questions and request documentation to verify the grade.
Part 6. Applications for different grades of LiFePO4 cells
Each grade of LiFePO4 cells is suitable for different applications. Understanding where each grade fits best can help you make an informed decision.
1. Grade A Applications
Grade A cells are ideal for high-performance and critical applications such as:
- Electric Vehicles: Where long cycle life and high efficiency are crucial.
- Solar Energy Storage: Where reliability and longevity are essential.
- Medical Devices: Where consistent performance and safety are paramount.
2. Grade B Applications
Grade B cells are suitable for less critical but still essential applications like:
- Consumer Electronics: Where moderate performance and longevity are sufficient.
- Backup Power Systems: Where occasional use does not warrant the highest grade.
- Electric Bikes and Scooters: Where good performance is needed but at a lower level.
3. Grade C Applications
Grade C cells are best for non-critical and low-performance applications such as:
- Toys and Gadgets: Where performance and longevity are not significant concerns.
- Low-end Consumer Electronics: Where cost is a significant factor.
- Prototyping and Testing: Where high quality is not necessary.
Part 7. How to source high-quality LiFePO4 cells?
Sourcing high-quality LiFePO4 cells involves several steps:
1. Research Manufacturers
Start by researching reputable manufacturers known for producing high-quality cells. Look for companies with a proven track record and positive reviews.
2. Verify Specifications
Ensure the specifications provided by the manufacturer match the grade you are seeking. Request detailed test results to verify performance.
3. Check Certifications
Look for certifications such as ISO, CE, and UL, which indicate that the cells meet international quality and safety standards.
4. Request Samples
Request samples to test the cells yourself. This can provide firsthand insight into their performance and quality.
5. Evaluate Supplier Transparency
A reliable supplier will be transparent about their products and willing to provide the necessary documentation to verify the grade of their cells.
Part 8. Common misconceptions about LiFePO4 cell grades
There are several misconceptions about LiFePO4 cell grades that can lead to confusion:
1. All Cells Are the Same
This is a common misconception. The grade of a cell significantly impacts its performance, longevity, and safety.
2. Higher Price Always Means Higher Quality
While price is an indicator, it is not the only factor. Always verify specifications and test results rather than relying solely on price.
3. Grade B and C Cells Are Useless
While they are not suitable for high-performance applications, Grade B and C cells still have their uses in less critical applications.
Artikel Terkait: What is LiFePO4 Battery Life?
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.
UN3481 vs UN1323: Classification Guide for Lithium Batteries
UN3481 vs UN1323: UN3481 is for lithium batteries in equipment, while UN1323 covers flammable solids and doesn't apply to batteries.
10000mAh Battery Explained: How Long It Lasts, How It Works
A full guide on 10000mAh li-ion batteries, voltage, usage time, and tips. Discover how a 10000mAh battery works, how long it lasts, and how to choose.